J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2022 Oct;39(4):322-331. 10.12701/jyms.2022.00325.
Regenerative potential of biphasic calcium phosphate and enamel matrix derivatives in the treatment of isolated interproximal intrabony defects: a randomized controlled trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Pacific Dental College and Hospital, PAHER University, Udaipur, India
- 2Department of Periodontology, Sibar Institute of Dental Sciences, Takkellapadu, Guntur, India
- 3Department of Periodontology, DR. R Ahmed Dental College and Hospital, Kolkata, India
- 4Department of Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge, Index Institute of Dental Sciences, Indore, India
- KMID: 2534660
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00325
Abstract
- Background
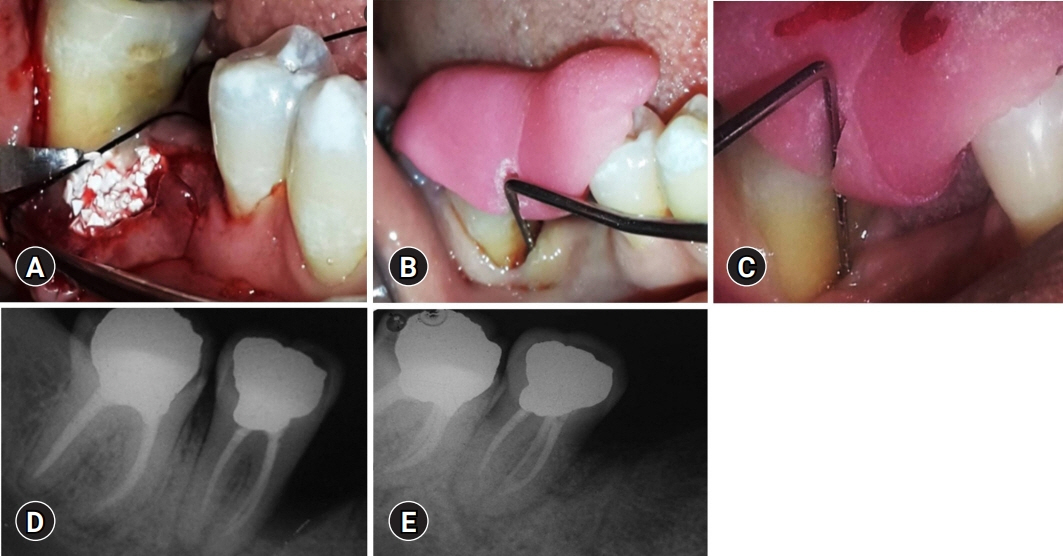
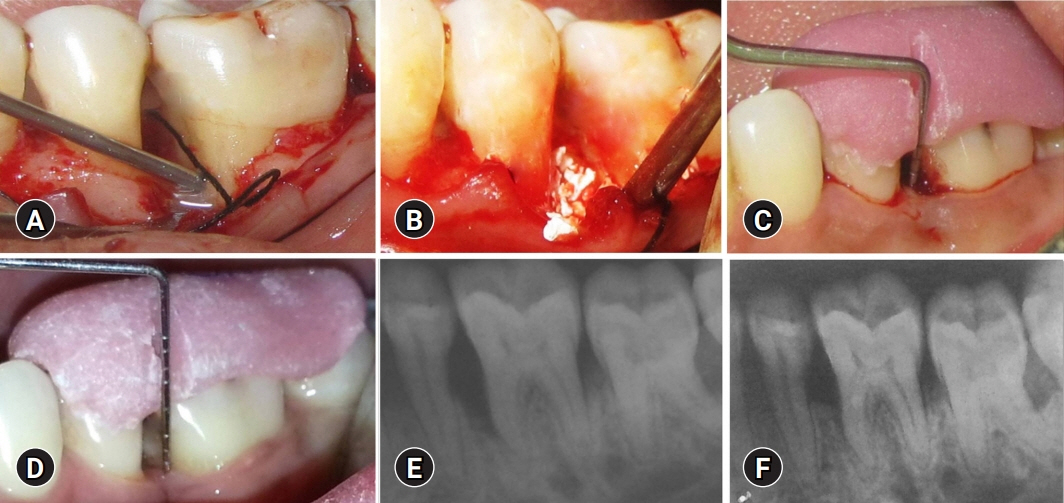
The combined use of biomaterials for regeneration may have great biological relevance. This study aimed to compare the regenerative potential of biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) alone and with growth factor enamel matrix derivatives (EMDs) for the regeneration of intrabony defects at 1 year.
Methods
This randomized controlled trial included 40 sites in 29 patients with stage II/III periodontitis and 2/3 wall intrabony defects that were treated with BCP alone (control group) or a combination of BCP and EMD (test group). BCP alloplastic bone grafts provide better bio-absorbability and accelerate bone formation. EMDs are commercially available amelogenins. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated for the following parameters: plaque index (PI), papillary bleeding index (PBI), vertical probing pocket depth (V-PPD), vertical clinical attachment level (V-CAL), and radiographic defect depth (RDD). Student paired and unpaired t-tests were used to compare the data from baseline to 12 months for each group and between the groups, respectively. The results were considered statistically significant at p<0.05.
Results
At 12 months, the PI and PBI scores of the control and test groups were not significantly different (p>0.05). The mean V-PPD difference, V-CAL gain, and RDD difference were statistically significant in both groups at 12 months (p<0.001 for all parameters). Intergroup comparisons showed that the mean V-PPD reduction (2.13±1.35 mm), V-CAL gain (2.53±1.2 mm), and RDD fill (1.33±1.0 mm) were statistically significant between the groups at 12 months (p<0.001 for all parameters).
Conclusion
BCP and EMDs combination is a promising modality for the regeneration of intrabony defects.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Gottlow J, Nyman S, Lindhe J, Karring T, Wennström J. New attachment formation in the human periodontium by guided tissue regeneration: case reports. J Clin Periodontol. 1986; 13:604–16.
Article2. Rose LF, Rosenberg E. Bone grafts and growth and differentiation factors for regenerative therapy: a review. Pract Proced Aesthet Dent. 2001; 13:725–34.3. Tonetti MS, Prato GP, Cortellini P. Factors affecting the healing response of intrabony defects following guided tissue regeneration and access flap surgery. J Clin Periodontol. 1996; 23:548–56.
Article4. Froum SJ, Kushner L, Stahl SS. Healing responses of human intraosseous lesions following the use of debridement, grafting and citric acid root treatment. I. Clinical and histologic observations six months postsurgery. J Periodontol. 1983; 54:67–76.
Article5. Barney VC, Levin MP, Adams DF. Bioceramic implants in surgical periodontal defects: a comparison study. J Periodontol. 1986; 57:764–70.
Article6. Snyder AJ, Levin MP, Cutright DE. Alloplastic implants of tricalcium phosphate ceramic in human periodontal osseous defects. J Periodontol. 1984; 55:273–7.
Article7. Döri F, Arweiler N, Gera I, Sculean A. Clinical evaluation of an enamel matrix protein derivative combined with either a natural bone mineral or beta-tricalcium phosphate. J Periodontol. 2005; 76:2236–43.8. Kim SK, Choi EH, Lee JS, Kim TG, Choi SH, Cho KS, et al. Evaluating intra- and inter-examiner reproducibility in histometric measurement: one-wall intrabony periodontal defects in beagle dogs. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2010; 40:172–9.
Article9. Pontoriero R, Wennström J, Lindhe J. The use of barrier membranes and enamel matrix proteins in the treatment of angular bone defects: a prospective controlled clinical study. J Clin Periodontol. 1999; 26:833–40.10. Heijl L, Heden G, Svärdström G, Ostgren A. Enamel matrix derivative (EMDOGAIN) in the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects. J Clin Periodontol. 1997; 24(9 Pt 2):705–14.
