J Rheum Dis.
2022 Jul;29(3):162-170. 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.3.162.
Use of Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs After Cancer Diagnosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2530680
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2022.29.3.162
Abstract
Objective
There is no recommendation for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who developed cancer. We examined changes in the DMARDs prescription patterns associated with cancer diagnosis in RA patients.
Methods
We reviewed the medical records of 2,161 RA patients who visited rheumatology clinic between January 2008 and February 2017 and found 40 patients who developed cancer during RA treatment. In these patients, we examined DMARDs prescription patterns before and right after cancer diagnosis and at recent outpatient clinic visits.
Results
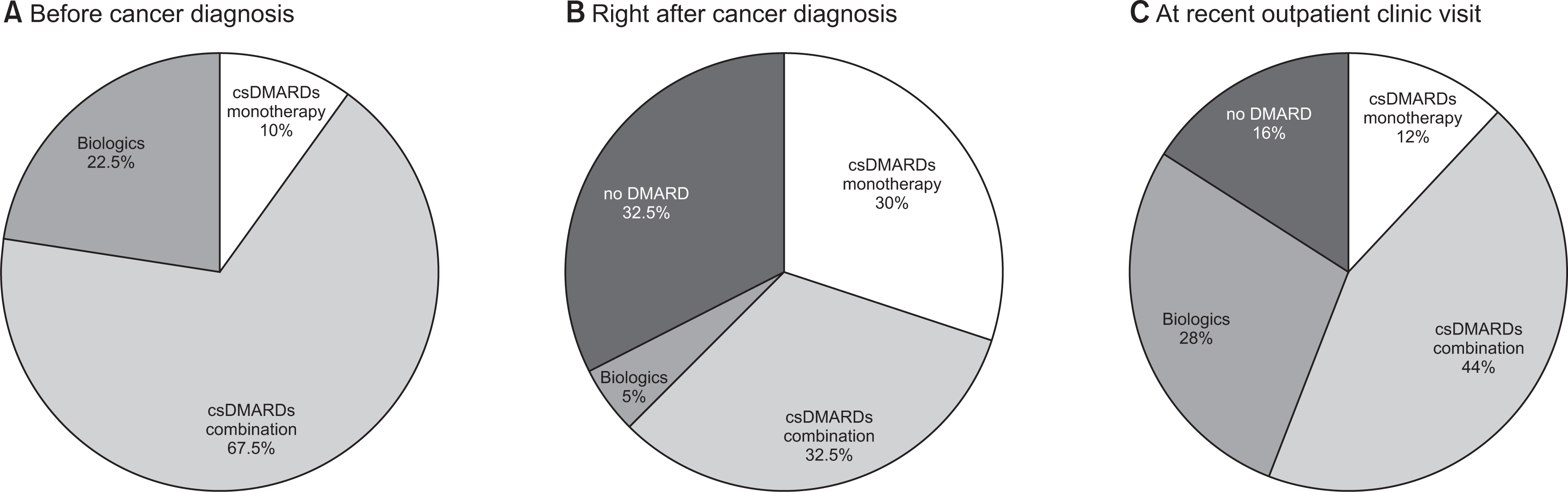
Before cancer diagnosis, methotrexate (MTX)-combined conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) were most commonly prescribed (22, 55.0%) and biological DMARDs (biologics) in nine patients (22.5%). For cancer treatment, 19 patients received chemotherapy (including adjuvant chemotherapy) and 21 patients had surgery only. Right after cancer diagnosis, changes in the DMARDs prescription patterns were similar in discontinuation (13, 32.5%), switching (14, 35.0%), and maintenance (13, 32.5%). DMARDs were discontinued more frequently in the chemotherapy group (9/19, 47.4%) than the surgery only group (4/2, 19.0%) (p<0.05). Among the 13 patients who discontinued DMARDs, nine (69.2%) resumed DMARDs after a median of 5.5 months (interquartile range [IQR] 2.9, 18.3) due to arthritis flare. At a median of 4.6 years (IQR 3.3, 6.7) after cancer diagnosis, 25 patients were evaluated at recent outpatient clinic visits. Four patients received no DMARD, three MTX monotherapies, 11 csDMARDs combination therapies, and seven biologics.
