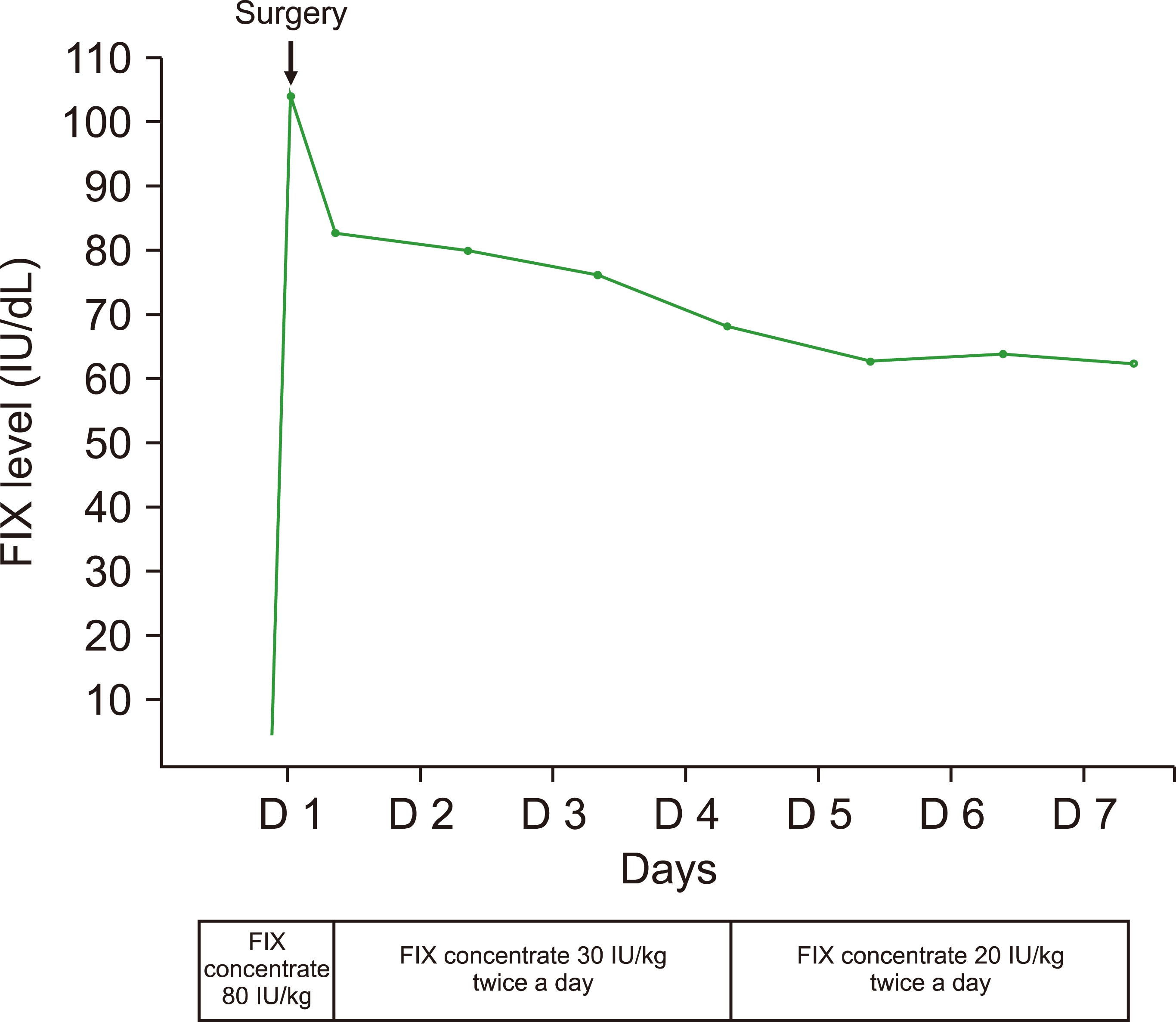
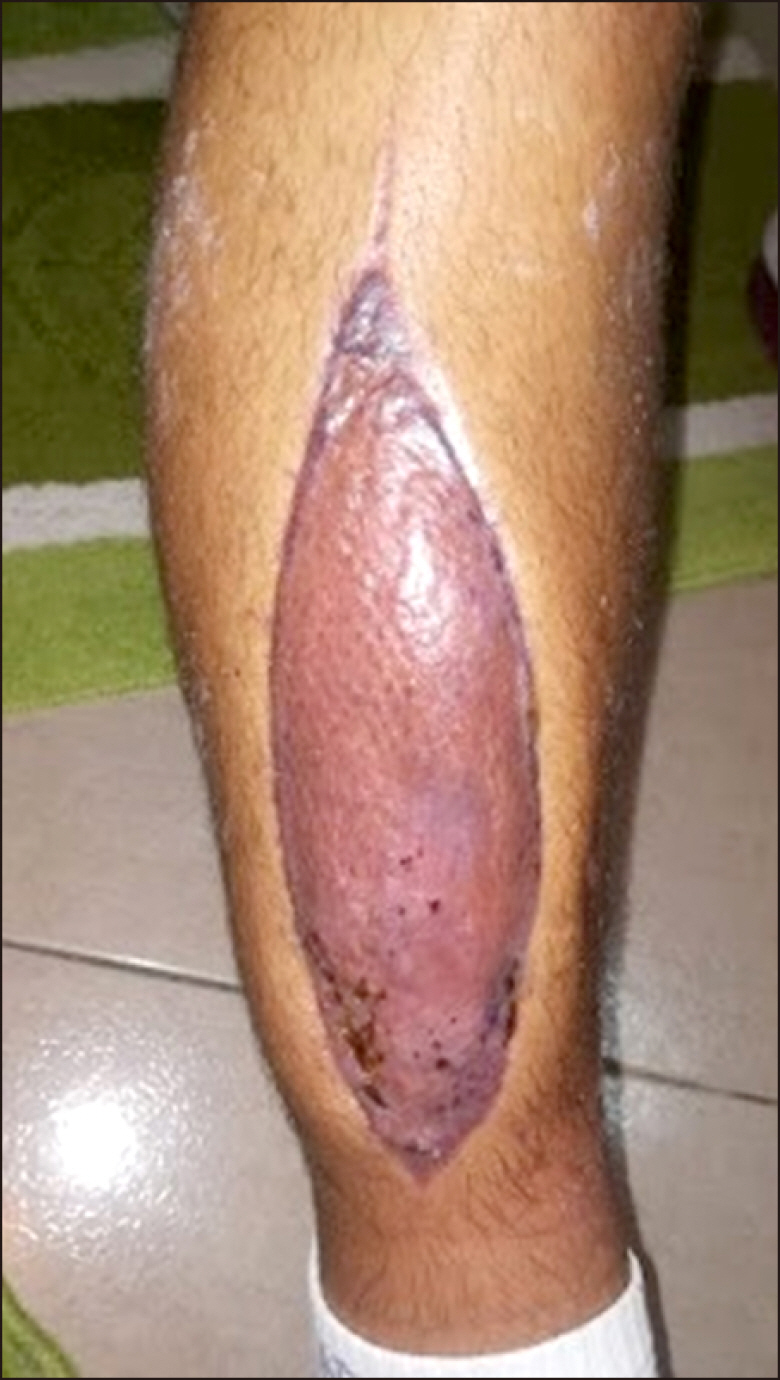
Blood Res.