Article11. Velasquez-Plata D, Scheyer ET, Mellonig JT. Clinical comparison of an enamel matrix derivative used alone or in combination with a bovine-derived xenograft for the treatment of periodontal osseous defects in humans. J Periodontol. 2002; 73:433–40.
Article12. Jensen SS, Yeo A, Dard M, Hunziker E, Schenk R, Buser D. Evaluation of a novel biphasic calcium phosphate in standardized bone defects: a histologic and histomorphometric study in the mandibles of minipigs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:752–60.
Article13. General Assembly of the World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J Am Coll Dent. 2014; 81:14–8.14. Caton JG, Armitage G, Berglundh T, Chapple ILC, Jepsen S, Kornman KS, et al. A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions: introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J Clin Periodontol. 2018; 45(Suppl 20):S1–8.15. Turesky S, Gilmore ND, Glickman I. Reduced plaque formation by the chloromethyl analogue of victamine C. J Periodontol. 1970; 41:41–3.
Article16. Mühlemann HR, Son S. Gingival sulcus bleeding: a leading symptom in initial gingivitis. Helv Odontol Acta. 1971; 15:107–13.17. Shetty S, Bose A. A clinical and radiographic evaluation of the management of periodontal osseous defects with alloplast and platelet rich plasma. J Regen Med Tissue Eng. 2013; 2:11.
Article18. Lee MJ, Kim BO, Yu SJ. Clinical evaluation of a biphasic calcium phosphate grafting material in the treatment of human periodontal intrabony defects. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2012; 42:127–35.
Article19. Stein JM, Fickl S, Yekta SS, Hoischen U, Ocklenburg C, Smeets R. Clinical evaluation of a biphasic calcium composite grafting material in the treatment of human periodontal intrabony defects: a 12-month randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2009; 80:1774–82.
Article20. Ozdemir B, Okte E. Treatment of intrabony defects with beta-tricalciumphosphate alone and in combination with platelet-rich plasma. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012; 100:976–83.21. Pietruska M, Pietruski J, Nagy K, Brecx M, Arweiler NB, Sculean A. Four-year results following treatment of intrabony periodontal defects with an enamel matrix derivative alone or combined with a biphasic calcium phosphate. Clin Oral Investig. 2012; 16:1191–7.
Article22. Francetti L, Trombelli L, Lombardo G, Guida L, Cafiero C, Roccuzzo M, et al. Evaluation of efficacy of enamel matrix derivative in the treatment of intrabony defects: a 24-month multicenter study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2005; 25:461–73.23. Parodi R, Santarelli GA, Gasparetto B. Treatment of intrabony pockets with Emdogain: results at 36 months. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2004; 24:57–63.24. Sculean A, Schwarz F, Chiantella GC, Arweiler NB, Becker J. Nine-year results following treatment of intrabony periodontal defects with an enamel matrix derivative: report of 26 cases. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2007; 27:221–9.25. Kaushick BT, Jayakumar ND, Padmalatha O, Varghese S. Treatment of human periodontal infrabony defects with hydroxyapatite + β tricalcium phosphate bone graft alone and in combination with platelet rich plasma: a randomized clinical trial. Indian J Dent Res. 2011; 22:505–10.
Article26. Pandit N, Gupta R, Gupta S. A comparative evaluation of biphasic calcium phosphate material and bioglass in the treatment of periodontal osseous defects: a clinical and radiological study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2010; 11:25–32.
Article27. Jasser RA, AlSubaie A, AlShehri F. Effectiveness of beta-tricalcium phosphate in comparison with other materials in treating periodontal infra-bony defects around natural teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2021; 21:219.
Article28. Dewi AH, Ana ID. The use of hydroxyapatite bone substitute grafting for alveolar ridge preservation, sinus augmentation, and periodontal bone defect: a systematic review. Heliyon. 2018; 4:e00884.
