Korean J Transplant.
2022 Sep;36(3):165-172. 10.4285/kjt.22.0023.
Anatomical limits in living donor liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
- KMID: 2533953
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.22.0023
Abstract
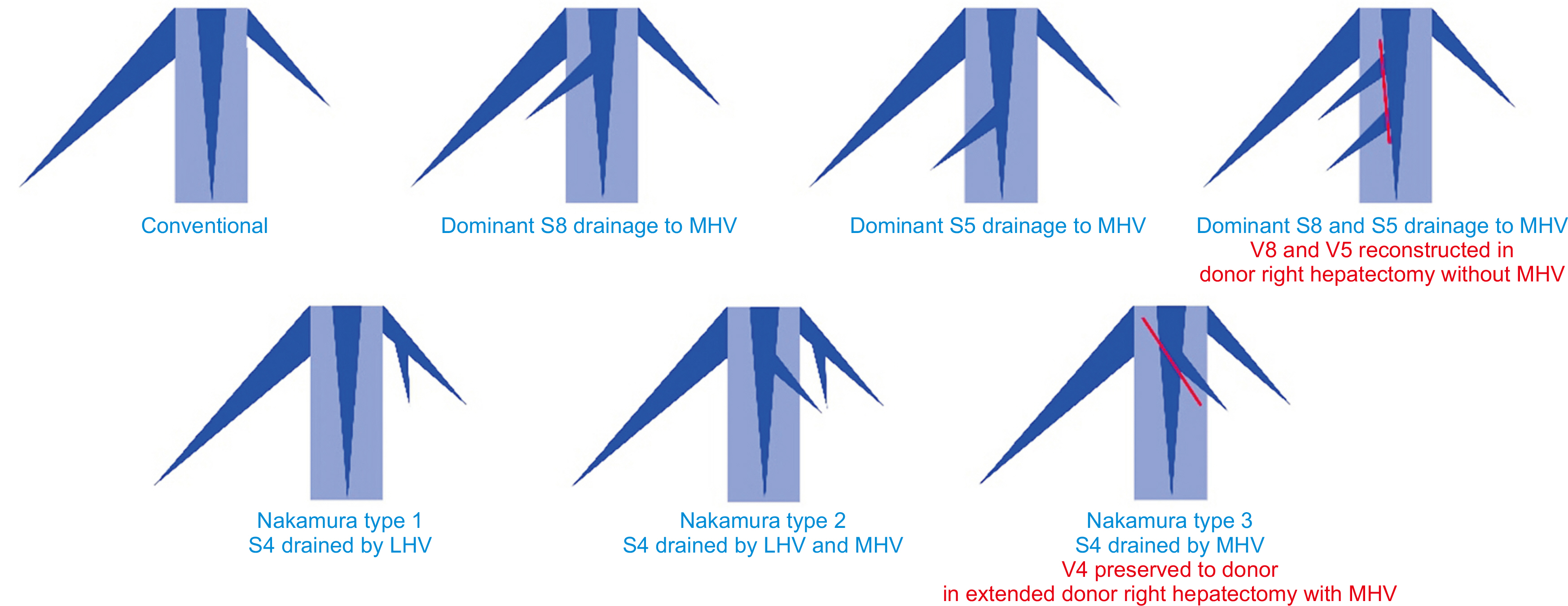
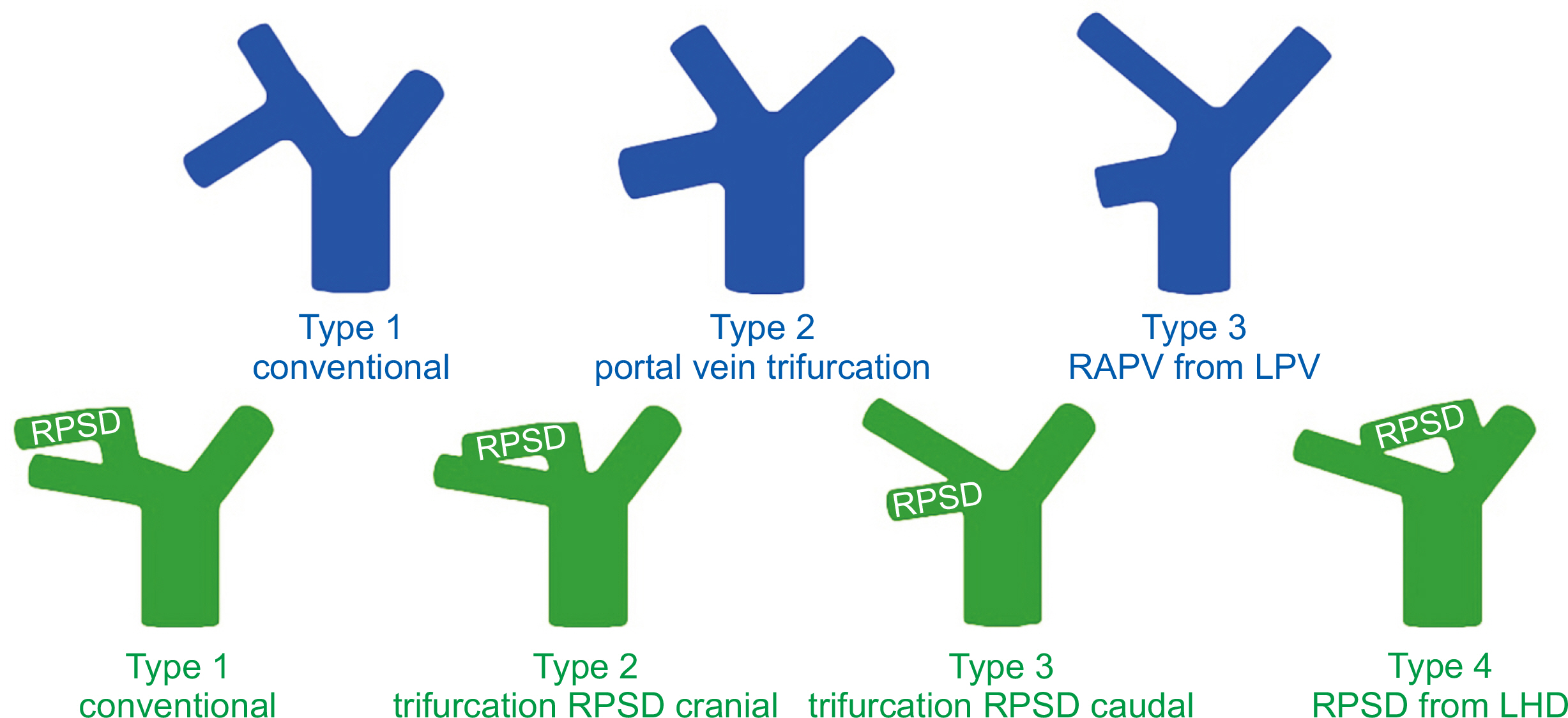
- We review the anatomical limits of living donor liver transplantation. Graft size is the fundamental challenge in partial liver transplantation. Insufficient graft size leads to small-for-size syndrome, graft failure, and graft loss. However, smaller grafts can be used safely with surgical techniques to optimize outflow and modulate inflow, thereby minimizing portal hyperperfusion. Meanwhile, anatomical variations are common in the vascular and biliary systems. These variants pose additional challenges for vascular and biliary reconstruction. Recognition and appropriate management of these variants ensure donor safety and reduce recipient morbidity. The ultimate principle of partial liver transplantation is to ensure a sufficient graft volume with unimpeded outflow and reconstructable vascular and biliary systems. On this basis, the anatomical limits of liv-ing donor liver transplantation can be safely expanded.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strong RW, Lynch SV, Ong TH, Matsunami H, Koido Y, Balderson GA. 1990; Successful liver transplantation from a living donor to her son. N Engl J Med. 322:1505–7. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199005243222106. PMID: 2336076.2. Lo CM, Fan ST, Liu CL, Wei WI, Lo RJ, Lai CL, et al. 1997; Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation using extended right lobe grafts. Ann Surg. 226:261–9. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199709000-00005. PMID: 9339932. PMCID: PMC1191019.3. Lo CM, Fan ST, Liu CL, Lo RJ, Lau GK, Wei WI, et al. 1997; Extending the limit on the size of adult recipient in living donor liver transplantation using extended right lobe graft. Transplantation. 63:1524–8. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199705270-00027. PMID: 9175822.4. Chan SC, Chan AC, Sharr WW, Chok KS, Cheung TT, Fan ST, et al. 2014; Perpetuating proficiency in donor right hepatectomy for living donor liver transplantation. Asian J Surg. 37:65–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2013.09.001. PMID: 24210956.5. Nakamura T, Tanaka K, Kiuchi T, Kasahara M, Oike F, Ueda M, et al. 2002; Anatomical variations and surgical strategies in right lobe living donor liver transplantation: lessons from 120 cases. Transplantation. 73:1896–903. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-200206270-00008. PMID: 12131684.6. Shoreem H, Gad EH, Soliman H, Hegazy O, Saleh S, Zakaria H, et al. 2017; Small for size syndrome difficult dilemma: lessons from 10 years single centre experience in living donor liver transplantation. World J Hepatol. 9:930–44. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i21.930. PMID: 28824744. PMCID: PMC5545138.7. Dahm F, Georgiev P, Clavien PA. 2005; Small-for-size syndrome after partial liver transplantation: definition, mechanisms of disease and clinical implications. Am J Transplant. 5:2605–10. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01081.x. PMID: 16212618.8. Kiuchi T, Kasahara M, Uryuhara K, Inomata Y, Uemoto S, Asonuma K, et al. 1999; Impact of graft size mismatching on graft prognosis in liver transplantation from living donors. Transplantation. 67:321–7. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199901270-00024. PMID: 10075602.9. Nishizaki T, Ikegami T, Hiroshige S, Hashimoto K, Uchiyama H, Yoshizumi T, et al. 2001; Small graft for living donor liver transplantation. Ann Surg. 233:575–80. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-200104000-00014. PMID: 11303141. PMCID: PMC1421288.10. Ikegami T, Masuda Y, Ohno Y, Mita A, Kobayashi A, Urata K, et al. 2009; Prognosis of adult patients transplanted with liver grafts < 35% of their standard liver volume. Liver Transpl. 15:1622–30. DOI: 10.1002/lt.21716. PMID: 19877227.11. Moon JI, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Jung GO, Choi GS, Park JB, et al. 2010; Safety of small-for-size grafts in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation using the right lobe. Liver Transpl. 16:864–9. DOI: 10.1002/lt.22094. PMID: 20583075.12. Lee SD, Kim SH, Kim YK, Lee SA, Park SJ. 2014; Graft-to-recipient weight ratio lower to 0.7% is safe without portal pressure modulation in right-lobe living donor liver transplantation with favorable conditions. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 13:18–24. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(14)60002-3.13. Au KP, Chan SC, Chok KS, Chan AC, Wong TC, Sharr WW, et al. 2015; Durability of small-for-size living donor allografts. Liver Transpl. 21:1374–82. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24205. PMID: 26123155.14. Ikegami T, Yoshizumi T, Sakata K, Uchiyama H, Harimoto N, Harada N, et al. 2016; Left lobe living donor liver transplantation in adults: what is the safety limit? Liver Transpl. 22:1666–75. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24611. PMID: 27540888.15. Liu C, Song JL, Lu WS, Yang JY, Jiang L, Yan LN, et al. 2016; Hepatic arterial buffer response maintains the homeostasis of graft hemodynamics in patient receiving living donor liver transplantation. Dig Dis Sci. 61:464–73. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-015-3881-8. PMID: 26441282.16. Wong TC, Fung JY, Cui TY, Sin SL, Ma KW, She BW, et al. 2021; The risk of going small: lowering GRWR and overcoming small-for-size syndrome in adult living donor liver transplantation. Ann Surg. 274:e1260–8. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003824. PMID: 32209906.17. Chan SC, Lo CM, Chok KS, Sharr WW, Cheung TT, Tsang SH, et al. 2011; Modulation of graft vascular inflow guided by flowmetry and manometry in liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 10:649–56. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(11)60110-0.18. Kelly DM, Demetris AJ, Fung JJ, Marcos A, Zhu Y, Subbotin V, et al. 2004; Porcine partial liver transplantation: a novel model of the "small-for-size" liver graft. Liver Transpl. 10:253–63. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20073. PMID: 14762864.19. Nakamura S, Sakaguchi S, Hachiya T, Suzuki S, Nishiyama R, Konno H, et al. 1993; Significance of hepatic vein reconstruction in hepatectomy. Surgery. 