2022 Dec;57(4):281-284. 10.5045/br.2022.2022112.
Rapid development of lower leg compartment syndrome following firearm injury in a patient with moderate hemophilia B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Clinic of Haematology, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia
- 2Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia.
- 3Clinic of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia.
- 4Clinic for Burns, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia.
- KMID: 2537552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2022.2022112
Figure
Reference
-
1. Srivastava A, Santagostino E, Dougall A, et al. 2020; WFH guidelines for the management of hemophilia, 3rd edition. Haemophilia. 26:1–158. DOI: 10.1111/hae.14046. PMID: 32744769.2. Sissolak G, Dippenaar A, Desai F, Karabus CD, Cruickshank AL, McDonald A. 2012; Trauma-related bleeding complications in South African patients with haemophilia. Haemophilia. 18:e405–7. DOI: 10.1111/hae.12025. PMID: 22994858.3. Fraenkel GJ, Honey GE. 1955; Gunshot wounds in a haemophilic patient; successful treatment by animal antihaemophilic globulin and surgery. Lancet. 269:1117–20. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(55)92953-6. PMID: 13272342.4. von Keudell AG, Weaver MJ, Appleton PT, et al. 2015; Diagnosis and treatment of acute extremity compartment syndrome. Lancet. 386:1299–310. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00277-9. PMID: 26460664.5. McQueen MM, Gaston P, Court-Brown CM. 2000; Acute compartment syndrome. Who is at risk? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 82:200–3. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.82B2 .9799. PMID: 10755426.6. Branco BC, Inaba K, Barmparas G, et al. 2011; Incidence and predictors for the need for fasciotomy after extremity trauma: a 10-year review in a mature level I trauma centre. Injury. 42:1157–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.07.243. PMID: 20678764.7. Mortensen SJ, Orman S, Serino J, Mohamadi A, Nazarian A, von Keudell A. 2021; Factors associated with development of traumatic acute compartment syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 9:263–71. DOI: 10.22038/abjs.2020.46684.2284. PMID: 34239953. PMCID: PMC8221439.8. Gonzalez RP, Scott W, Wright A, Phelan HA, Rodning CB. 2009; Anatomic location of penetrating lower-extremity trauma predicts compartment syndrome development. Am J Surg. 197:371–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.11.013. PMID: 19245917.9. Rorabeck CH, Macnab I. 1975; The pathophysiology of the anterior tibial compartmental syndrome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (113):52–7. DOI: 10.1097/00003086-197511000-00008. PMID: 1192675.10. Sheridan GW, Matsen FA 3rd. 1976; Fasciotomy in the treatment of the acute compartment syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 58:112–5. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-197658010-00020. PMID: 1249096.11. Lancourt JE, Gilbert MS, Posner MA. 1977; Management of bleeding and associated complications of hemophilia in the hand and forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 59:451–60. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-197759040-00003. PMID: 863937.12. Dumontier C, Sautet A, Man M, Bennani M, Apoil A. 1994; Entrapment and compartment syndromes of the upper limb in haemophilia. J Hand Surg Br. 19:427–9. DOI: 10.1016/0266-7681(94)90204-6. PMID: 7964091.13. Kim J, Zelken J, Sacks JM. 2013; Case report - spontaneous forearm compartment syndrome in a boy with hemophilia A: a therapeutic dilemma. Eplasty. 13:e16. PMID: 23573336. PMCID: PMC3601454.14. Jones G, Thompson K, Johnson M. 2013; Acute compartment syndrome after minor trauma in a patient with undiagnosed mild haemophilia B. Lancet. 382:1678. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61954-6. PMID: 24238556.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Compartment Syndrome of the Lower Leg and Foot
- Anterior Compartment Syndrome after Surgery of Bosworth Fracture-Dislocation of the Ankle: A Case Report
- Acute Compartment Syndrome after Non-Contact Peroneus Longus Muscle Rupture
- Compartment Syndrome of the Gluteus Medius Occurred without Bleeding or Trauma: A Case Report
- Thenar Compartment syndrome: A Case Report