Clin Endosc.
2022 Nov;55(6):810-814. 10.5946/ce.2021.003.
Extracutaneous mastocytoma of colon: a case report and literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeonju Korea Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- KMID: 2536082
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.003
Abstract
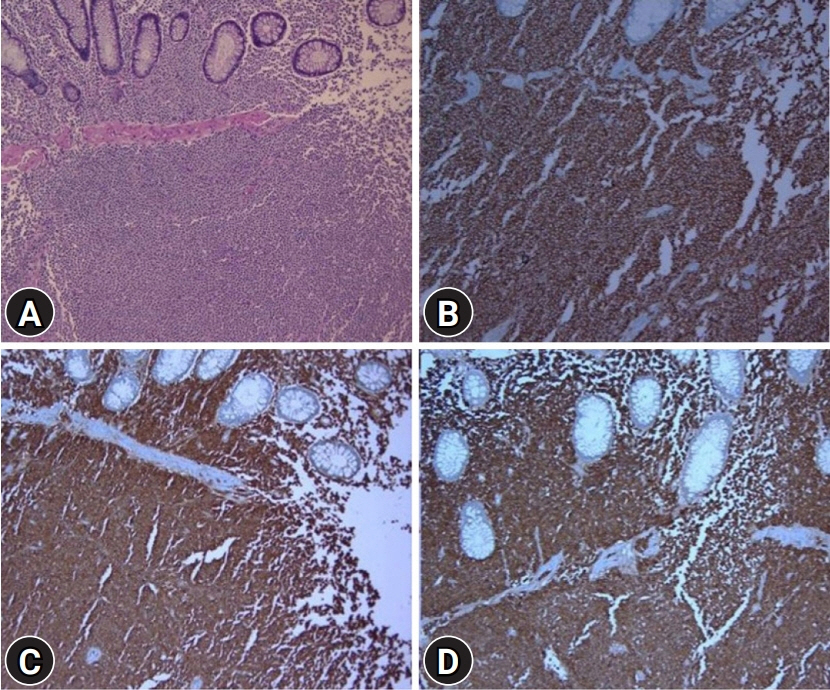
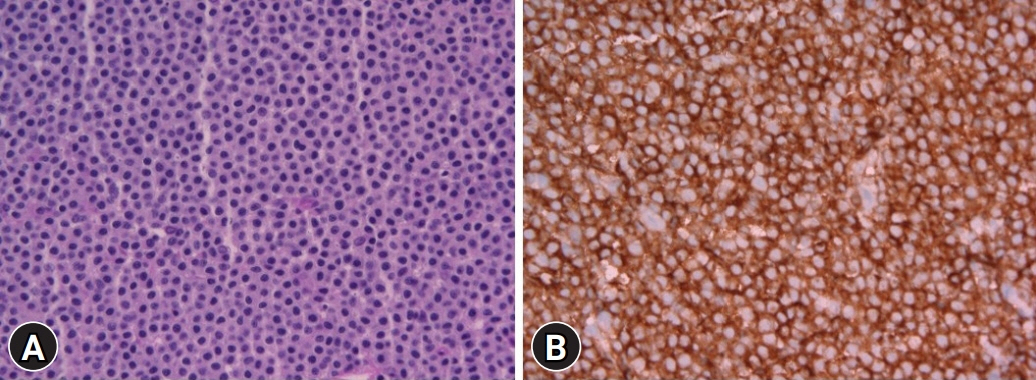
- Extracutaneous mastocytoma is a rare benign tumor composed of mature mast cells and is located in tissues other than the skin. We report the case of a 61-year-old male who was diagnosed with extracutaneous mastocytoma via colonoscopic polypectomy and biopsy. To our knowledge, this was the first case of a solitary extracutaneous mastocytoma of the colon. We reported this case and reviewed the literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Valent P, Akin C, Metcalfe DD. Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood. 2017; 129:1420–1427.
Article2. Gotlib J, Gerds AT, Bose P, et al. Systemic mastocytosis, Version 2. 2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018; 16:1500–1537.
Article3. Brockow K. Epidemiology, prognosis, and risk factors in mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2014; 34:283–295.
Article4. Matito A, Azaña JM, Torrelo A, et al. Cutaneous mastocytosis in adults and children: new classification and prognostic factors. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2018; 38:351–363.5. Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF. Childhood solitary cutaneous mastocytoma: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, evaluation, and management. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2019; 15:42–46.
Article6. Cohen PR. Solitary mastocytoma presenting in an adult: report and literature review of adult-onset solitary cutaneous mastocytoma with recommendations for evaluation and treatment. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016; 6:31–38.
Article7. Valent P, Horny HP, Escribano L, et al. Diagnostic criteria and classification of mastocytosis: a consensus proposal. Leuk Res. 2001; 25:603–625.
Article8. Jensen RT. Gastrointestinal abnormalities and involvement in systemic mastocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000; 14:579–623.
Article9. Sherwin RP, Kern WH, Jones JC. Solitary mast cell granuloma (histiocytoma) of the lung; a histopathologic, tissue culture and time-lapse cinematographic study. Cancer. 1965; 18:634–641.
Article10. Charrette EE, Mariano AV, Laforet EG. Solitary mast cell “tumor” of lung. Its place in the spectrum of mast cell disease. Arch Intern Med. 1966; 118:358–362.
Article11. Kudo H, Morinaga S, Shimosato Y, et al. Solitary mast cell tumor of the lung. Cancer. 1988; 61:2089–2094.
Article12. Castells MC. Extracutaneous mastocytoma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:1513–1515.
Article13. Khan K, Kupferman ME, Gardner JM, et al. Solitary mastocytoma in an adult with an unusual clinical presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011; 65:683–684.
Article14. Ayadi L, Abid N, Makni S, et al. An unusual tumour of the lung. Pathologica. 2015; 107:14–18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 5 Cases of Solitary Mastocytoma
- A Case of Solitary Bullous Mastocytoma Occurring at a Site of Spinal Tap
- Solitary Mastocytoma on the Scalp
- Suppression of the Ly6 antigens expression on P815 mastocytoma cells by expressing antisense RNA
- Combined Mastocytoma-hemangioma in a Patient with Urticaria Pigmentosa