114:59–64.20. Lee SG, Park KM, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ahn CS, et al. 2002; Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation at the Asan Medical Center, Korea. Asian J Surg. 25:277–84. DOI: 10.1016/S1015-9584(09)60192-5.21. Pollard JJ, Nebesar RA. 1967; Altered hemodynamics in the Budd-Chiari syndrome demonstrated by selective hepatic and selective splenic angiography. Radiology. 89:236–43. DOI: 10.1148/89.2.236.22. Liu CL, Zhao Y, Lo CM, Fan ST. 2003; Hepatic venoplasty in right lobe live donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 9:1265–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.lts.2003.09.014. PMID: 14625826.23. Nakamura S, Tsuzuki T. 1981; Surgical anatomy of the hepatic veins and the inferior vena cava. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 152:43–50.24. Chan SC, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong Y, Fan ST, Wong J. 2004; Tailoring donor hepatectomy per segment 4 venous drainage in right lobe live donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 10:755–62. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20114. PMID: 15162470.25. Del Guercio LR, Cohn JD, Kazarian KK, Kinkhabwalla M. 1978; A shunt equation for estimating the splenic component of portal hypertension. Am J Surg. 135:70–5. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90012-0.26. Luca A, Miraglia R, Caruso S, Milazzo M, Gidelli B, Bosch J. 2006; Effects of splenic artery occlusion on portal pressure in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Transpl. 12:1237–43. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20762. PMID: 16741929.27. Yoshizumi T, Mori M. 2020; Portal flow modulation in living donor liver transplantation: review with a focus on splenectomy. Surg Today. 50:21–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00595-019-01881-y. PMID: 31555908. PMCID: PMC6949207.28. Boillot O, Delafosse B, Méchet I, Boucaud C, Pouyet M. 2002; Small-for-size partial liver graft in an adult recipient; a new transplant technique. Lancet. 359:406–7. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07593-1.29. Iida T, Yagi S, Taniguchi K, Hori T, Uemoto S. 2007; Improvement of morphological changes after 70% hepatectomy with portocaval shunt: preclinical study in porcine model. J Surg Res. 143:238–46. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.11.020. PMID: 18023647.30. Chan SC, Lo CM, Ng KK, Fan ST. 2010; Alleviating the burden of small-for-size graft in right liver living donor liver transplantation through accumulation of experience. Am J Transplant. 10:859–67. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03017.x. PMID: 20148811.31. Yagi S, Uemoto S. 2012; Small-for-size syndrome in living donor liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 11:570–6. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(12)60227-6.32. Lei JY, Wang WT, Yan LN. 2012; Risk factors of SFSS in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation using the right liver: a single-center analysis of 217 cases. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1491–7. DOI: 10.5754/hge11634.33. Ma KW, Wong KH, Chan AC, Cheung TT, Dai WC, Fung JY, et al. 2019; Impact of small-for-size liver grafts on medium-term and long-term graft survival in living donor liver transplantation: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 25:5559–68. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5559. PMID: 31576100. PMCID: PMC6767984.34. Sureka B, Patidar Y, Bansal K, Rajesh S, Agrawal N, Arora A. 2015; Portal vein variations in 1000 patients: surgical and radiological importance. Br J Radiol. 88:20150326. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20150326. PMID: 26283261. PMCID: PMC4743455.35. Schmidt S, Demartines N, Soler L, Schnyder P, Denys A. 2008; Portal vein normal anatomy and variants: implication for liver surgery and portal vein embolization. Semin Intervent Radiol. 25:86–91. DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1076688. PMID: 21326549. PMCID: PMC3036482.36. Covey AM, Brody LA, Getrajdman GI, Sofocleous CT, Brown KT. 2004; Incidence, patterns, and clinical relevance of variant portal vein anatomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 183:1055–64. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.183.4.1831055. PMID: 15385304.37. Thayer WP, Claridge JA, Pelletier SJ, Oh CK, Sanfey HA, Sawyer RG, et al. 2002; Portal vein reconstruction in right lobe living-donor liver transplantation. J Am Coll Surg. 194:96–8. DOI: 10.1016/S1072-7515(01)01085-7.38. Lee SG, Hwang S, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Park KM, Lee YJ, et al. 2003; Approach to anatomic variations of the graft portal vein in right lobe living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 75(3 Suppl):S28–32. DOI: 10.1097/01.TP.0000047028.97031.66. PMID: 12589136.39. Yoshizumi T, Ikegami T, Kimura K, Uchiyama H, Ikeda T, Shirabe K, et al. 2014; Selection of a right posterior sector graft for living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 20:1089–96. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23924. PMID: 24890095.40. Hori T, Kirino I, Uemoto S. 2015; Right posterior segment graft in living donor liver transplantation. Hepatol Res. 45:1076–82. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12469. PMID: 25559984.41. Lee S, Hwang S, Park K, Lee Y, Choi D, Ahn C, et al. 2001; An adult-to-adult living donor liver transplant using dual left lobe grafts. Surgery. 129:647–50. DOI: 10.1067/msy.2001.114218. PMID: 11331460.42. Lee SG, Moon DB. Oniscu GC, Forsythe JL, Pomfret EA, editors. 2019. Dual-graft liver transplantation. Transplantation surgery. Springer;Berlin, Germany: p. 331–52. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-73796-4_14.43. Xu Y, Chen H, Yeh H, Wang H, Leng J, Dong J. 2015; Living donor liver transplantation using dual grafts: Experience and lessons learned from cases worldwide. Liver Transpl. 21:1438–48. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24315. PMID: 26336078.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unilateral Versus Bilateral Biliary Drainage for Post-Transplant Anastomotic Stricture
- Liver retransplantation for adult recipients
- Hepatic Artery Reconstruction Using the Right Gastroepiploic Artery for Hepatic Artery Inflow in a Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Left at right heterotopic implantation of left liver graft in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: the technical concern for decision-making
- Current Status and Perspectives of Living Donor Liver Transplantation