J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Dec;37(50):e348. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e348.
Citation Activity of Journal of Korean Medical Science in 2011–2020: Reflection on the Most and Least Cited Items
- Affiliations
-
- 1Journal of Korean Medical Science, Korean Academy of Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2537051
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e348
Abstract
- Background
The Journal of Korean Medical Science (JKMS) is a weekly periodical published by the Korean Academy of Medical Sciences. JKMS invites global researchers to submit articles covering various areas in general medicine. The present article’s aim was to analyze citations of JKMS articles in 2011–2020 for updating editorial policies.
Methods
Citation records of JKMS articles were tracked in Web of Science (WoS), Clarivate ®from August 2021 to June 2022.
Results
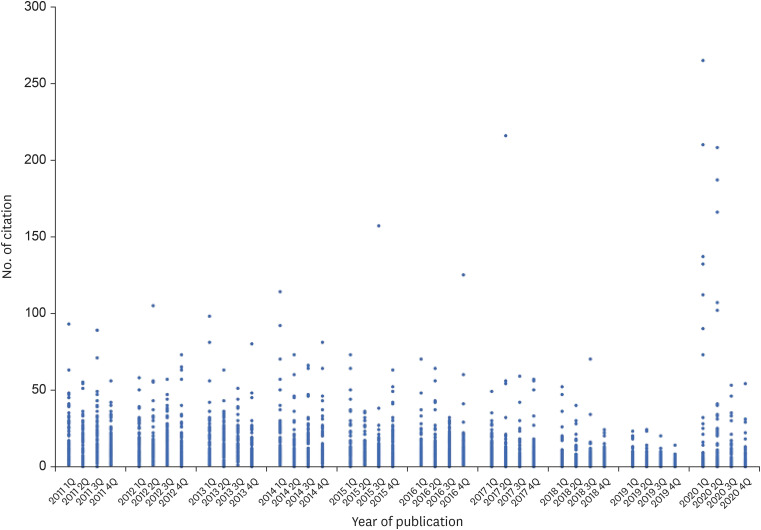
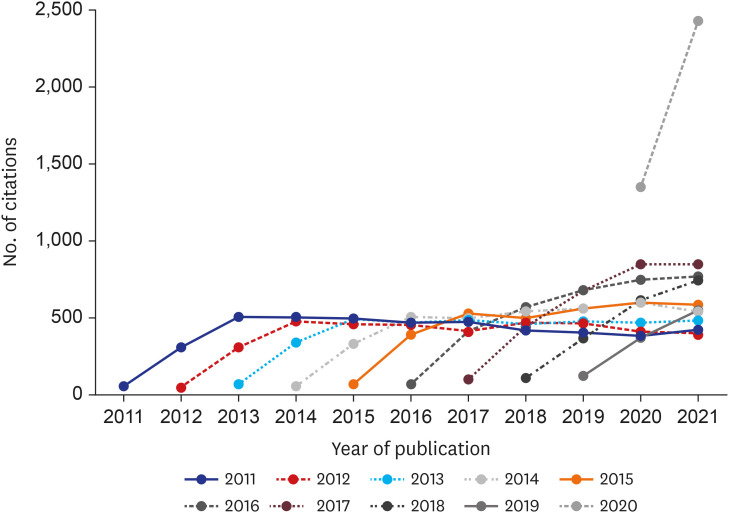
In 2011–2020, JKMS published 2,880 articles, including 2,757 (96.0%) ever cited. All reviews (57/57) and 96% of original research reports (2,184 out of 2,264) received at least one citation. Brief communications, opinions, and images were least cited items. Of 36 subject categories covered by JKMS, only biomedical engineering was significantly less advantageous citation-wise. Five articles published in 2012–2017 attracted more than 100 citations. Most other articles were cited less than 50 times. Article categories of nationwide epidemiology, disease or patient registries, clinical trials, and infectious diseases were distinguished as well cited. Of 378 articles published in 2020, 10 were cited at least 100 times; all these ten items were related to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and coronavirus disease 2019. In the past 5 years, studies on health care laws, management, and some specific topics in clinical specialties were not cited. The citation trends in WoS, Crossref, and Scopus were similar while PubMed Central records were roughly twice less.
Conclusion
Most of JKMS articles are cited during 5 years post publication, with 1.4% noncitation rate. The obtained results suggest that inviting review articles in clinical sciences, research reports on hot medical topics, and nationwide database analyses may attract more author interest and related citations.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Academy of Medical Sciences. Journal of Korean Medical Science. Updated 2022. Accessed August 22, 2022. https://jkms.org .2. Hong ST, Youn HS. Status of editing and publishing of scholarly journals by academic societies of science and technology in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(25):e208. PMID: 32597044.3. Ganatra K, Gasparyan AY, Gupta L. Modern health journalism and impact of social media. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(22):e162. PMID: 34100565.4. Van der Veer T, Baars JE, Birnie E, Hamberg P. Citation analysis of the ‘Big Six’ journals in internal medicine. Eur J Intern Med. 2015; 26(6):458–459. PMID: 26066401.5. Weale AR, Bailey M, Lear PA. The level of non-citation of articles within a journal as a measure of quality: a comparison to the impact factor. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2004; 4(1):14. PMID: 15169549.6. Asaad M, Kallarackal AP, Meaike J, Rajesh A, de Azevedo RU, Tran NV. Citation skew in plastic surgery journals: does the journal impact actor predict individual article citation rate? Aesthet Surg J. 2020; 40(10):1136–1142. PMID: 31745562.7. National Library of Medicine. PubMed Central. Updated 2022. Accessed August 22, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/ .8. Kulkarni AV, Aziz B, Shams I, Busse JW. Comparisons of citations in Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar for articles published in general medical journals. JAMA. 2009; 302(10):1092–1096. PMID: 19738094.9. Ayoub F, Ouni A, Case R, Ladna M, Shah H, Rubin DT. Dissemination of gastroenterology and hepatology research on social media platforms is associated with increased citation count. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021; 116(10):2137–2139. PMID: 33767107.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Highly Cited Articles in Periacetabular Osteotomy Research
- Top 50 cited articles on dental stem cell research
- Citation Analysis of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from KoMCI, Web of Science, and Scopus
- A bibliometric analysis on the most-cited publications on carotid endarterectomy throughout history
- Contemporary research trends on nanoparticles in endodontics: a bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles