Anat Cell Biol.
2023 Sep;56(3):322-327. 10.5115/acb.23.087.
Intramuscular neural distribution of the teres minor muscle using Sihler’s stain: application to botulinum neurotoxin injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Human Identification Research Institute, BK21 PLUS Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anatomy and Acupoint, College of Korean Medicine, Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Anatomy, Catholic Institute for Applied Anatomy, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2546328
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.23.087
Abstract
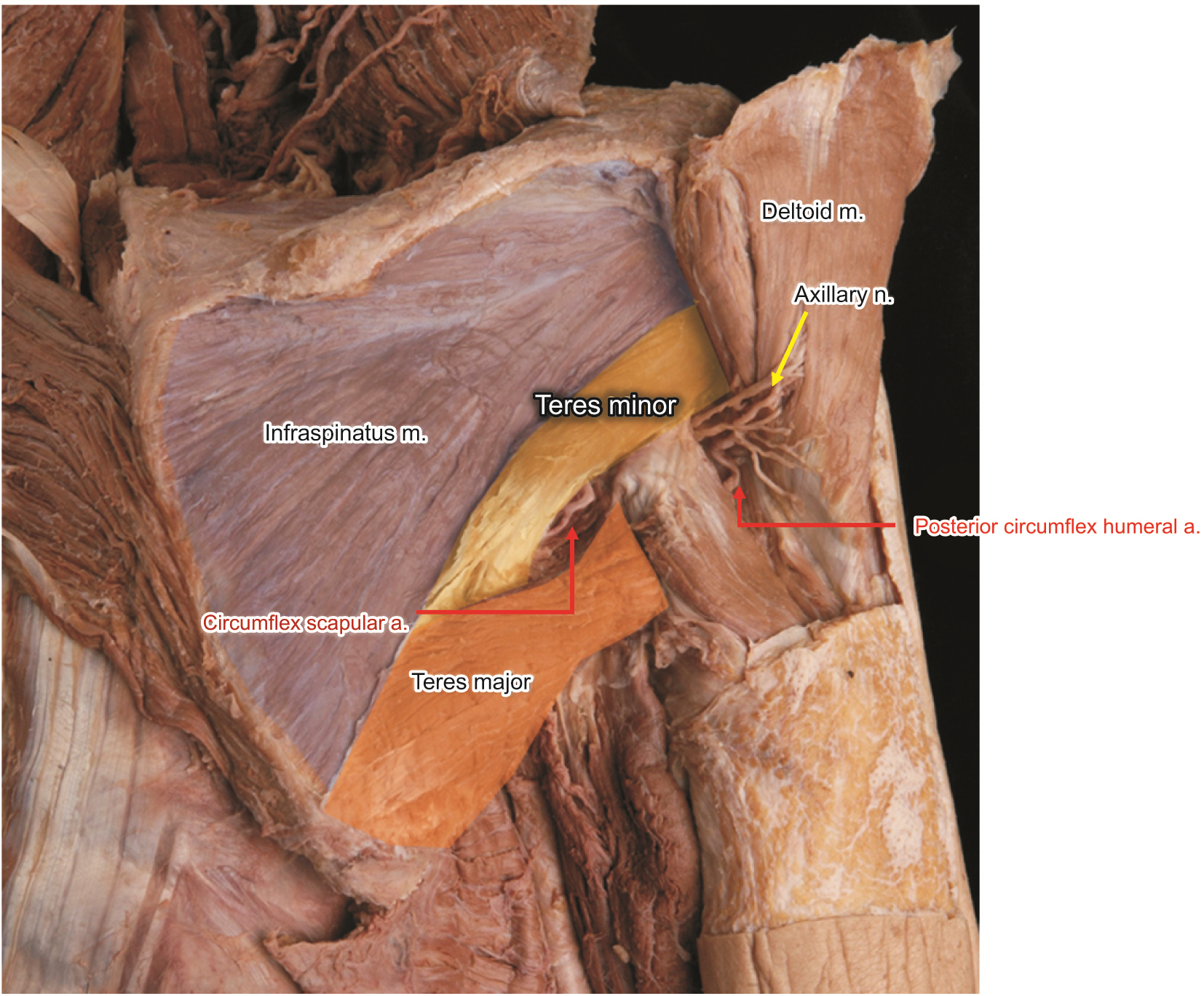
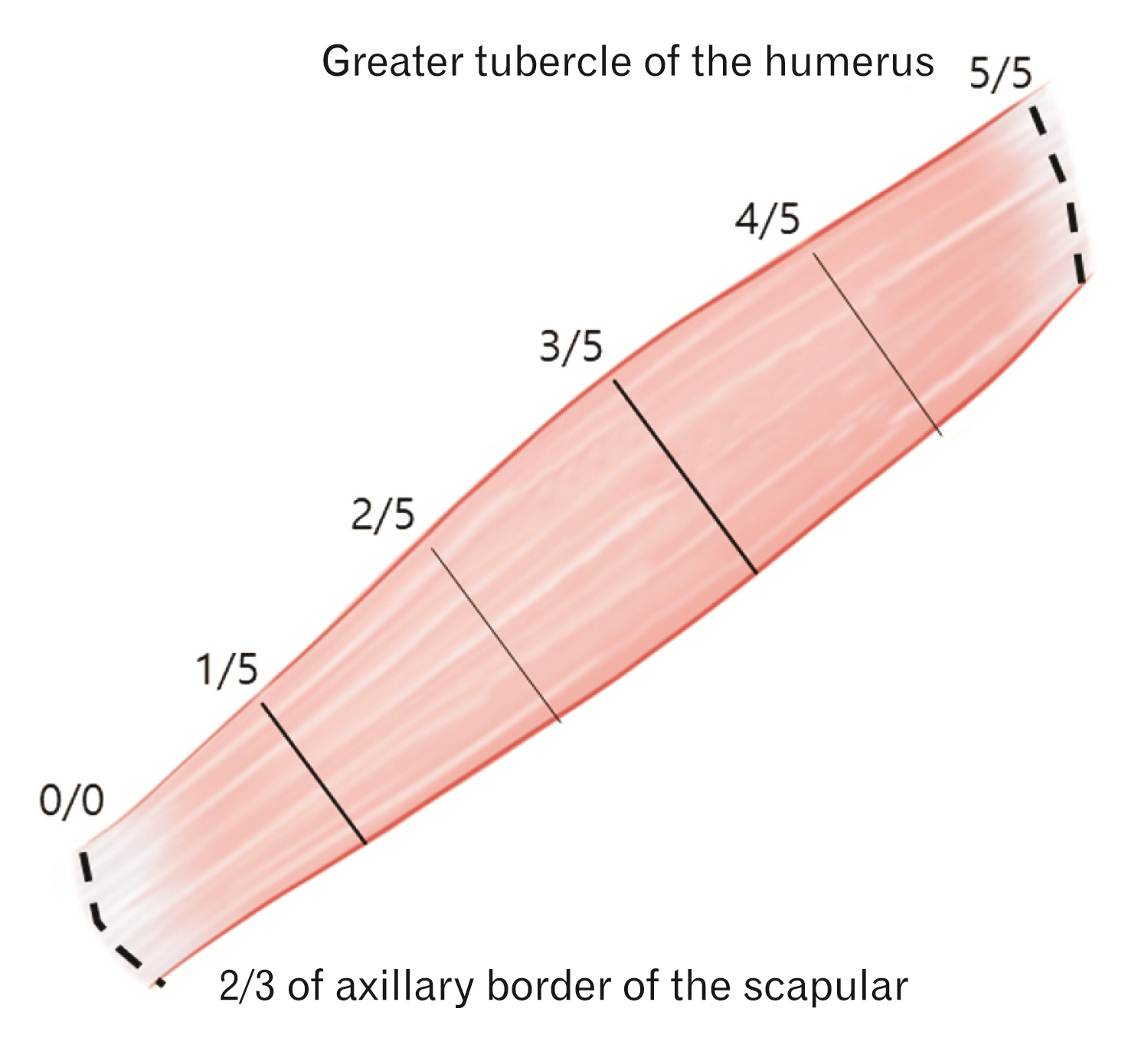
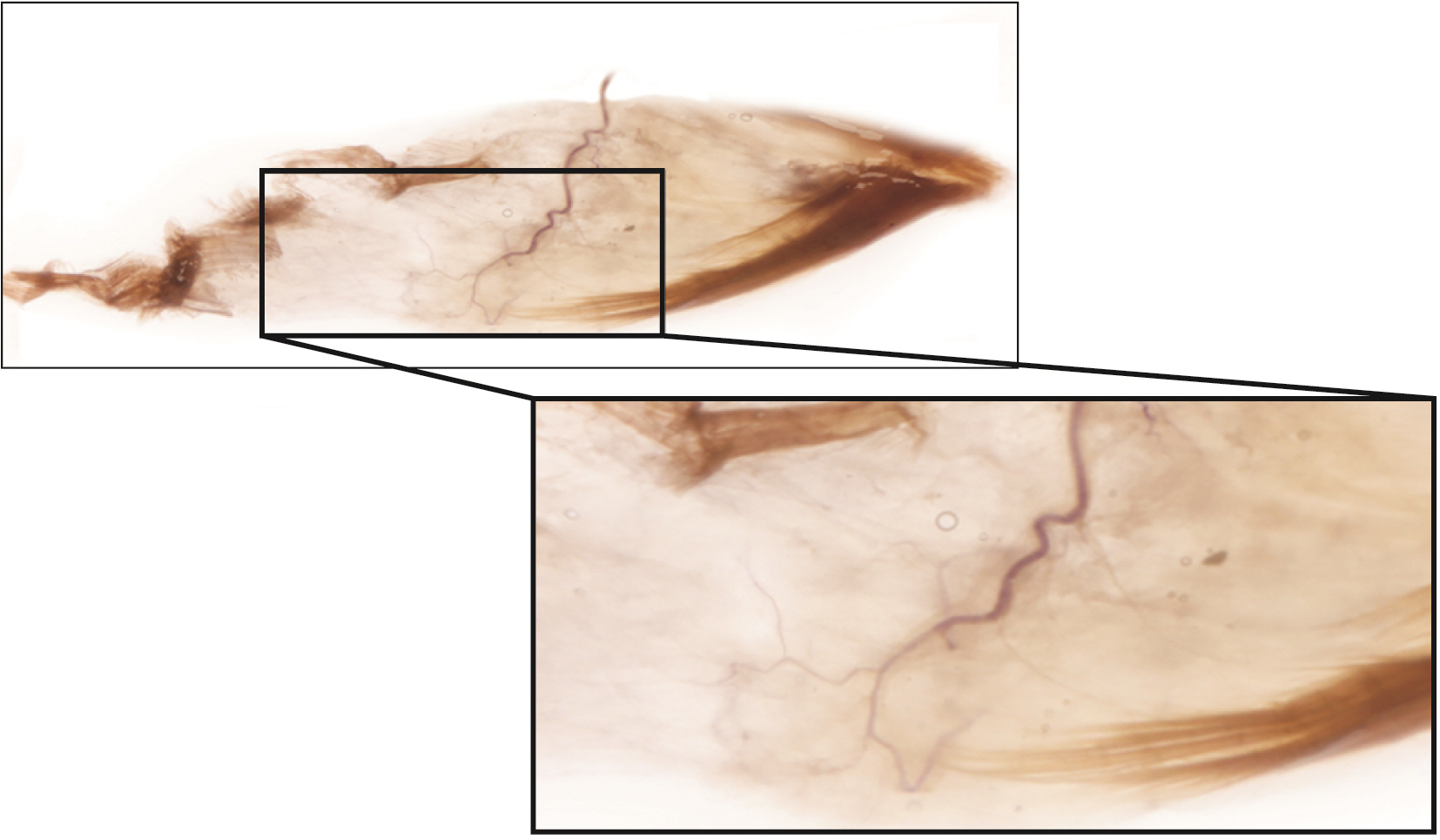
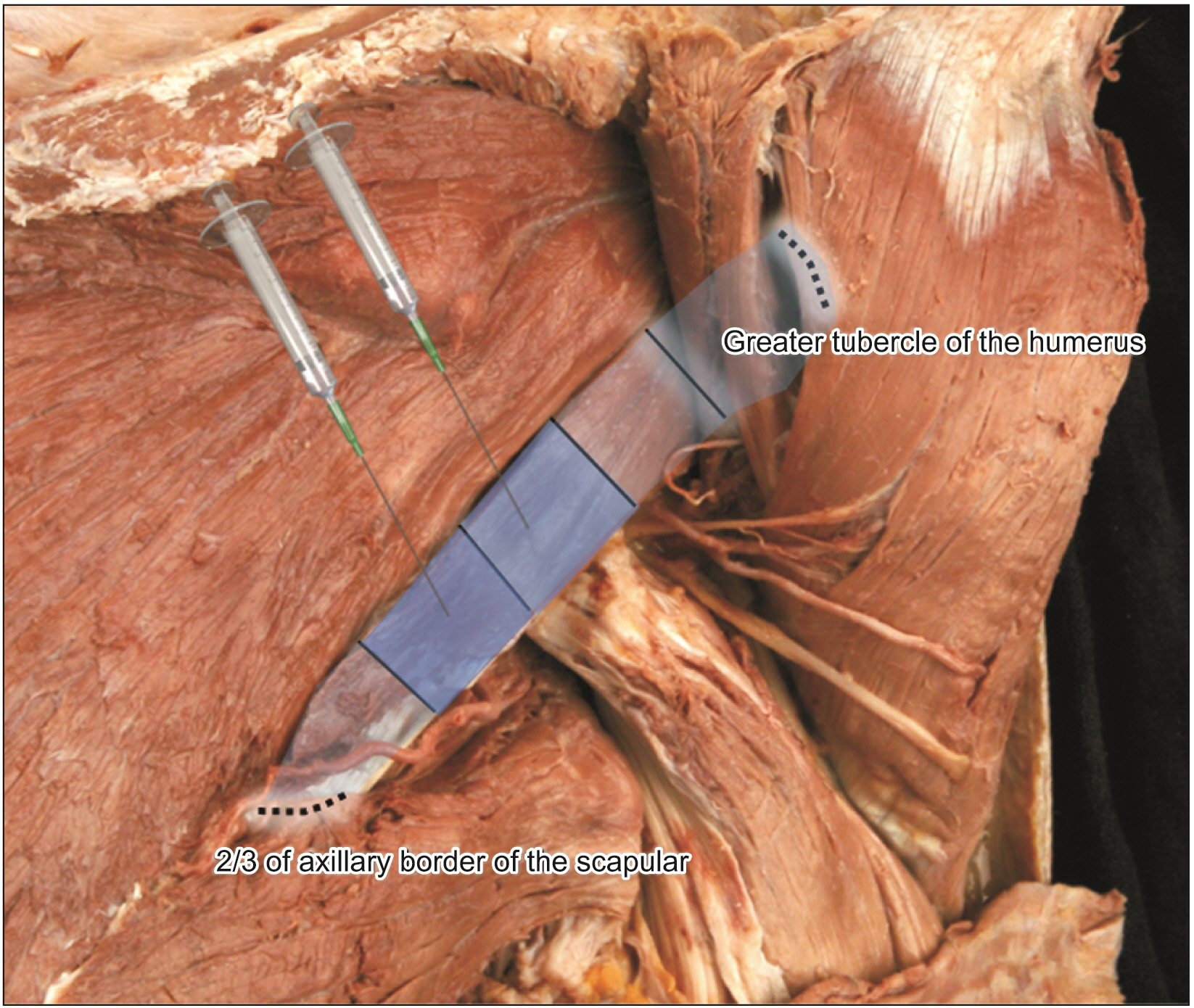
- The aim of this study was to elucidate the intramuscular arborization of the teres minor muslce for effective botulinum neurotoxin injection. Twelve specimens from 6 adult Korean cadavers (3 males and 3 females, age ranging from 66 to 78 years) were used in the study. The reference line between the 2/3 point of the axillary border of the scapula (0/5), where the muscle originates ant the insertion point of the greater tubercle of the humerus (5/5). The most intramuscular neural distribution was located on 1/5–3/5 of the muscle. The tendinous portion was observed in the 3/5–5/5. The result suggests the botulinum neurotoxin should be delivered in the 1/5–3/5 area of the teres minor muscle.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jacinto J, Camões-Barbosa A, Carda S, Hoad D, Wissel J. 2022; A practical guide to botulinum neurotoxin treatment of shoulder spasticity 1: anatomy, physiology, and goal setting. Front Neurol. 13:1004629. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1004629. PMID: 36324373. PMCID: PMC9618862. PMID: ffeba5c71fd142ffaeffa4fd6e8900b8.