Article29. Cãlin C, Pãtraşcu I. Growth factors and beta-tricalcium phosphate in the treatment of periodontal intraosseous defects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Arch Oral Biol. 2016; 66:44–54.
Article30. Stavropoulos A, Bertl K, Sculean A, Kantarci A. Regenerative periodontal therapy in intrabony defects and long-term tooth prognosis. Dent Clin North Am. 2022; 66:103–9.
Article31. Vandana KL, Shah K, Prakash S. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of Emdogain as a regenerative material in the treatment of interproximal vertical defects in chronic and aggressive periodontitis patients. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2004; 24:185–91.32. Okuda K, Tai H, Tanabe K, Suzuki H, Sato T, Kawase T, et al. Platelet-rich plasma combined with a porous hydroxyapatite graft for the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects in humans: a comparative controlled clinical study. J Periodontol. 2005; 76:890–8.
Article33. Stavropoulos A, Windisch P, Szendröi-Kiss D, Peter R, Gera I, Sculean A. Clinical and histologic evaluation of granular beta-tricalcium phosphate for the treatment of human intrabony periodontal defects: a report on five cases. J Periodontol. 2010; 81:325–34.
Article34. Lynch KL, Toth JM, Hamson KR, Ho KC, Hirthe WM. Osteoinductivity by subcutaneous implantation of type I fibrillar collagen and a ca1cium phosphate ceramic. In: Hulbert JE, Hulbert SF, editors. Bioceramics: volume 3: proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine, Terre Haute, IN, USA, November 1990. Terre Haute: Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology; 1992. p. 295-304.35. Gestrelius S, Andersson C, Johansson AC, Persson E, Brodin A, Rydhag L, et al. Formulation of enamel matrix derivative for surface coating: kinetics and cell colonization. J Clin Periodontol. 1997; 24(9 Pt 2):678–84.
Article36. Van der Pauw MT, Van den Bos T, Everts V, Beertsen W. Enamel matrix-derived protein stimulates attachment of periodontal ligament fibroblasts and enhances alkaline phosphatase activity and transforming growth factor beta1 release of periodontal ligament and gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 2000; 71:31–43.
Article37. Zetterström O, Andersson C, Eriksson L, Fredriksson A, Friskopp J, Heden G, et al. Clinical safety of enamel matrix derivative (EMDOGAIN) in the treatment of periodontal defects. J Clin Periodontol. 1997; 24(9 Pt 2):697–704.
Article38. Ellegaard B, Löe H. New attachment of periodontal tissues after treatment of intrabony lesions. J Periodontol. 1971; 42:648–52.
Article39. Meyle J, Hoffmann T, Topoll H, Heinz B, Al-Machot E, Jervøe-Storm PM, et al. A multi-centre randomized controlled clinical trial on the treatment of intra-bony defects with enamel matrix derivatives/synthetic bone graft or enamel matrix derivatives alone: results after 12 months. J Clin Periodontol. 2011; 38:652–60.
Article40. Schallhorn RG, Hiatt WH, Boyce W. Iliac transplants in periodontal therapy. J Periodontol. 1970; 41:566–80.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Additional use of autogenous periosteal barrier membrane combined with regenerative therapy in the interproximal intrabony defects: case series
- Histometrical evaluation of biphasic calcium phosphate in surgically created 1-wall periodontal intrabony defects in dogs
- Effectiveness of porcine-derived xenograft with enamel matrix derivative for periodontal regenerative treatment of intrabony defects associated with a fixed dental prosthesis: a 2-year follow-up retrospective study
- The Effects of Enamel Matrix Derivative and Calcium Sulfate Paste on the Healing of 1-Wall Intrabony Defects in Beagle Dogs
- Histologic evaluation of macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate(MBCP(R)) and flouorohydrxyapatite(Algipore(R)) in surgically created 1-wall periodontal intrabony defects of minipigs