Clin Endosc.
2023 Sep;56(5):578-589. 10.5946/ce.2023.027.
Safety of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in cirrhosis compared to non-cirrhosis and effect of Child-Pugh score on post-ERCP complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO, USA
- 2Department of Medicine, Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY, USA
- 3Department of Medicine, Sunrise Hospital and Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV, USA
- 4Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Charleston area Medical Center, West Virginia University School of Medicine, Charleston, WV, USA
- KMID: 2546135
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.027
Abstract
- Background/Aims
The safety of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in hepatic cirrhosis and the impact of Child-Pugh class on post-ERCP complications need to be better studied. We investigated the post-ERCP complication rates in patients with cirrhosis compared with those without cirrhosis.
Methods
We conducted a literature search of relevant databases to identify studies that reported post-ERCP complications in patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Results
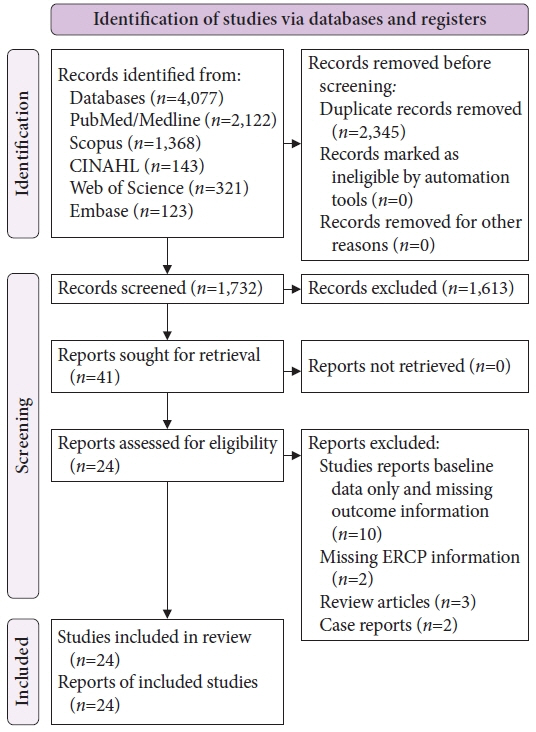
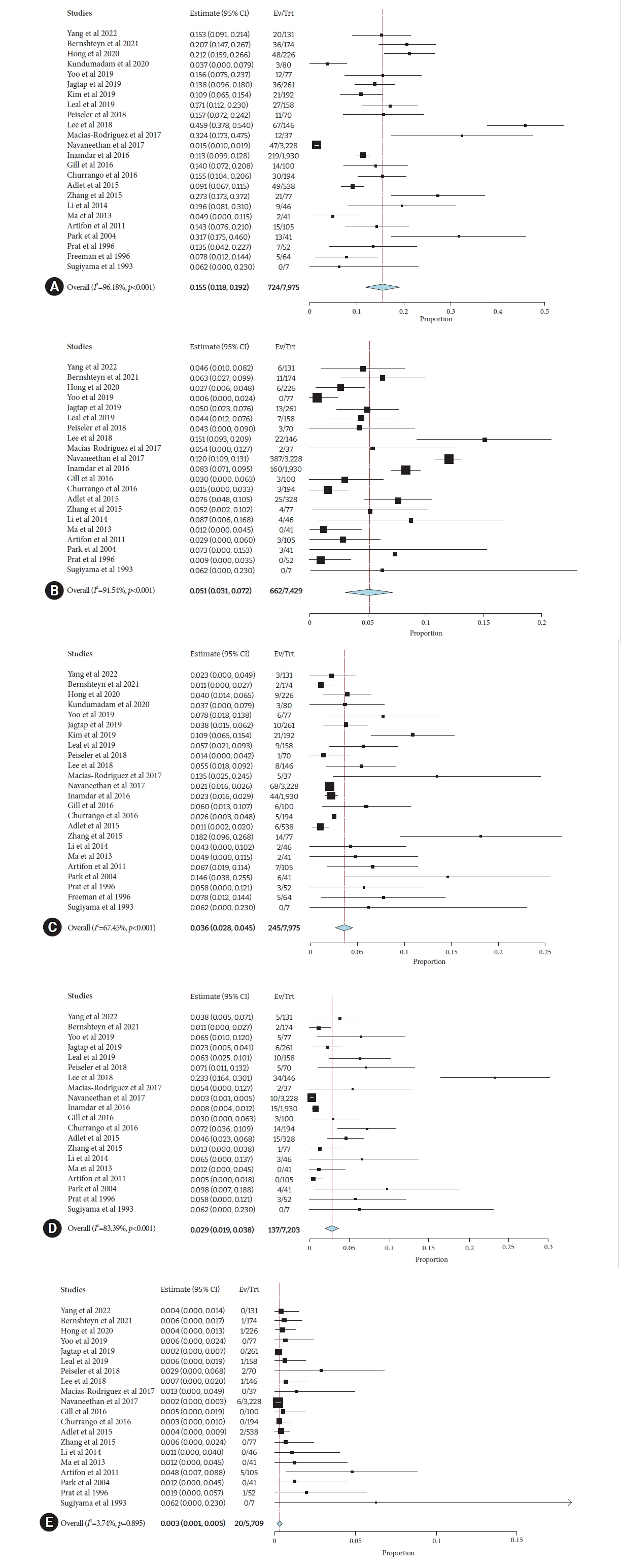
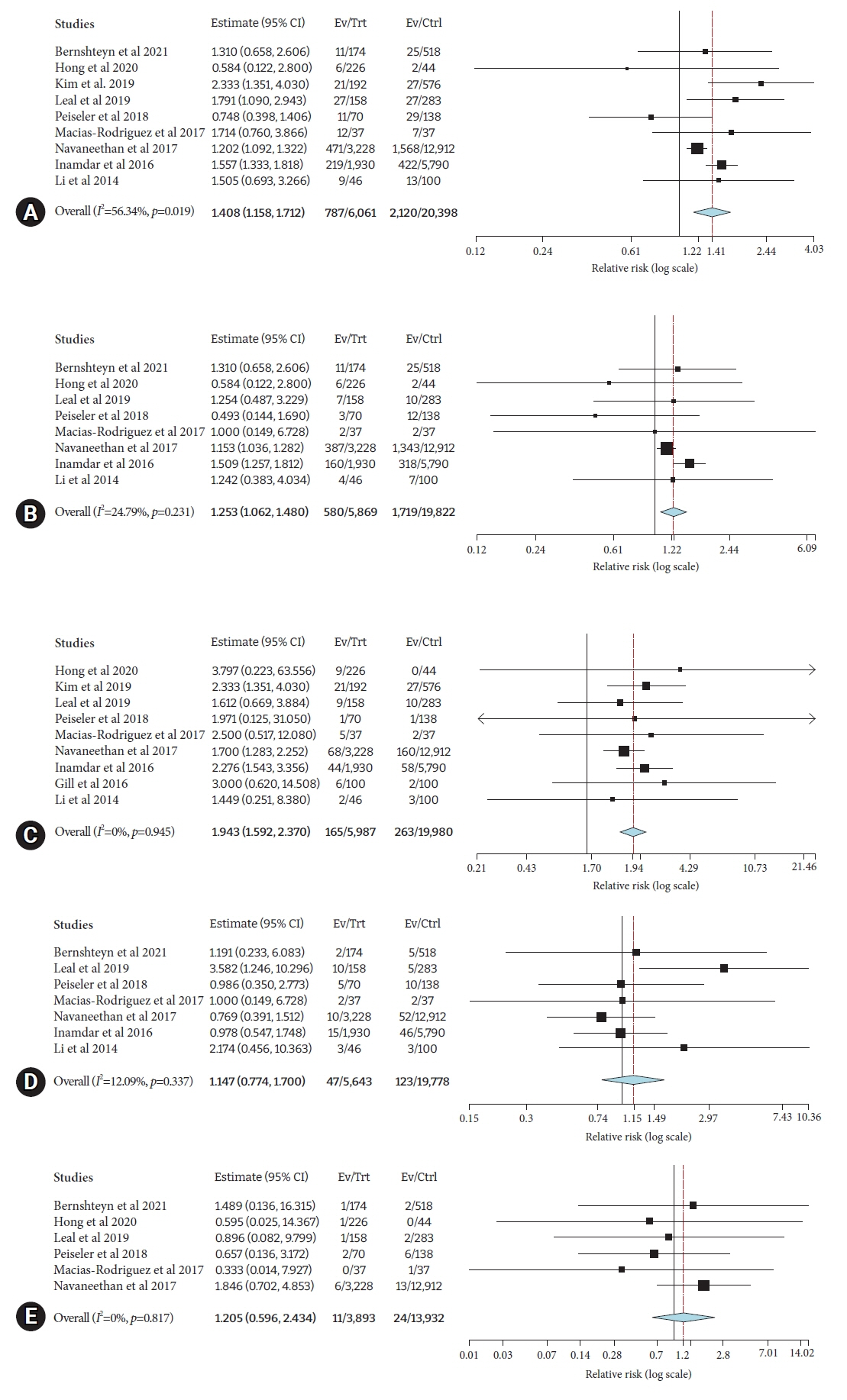
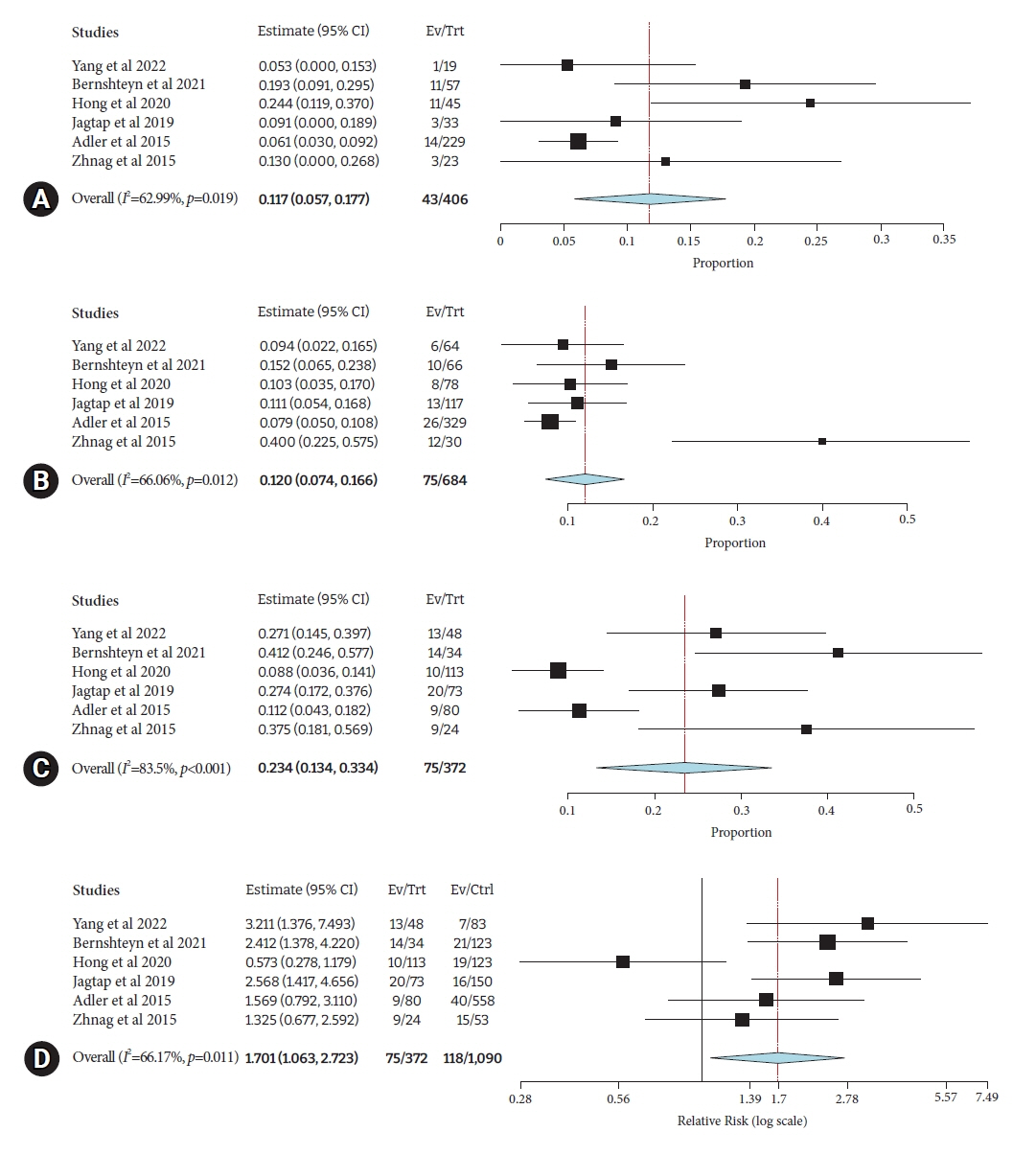
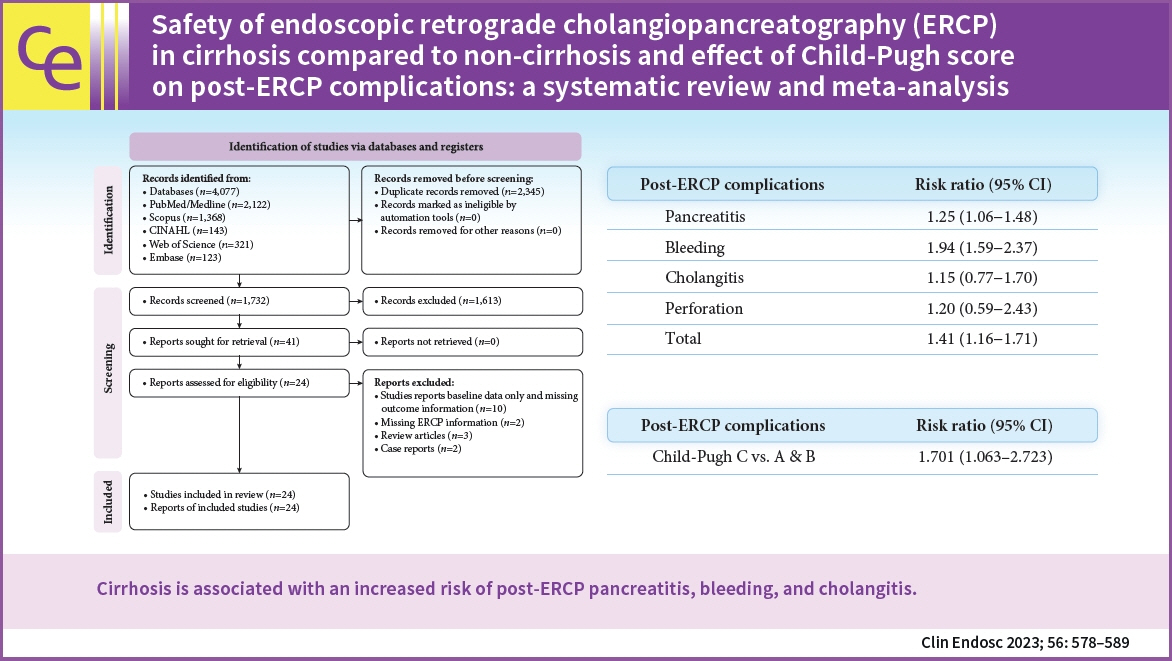
Twenty-four studies comprising 28,201 patients were included. The pooled incidence of post-ERCP complications in cirrhosis was 15.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 11.8%–19.2%; I2=96.2%), with an individual pooled incidence of pancreatitis 5.1% (95% CI, 3.1%–7.2%; I2=91.5%), bleeding 3.6% (95% CI, 2.8%–4.5%; I2=67.5%), cholangitis 2.9% (95% CI, 1.9%–3.8%; I2=83.4%), and perforation 0.3% (95% CI, 0.1%–0.5%; I2=3.7%). Patients with cirrhosis had a greater risk of post-ERCP complications (risk ratio [RR], 1.41; 95% CI, 1.16–1.71; I2=56.3%). The risk of individual odds of adverse events between cirrhosis and non-cirrhosis was as follows: pancreatitis (RR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.06–1.48; I2=24.8%), bleeding (RR, 1.94; 95% CI, 1.59–2.37; I2=0%), cholangitis (RR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.77–1.70; I2=12%), and perforation (RR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.59–2.43; I2=0%).
Conclusions
Cirrhosis is associated with an increased risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis, bleeding, and cholangitis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Trap R, Adamsen S, Hart-Hansen O, et al. Severe and fatal complications after diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: a prospective series of claims to insurance covering public hospitals. Endoscopy. 1999; 31:125–130.2. Adler DG, Baron TH, Davila RE, et al. ASGE guideline: the role of ERCP in diseases of the biliary tract and the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:1–8.3. Alkhatib AA, Hilden K, Adler DG. Comorbidities, sphincterotomy, and balloon dilation predict post-ERCP adverse events in PSC patients: operator experience is protective. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:3685–3688.4. Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, et al. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1781–1788.5. Coelho-Prabhu N, Shah ND, Van Houten H, et al. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: utilisation and outcomes in a 10-year population-based cohort. BMJ Open. 2013; 3:e002689.6. Zhang J, Ye L, Zhang J, et al. MELD scores and Child-Pugh classifications predict the outcomes of ERCP in cirrhotic patients with choledocholithiasis: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e433.7. Navaneethan U, Njei B, Zhu X, et al. Safety of ERCP in patients with liver cirrhosis: a national database study. Endosc Int Open. 2017; 5:E303–E314.8. Farooq U, Tarar Z, Malik A, Amin M, Sifuentes H. How does cirrhosis impact mortality, morbidity, and resource utilization in non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding? A nationwide analysis. Gastroenterol Rev/Prz Gastroenterol. 