Korean J Pain.
2023 Jan;36(1):98-105. 10.3344/kjp.22227.
Measurement of S1 foramen depth for ultrasound-guided S1 transforaminal epidural injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea
- 3Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2537616
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.22227
Abstract
- Background
Ultrasound-guided first sacral transforaminal epidural steroid injection (S1 TFESI) is a useful and easily applicable alternative to fluoroscopy or computed tomography (CT) in lumbosacral radiculopathy. When a needle approach is used, poor visualization of the needle tip reduces the accuracy of the procedure, increasing its difficulty. This study aimed to improve ultrasound-guided S1 TFESI by evaluating radiological S1 posterior foramen data obtained using three-dimensional CT (3D-CT).
Methods
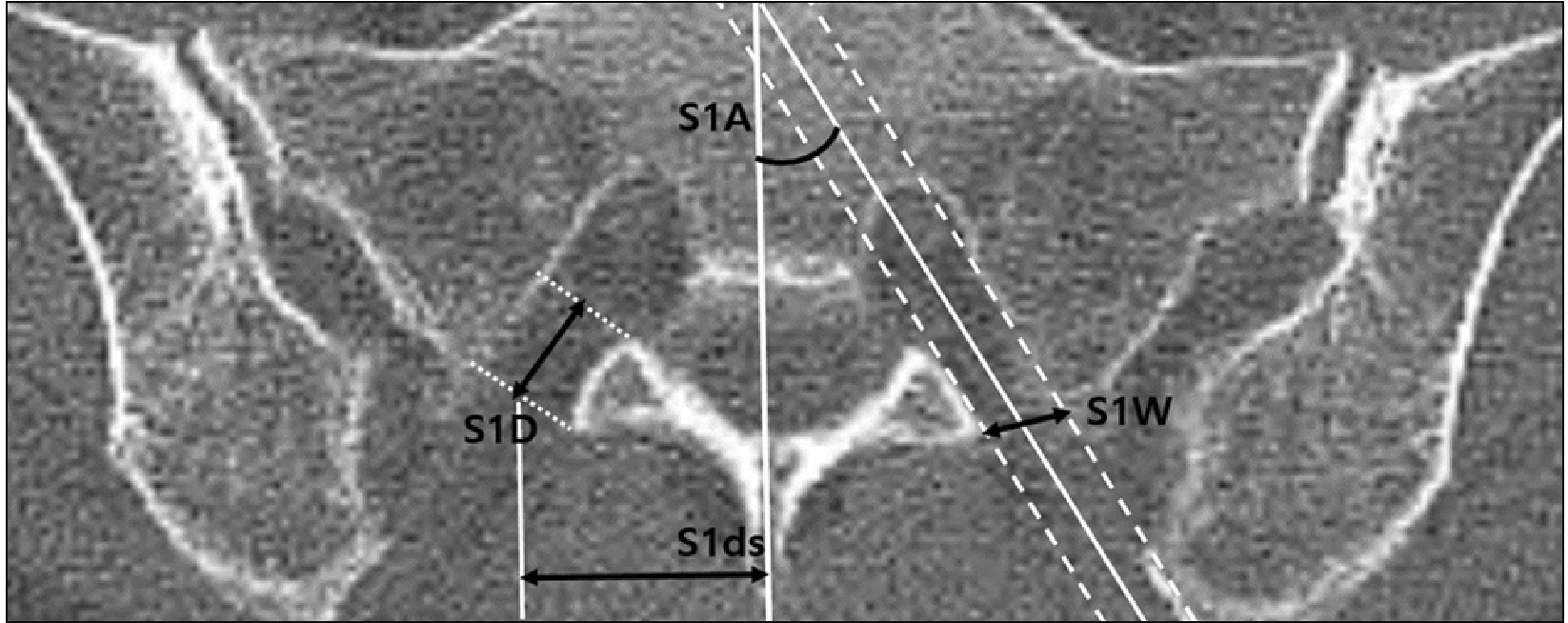
Axial 3D-CT images of the pelvis were retrospectively analyzed. The radiological measurements obtained from the images included 1st posterior sacral foramen depth (S1D, mm), 1st posterior sacral foramen width (S1W, mm), the angle of the 1st posterior sacral foramen (S1A, °), and 1st posterior sacral foramen distance (S1ds, mm). The relationship between the demographic factors and measured values were then analyzed.
Results
A total of 632 patients (287 male and 345 female) were examined. The mean S1D values for males and females were 11.9 ± 1.9 mm and 10.6 ± 1.8 mm, respectively (P < 0.001); the mean S1A 28.2 ± 4.8° and 30.1 ± 4.9°, respectively (P < 0.001); and the mean S1ds, 24.1 ± 2.9 mm and 22.9 ± 2.6 mm, respectively (P < 0.001); however, the mean S1W values were not significantly different. Height was the only significant predictor of S1D (β = 0.318, P = 0.004).
Conclusions
Ultrasound-guided S1 TFESI performance and safety may be improved with adjustment of needle insertion depth congruent with the patient’s height.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Manchikanti L, Buenaventura RM, Manchikanti KN, Ruan X, Gupta S, Smith HS, et al. 2012; Effectiveness of therapeutic lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections in managing lumbar spinal pain. Pain Physician. 15:E199–245. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2012/15/E199. PMID: 22622912.2. Roberts ST, Willick SE, Rho ME, Rittenberg JD. 2009; Efficacy of lumbosacral transforaminal epidural steroid injections: a systematic review. PM R. 1:657–68. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2009.04.008. PMID: 19627959.3. Chun EH, Park HS. 2015; Effect of high-volume injectate in lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections: a randomized, active control trial. Pain Physician. 18:519–25. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2015/18/E519. PMID: 26606003.4. Bhatia A, Flamer D, Shah PS, Cohen SP. 2016; Transforaminal epidural steroid injections for treating lumbosacral radicular pain from herniated intervertebral discs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 122:857–70. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001155. PMID: 26891397.5. Jordan J, Konstantinou K, O'Dowd J. 2009; Herniated lumbar disc. BMJ Clin Evid. 2009:1118. DOI: 10.3171/jns.1994.81.5.0806b. PMID: 21711958. PMCID: PMC3275148.6. Sato M, Mikawa Y, Matuda A. 2013; Ultrasound and electrical nerve stimulation-guided S1 nerve root block. J Anesth. 27:775–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-013-1591-y. PMID: 23494676. PMCID: PMC3825138.7. Arman C, Naderi S, Kiray A, Aksu FT, Yilmaz HS, Tetik S, et al. 2009; The human sacrum and safe approaches for screw placement. J Clin Neurosci. 16:1046–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocn.2008.07.081. PMID: 19442524.8. Cheng JS, Song JK. 2003; Anatomy of the sacrum. Neurosurg Focus. 15:E3. DOI: 10.3171/foc.2003.15.2.3. PMID: 15350034.9. Povo A, Arantes M, Matzel KE, Barbosa J, Ferreira MA, Pais D, et al. 2016; Surface anatomical landmarks for the location of posterior sacral foramina in sacral nerve stimulation. Tech Coloproctol. 20:859–64. DOI: 10.1007/s10151-016-1543-2. PMID: 27844258.10. Park YJ, Lee SH, Ryu KH, Kim YK, Shim J, Lee HW, et al. 2020; Novel method for S1 transforaminal epidural steroid injection. World Neurosurg. 133:e443–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.09.051. PMID: 31526885.11. Hwang BY, Park JH, Ji HT, Kim GE, Kim SK, Lee YK, et al. 2022; Retrospective lumbosacral CT analysis and prospective observational study of the ipsilateral tunnel view technique for fluoroscopy-guided selective S1 transforaminal epidural injection. Pain Pract. 22:83–90. DOI: 10.1111/papr.13061. PMID: 34291569.12. Cha YD, Choi JK, Yang CW, Lim HK, Heo GA, Kim BG. 2017; Relationship between first dorsal sacral foramen and lumbar facet joint connecting line in South Korea populations: retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e7544. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007544. PMID: 28723774. PMCID: PMC5521914.13. Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J. 2005; Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:346–53. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000152379.54463.65. PMID: 15682018.14. Park D. 2018; Can ultrasound-guided S1 transforaminal epidural injection using the in-plane approach and color Doppler imaging be a safer alternative to lumbar inter-laminar epidural injection? Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 97:e66–7. DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000856. PMID: 29087968.15. Gofeld M, Bristow SJ, Chiu SC, McQueen CK, Bollag L. 2012; Ultrasound-guided lumbar transforaminal injections: feasibility and validation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:808–12. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182340096. PMID: 21912311.16. Evansa I, Logina I, Vanags I, Borgeat A. 2015; Ultrasound versus fluoroscopic-guided epidural steroid injections in patients with degenerative spinal diseases: a randomised study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 32:262–8. DOI: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000103. PMID: 24841502.17. Hashemi M, Dadkhah P, Taheri M, Haji Seyed Abootorabi SM, Naderi-Nabi B. 2019; Ultrasound-guided lumbar transforaminal epidural injections; a single center fluoroscopic validation study. Bull Emerg Trauma. 7:251–5. DOI: 10.29252/beat-070307. PMID: 31392224. PMCID: PMC6681880.18. McGrath MC, Stringer MD. 2011; Bony landmarks in the sacral region: the posterior superior iliac spine and the second dorsal sacral foramina: a potential guide for sonography. Surg Radiol Anat. 33:279–86. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-010-0735-0. PMID: 21063707.19. Kim SH, Yoon KB, Yoon DM, Choi SA, Kim EM. 2010; An analysis of location of needle entry point and palpated PSIS in S1 nerve root block. Korean J Pain. 23:242–6. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.242. PMID: 21217887. PMCID: PMC3000620.20. Lee BJ, Han J, Park D. 2020; A video of ultrasound-guided S1 transforaminal epidural injection using color Doppler: technical reports. Pain Pract. 20:396–8. DOI: 10.1111/papr.12858. PMID: 31816174.21. Price R, Okamoto M, Le Huec JC, Hasegawa K. 2016; Normative spino-pelvic parameters in patients with the lumbarization of S1 compared to a normal asymptomatic population. Eur Spine J. 25:3694–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-016-4794-8. PMID: 27671281.22. Plaikner M, Gruber H, Schwabl C, Brenner E, Bale R, Skalla E, et al. 2019; A simple approach for ultrasound-guided pararadicular injections in the sacral spine: a pilot computer tomography controlled cadaver study. Med Ultrason. 21:125–30. DOI: 10.11152/mu-1823. PMID: 31063514.23. Park D. 2018; Ultrasound-guided S1 transforaminal epidural injection using the in-plane approach and color Doppler imaging. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 97:e14–6. DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000754. PMID: 28406801.24. Bagheri H, Govsa F. 2019; Anatomical considerations of safe drilling corridor upper sacral segment screw insertion. J Orthop. 16:543–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2019.04.010. PMID: 31660021. PMCID: PMC6806658.25. Watanabe N, Takigawa T, Uotani K, Oda Y, Misawa H, Tanaka M, et al. 2022; Three-dimensional analysis of the ideal entry point for sacral alar iliac screws. Asian Spine J. doi: 10.31616/asj.2021.0268. DOI: 10.31616/asj.2021.0268. PMID: 35184519.26. Oura P, Nurkkala M, Auvinen J, Niinimäki J, Karppinen J, Junno JA. 2019; The association of body size, shape and composition with vertebral size in midlife - the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966 study. Sci Rep. 9:3944. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40880-4. PMID: 30850701. PMCID: PMC6408584.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Influencing Factors to Depth of Epidural Space for Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Block in Korean
- Effects of L4-5 Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection in L5 Radiculopathy
- Feasibility of Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar and S1 Nerve Root Block: A Cadaver Study
- Comparison of Radiation Exposure during Fluoroscopy-Guided Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections at Different Vertebral Levels
- Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injection: A Narrative Review