Article2. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection for glabellar frown lines. Toxins (Basel). 14:268. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14040268. PMID: 35448877. PMCID: PMC9032255. PMID: dd131953c6e14366befdc986e94b15dd.
Article3. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Lee K, Lee JH, Kim HJ. 2021; Anatomical guide for botulinum neurotoxin injection: application to cosmetic shoulder contouring, pain syndromes, and cervical dystonia. Clin Anat. 34:822–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23690. PMID: 32996645.
Article4. Yi KH, Lee JH, Lee K, Hu HW, Lee HJ, Kim HJ. 2022; Anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting the platysma muscle for treating platysmal band and jawline lifting: a review. Toxins (Basel). 14:868. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14120868. PMID: 36548765. PMCID: PMC9783622. PMID: 1fab78f1f2fb436e8f0adab9755ed1d2.
Article5. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim GY, Yoon SW, Oh W, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting lateral canthal rhytids. Toxins (Basel). 14:462. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070462. PMID: 35878200. PMCID: PMC9316553. PMID: 46755210c7064a99b625f2d6b6dc6e0a.
Article6. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical guidelines on botulinum neurotoxin injection for wrinkles in the nose region. Toxins (Basel). 14:342. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050342. PMID: 35622589. PMCID: PMC9144745. PMID: 95ea3c07c66d4527b5265c5ec719f652.
Article7. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Hur HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection for facial contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 150:562e–71e. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009444. PMID: 35759641.
Article8. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Choi YJ, Lee K, Lee HJ, Kim HJ. 2023; Feb. 21. Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting depressor anguli oris for treating drooping mouth corner. Anat Cell Biol. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.258. DOI: 10.5115/acb.22.258. PMID: 36808109. PMCID: PMC10319486.
Article9. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Park HJ, Bae H, Lee K, Kim HJ. 2023; Feb. 13. Novel anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection in the mentalis muscle: a review. Anat Cell Biol. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.266. DOI: 10.5115/acb.22.266. PMID: 36796830.10. Wissel J, Bensmail D, Scheschonka A, Flatau-Baqué B, Simon O, Althaus M, Simpson DM. 2020; Post hoc analysis of the improvement in shoulder spasticity and safety observed following treatment with incobotulinumtoxinA. J Rehabil Med. 52:jrm00028. DOI: 10.2340/16501977-2651. PMID: 32025741.11. Lim JY, Koh JH, Paik NJ. 2008; Intramuscular botulinum toxin-A reduces hemiplegic shoulder pain: a randomized, double-blind, comparative study versus intraarticular triamcinolone acetonide. Stroke. 39:126–31. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.484048. PMID: 18048857.
Article12. Yelnik AP, Colle FM, Bonan IV, Vicaut E. 2007; Treatment of shoulder pain in spastic hemiplegia by reducing spasticity of the subscapular muscle: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study of botulinum toxin A. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 78:845–8. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.103341. PMID: 17088333. PMCID: PMC2117719.
Article13. Marco E, Duarte E, Vila J, Tejero M, Guillen A, Boza R, Escalada F, Espadaler JM. 2007; Is botulinum toxin type A effective in the treatment of spastic shoulder pain in patients after stroke? A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Rehabil Med. 39:440–7. DOI: 10.2340/16501977-0066. PMID: 17624477.
Article14. Turner-Stokes L, Fheodoroff K, Jacinto J, Maisonobe P. 2013; Results from the Upper Limb International Spasticity Study-II (ULISII):a large, international, prospective cohort study investigating practice and goal attainment following treatment with botulinum toxin A in real-life clinical management. BMJ Open. 3:e002771. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-002771. PMID: 23794582. PMCID: PMC3686177.15. Wissel J, Bensmail D, Ferreira JJ, Molteni F, Satkunam L, Moraleda S, Rekand T, McGuire J, Scheschonka A, Flatau-Baqué B, Simon O, Rochford ET, Dressler D, Simpson DM. 2017; Safety and efficacy of incobotulinumtoxinA doses up to 800 U in limb spasticity: the TOWER study. Neurology. 88:1321–8. DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003789. PMID: 28283596. PMCID: PMC5379931.
Article16. Gracies JM, Brashear A, Jech R, McAllister P, Banach M, Valkovic P, Walker H, Marciniak C, Deltombe T, Skoromets A, Khatkova S, Edgley S, Gul F, Catus F, De Fer BB, Vilain C, Picaut P. 2015; Safety and efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA for hemiparesis in adults with upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 14:992–1001. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00216-1. PMID: 26318836.
Article17. Khan P, Riberto M, Frances JA, Chueire R, Amorim ACFG, Xerez D, Chung TM, Mercuri LHC, Longo AL, Lianza S, Maisonobe P, Ruiz-Schutz VC. 2020; The effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) treatment in Brazilian patients with chronic post-stroke spasticity: results from the observational, multicenter, prospective BCause study. Toxins (Basel). 12:770. DOI: 10.3390/toxins12120770. PMID: 33291807. PMCID: PMC7762077. PMID: f655308c31804bc78bdfd0a1c059f2d1.
Article18. Gracies JM, Lugassy M, Weisz DJ, Vecchio M, Flanagan S, Simpson DM. 2009; Botulinum toxin dilution and endplate targeting in spasticity: a double-blind controlled study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 90:9–16.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2008.04.030. PMID: 19154823.19. Van Campenhout A, Verhaegen A, Pans S, Molenaers G. 2013; Botulinum toxin type A injections in the psoas muscle of children with cerebral palsy: muscle atrophy after motor end plate-targeted injections. Res Dev Disabil. 34:1052–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2012.11.016. PMID: 23295965.20. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Botulinum neurotoxin injection guidelines regarding flap surgeries in breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 75:503–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjps.2021.09.081. PMID: 34776389.
Article21. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Application of botulinum neurotoxin injections in TRAM flap for breast reconstruction: intramuscular neural arborization of the rectus abdominis muscle. Toxins (Basel). 13:269. DOI: 10.3390/toxins13040269. PMID: 33918558. PMCID: PMC8070362. PMID: 15169c322e5c4f158142057c4d95936b.
Article22. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Lee KL, Kim HJ. 2021; Effective botulinum neurotoxin injection in treating iliopsoas spasticity. Clin Anat. 34:431–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23670. PMID: 32805076.
Article23. Yi KH, Choi YJ, Cong L, Lee KL, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2020; Effective botulinum toxin injection guide for treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin Anat. 33:192–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23430. PMID: 31301235.
Article24. Yi KH, Rha DW, Kim HJ, Hu KS. 2016; Reply: optimizing efficacy of botulinum toxin injections using ultrasound guidance. Muscle Nerve. 54:513–4. DOI: 10.1002/mus.25213. PMID: 27287828.25. Lee JH, Lee BN, An X, Chung RH, Han SH. 2011; Location of the motor entry point and intramuscular motor point of the tibialis posterior muscle: for effective motor point block. Clin Anat. 24:91–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.21062. PMID: 21154644.
Article26. Oddy MJ, Brown C, Mistry R, Eastwood DM. 2006; Botulinum toxin injection site localization for the tibialis posterior muscle. J Pediatr Orthop B. 15:414–7. DOI: 10.1097/01.bpb.0000228387.94065.ff. PMID: 17001247.