2022; 17.9. Mosko JD, Nguyen GC. Increased perioperative mortality following bariatric surgery among patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9:897–901.10. Yang H, Mou Y, Hu B. Safety and efficacy of common endoscopic treatments in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Ann Hepatol. 2022; 27:100689.11. Bernshteyn M, Hu L, Masood U, et al. Retrospective analysis of complications related to endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography in patients with cirrhosis vs patients without cirrhosis. World J Hepatol. 2021; 13:472–482.12. Hong J, Zuo W, Wang A, et al. Efficacy and safety of ERCP in patients with gastroesophageal varices. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99:e22051.13. Kundumadam S, Phatharacharukul P, Reinhart K, et al. Bleeding after elective interventional endoscopic procedures in a large cohort of patients with cirrhosis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020; 11:e00288.14. Kim JY, Lee HS, Chung MJ, et al. Bleeding complications and clinical safety of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients with liver cirrhosis. Yonsei Med J. 2019; 60:440–445.15. Yoo T, Epistola R, Epistola J, et al. Evaluating the risk of adverse events with interventional endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound procedures in cirrhotic patients. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 11:523–530.16. Jagtap N, Nabi Z, Tandan M, et al. Is it safe to perform endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in decompensated cirrhosis? J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019; 9:554–560.17. Leal C, Prado V, Colan J, et al. Adverse events and acute chronic liver failure in patients with cirrhosis undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a multicenter matched-cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019; 114:89–97.18. Lee JC, Kim JS, Kim HW, et al. Outcome of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients with clinically defined decompensated liver cirrhosis. J Dig Dis. 2018; 19:605–613.19. Peiseler M, Reiners D, Pinnschmidt HO, et al. Risk of endoscopic biliary interventions in primary sclerosing cholangitis is similar between patients with and without cirrhosis. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0202686.20. Macías-Rodríguez RU, Ruiz-Margáin A, Rodriguez-Garcia JL, et al. Risk factors associated with complications in cirrhotic patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 29:238–243.21. Adler DG, Haseeb A, Francis G, et al. Efficacy and safety of therapeutic ERCP in patients with cirrhosis: a large multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:353–359.22. Inamdar S, Berzin TM, Berkowitz J, et al. Decompensated cirrhosis may be a risk factor for adverse events in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Liver Int. 2016; 36:1457–1463.23. Churrango J, Doppalapudi K, Hsieh A, et al. Sa1171 Predictors of post-ERCP complications in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:AB240–AB241.24. Gill M, Yousuf SGN, Nawaz A, Nazir R. Outcomes of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2016; 64:S278.25. Li DM, Zhao J, Zhao Q, et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for common bile duct stones in liver cirrhotic patients. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014; 34:612–615.26. Ma MY, Jiang GB, Wang X, Miao L, Ji GZ, Wang M. ERCP for treatment of choledocholithiasis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2013; 21:3736–3741.27. Artifon EL, da Silveira EB, Aparicio D, et al. Management of common bile duct stones in cirrhotic patients with coagulopathy: a comparison of supra-papillary puncture and standard cannulation technique. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:1904–1911.28. Park DH, Kim MH, Lee SK, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy vs. endoscopic papillary balloon dilation for choledocholithiasis in patients with liver cirrhosis and coagulopathy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:180–185.29. Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, et al. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335:909–918.30. Prat F, Tennenbaum R, Ponsot P, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 43(2 Pt 1):127–131.31. Sugiyama M, Atomi Y, Kuroda A, et al. Treatment of choledocholithiasis in patients with liver cirrhosis: surgical treatment or endoscopic sphincterotomy? Ann Surg. 1993; 218:68–73.32. Farooq U, Gondal AB, Franco D, et al. Validation of Tokyo guidelines 2018 for safety and mortality benefit from urgent ERCP in acute cholangitis across different age groups. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2023; 30:737–744.33. Kullman E, Borch K, Lindström E, et al. Bacteremia following diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:444–449.34. Szary NM, Al-Kawas FH. Complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: how to avoid and manage them. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2013; 9:496–504.35. Enns R, Eloubeidi MA, Mergener K, et al. ERCP-related perforations: risk factors and management. Endoscopy. 2002; 34:293–298.36. Fatima J, Baron TH, Topazian MD, et al. Pancreaticobiliary and duodenal perforations after periampullary endoscopic procedures: diagnosis and management. Arch Surg. 2007; 142:448–455.37. Mashiana HS, Dhaliwal AS, Sayles H, et al. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis focused on adverse events. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 10:354–366.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bleeding Complications and Clinical Safety of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
- Basic knowledge of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography complications: Techniques to reduce risk and management strategies
- Clinical Usefulness of ERCP in Acute Pancreatitis
- Quality indicators in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a brief review of established guidelines