Article27. Rha DW, Yi KH, Park ES, Park C, Kim HJ. 2016; Intramuscular nerve distribution of the hamstring muscles: application to treating spasticity. Clin Anat. 29:746–51. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22735. PMID: 27213466.
Article28. Yi KH, Rha DW, Lee SC, Cong L, Lee HJ, Lee YW, Kim HJ, Hu KS. 2016; Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of ankle invertor muscles in human cadaver using Sihler stain. Muscle Nerve. 53:742–7. DOI: 10.1002/mus.24939. PMID: 26467315.
Article29. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Lee K, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injections in piriformis syndrome. Clin Anat. 34:1028–34. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23711. PMID: 33347678.
Article30. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidance to trigger point injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome: intramuscular neural distribution of the quadratus lumborum. Clin Anat. 35:1100–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23918. PMID: 35655442.
Article31. Yi KH, Lee JH, Lee DK, Hu HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Anatomical locations of the motor endplates of sartorius muscle for botulinum toxin injections in treatment of muscle spasticity. Surg Radiol Anat. 43:2025–30. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-021-02813-7. PMID: 34378107. PMCID: PMC8354843.
Article32. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HM, Kim HJ. 2022; The botulinum neurotoxin for pain control after breast reconstruction: neural distribution of the pectoralis major muscle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 47:322–6. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-102653. PMID: 35039438.
Article33. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural distribution of the serratus anterior muscle: regarding botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome. Toxins (Basel). 14:271. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14040271. PMID: 35448880. PMCID: PMC9033065. PMID: c4ef8fa6e12442a990c0be9185a526e5.
Article34. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hur HW, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Kim HJ. 2023; Jan. 6. Distribution of the intramuscular innervation of the triceps brachii: clinical importance in the treatment of spasticity with botulinum neurotoxin. Clin Anat. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.24004. DOI: 10.1002/ca.24004. PMID: 36606364.
Article35. Hung CJ, Hsieh CL, Yang PL, Lin JJ. 2010; Relationships between posterior shoulder muscle stiffness and rotation in patients with stiff shoulder. J Rehabil Med. 42:216–20. DOI: 10.2340/16501977-0504. PMID: 20411215.36. Deltombe T, De Wispelaere JF, Gustin T, Jamart J, Hanson P. 2004; Selective blocks of the motor nerve branches to the soleus and tibialis posterior muscles in the management of the spastic equinovarus foot. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 85:54–8. DOI: 10.1016/S0003-9993(03)00405-2. PMID: 14970968.37. Bhakta BB, Cozens JA, Bamford JM, Chamberlain MA. 1996; Use of botulinum toxin in stroke patients with severe upper limb spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 61:30–5. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.61.1.30. PMID: 8676154. PMCID: PMC486452.
Article38. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural arborization of the latissimus dorsi muscle: application of botulinum neurotoxin injection in flap reconstruction. Toxins (Basel). 14:107. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14020107. PMID: 35202134. PMCID: PMC8878018. PMID: 0c7534ebd76b4902bff96b4bfe81c6b3.
Article39. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Lee JH, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2020; Intramuscular neural distribution of rhomboid muscles: evaluation for botulinum toxin injection using modified Sihler's method. Toxins (Basel). 12:289. DOI: 10.3390/toxins12050289. PMID: 32375284. PMCID: PMC7291336. PMID: 2a43e00b63b34292bd34bcaa4ce50d09.
Article40. Lin JJ, Yang JL. 2006; Reliability and validity of shoulder tightness measurement in patients with stiff shoulders. Man Ther. 11:146–52. DOI: 10.1016/j.math.2005.05.002. PMID: 16095946.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intramuscular Neural Distribution of Adductor Pollicis Muscle Spasticity in Cadaver Model Regarding Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment
- Intramuscular Neural Distribution of the Gastrocnemius for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection: Application to Cosmetic Calf Shaping
- Clinical and anatomical approach using Sihler's staining technique (whole mount nerve stain)
- Novel anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection in the mentalis muscle: a review
- Application of Botulinum Toxin Injection in Plastic Surgery