Conclusion
A significant number of RA patients who developed cancer during RA treatment were still receiving DMARDs including biologics after cancer diagnosis.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Malignancy: What Should We Do With DMARDs?
Chan Hong Jeon
J Rheum Dis. 2022;29(4):191-192. doi: 10.4078/jrd.22.0034.
Reference
-
1. Khurana R, Wolf R, Berney S, Caldito G, Hayat S, Berney SM. 2008; Risk of development of lung cancer is increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a large case control study in US veterans. J Rheumatol. 35:1704–8.2. Smitten AL, Simon TA, Hochberg MC, Suissa S. 2008; A meta-analysis of the incidence of malignancy in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R45. DOI: 10.1186/ar2404. PMID: 18433475. PMCID: PMC2453765.
Article3. Yamada T, Nakajima A, Inoue E, Tanaka E, Taniguchi A, Momohara S, et al. 2011; Incidence of malignancy in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 31:1487–92. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-010-1524-0. PMID: 20473757.
Article4. Lopez-Olivo MA, Colmegna I, Karpes Matusevich AR, Qi SR, Zamora NV, Sharma R, et al. 2020; Systematic review of recommendations on the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and cancer. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 72:309–18. DOI: 10.1002/acr.23865. PMID: 30821928.
Article5. Strangfeld A, Hierse F, Rau R, Burmester GR, Krummel-Lorenz B, Demary W, et al. 2010; Risk of incident or recurrent malignancies among patients with rheumatoid arthritis exposed to biologic therapy in the German biologics register RABBIT. Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R5. DOI: 10.1186/ar2904. PMID: 20064207. PMCID: PMC2875631.
Article6. Xie W, Xiao S, Huang Y, Sun X, Gao D, Ji L, et al. 2020; A meta-analysis of biologic therapies on risk of new or recurrent cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a prior malignancy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 59:930–9. Erratum in: Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021;60:2495. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez475. PMID: 31620795.
Article7. Singh N, Li CI. 2021; Impact of rheumatoid arthritis and biologic and targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic agents on cancer risk and recurrence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 33:292–9. DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000796. PMID: 33741804.
Article8. Elandt K, Aletaha D. 2011; Treating rheumatic patients with a malignancy. Arthritis Res Ther. 13:223. DOI: 10.1186/ar3352. PMID: 21722342. PMCID: PMC3218895.
Article9. Llorca J, Lopez-Diaz MJ, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Ollier WE, Martin J, Gonzalez-Gay MA. 2007; Persistent chronic inflammation contributes to the development of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from a defined population of northwestern Spain. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 37:31–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.01.002. PMID: 17360028.
Article10. Raaschou P, Frisell T, Askling J. 2015; TNF inhibitor therapy and risk of breast cancer recurrence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:2137–43. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205745. PMID: 25107559.
Article11. Regierer AC, Strangfeld A. 2018; Rheumatoid arthritis treatment in patients with a history of cancer. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 30:288–94. DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000492. PMID: 29389831.
Article12. Dreyer L, Cordtz RL, Hansen IMJ, Kristensen LE, Hetland ML, Mellemkjaer L. 2018; Risk of second malignant neoplasm and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological DMARDs: a Danish population-based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 77:510–4. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212086. PMID: 29217620.
Article13. Raaschou P, Söderling J, Turesson C, Askling J. 2018; Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and cancer recurrence in Swedish patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 169:291–9. DOI: 10.7326/M17-2812. PMID: 30105374.
Article14. Koc ÖM, van Kampen RJW, van Bodegraven AA. 2018; Cancer-associated chemotherapy induces less IBD exacerbations and a reduction of IBD medication afterwards. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 24:1606–11. DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izy053. PMID: 29669052.
Article15. Shelton E, Laharie D, Scott FI, Mamtani R, Lewis JD, Colombel JF, et al. 2016; Cancer recurrence following immune-suppressive therapies in patients with immune-mediated diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 151:97–109.e4. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.037. PMID: 27039969. PMCID: PMC4925196.
Article16. Raaschou P, Simard JF, Neovius M, Askling J. 2011; Does cancer that occurs during or after anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy have a worse prognosis? A national assessment of overall and site-specific cancer survival in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with biologic agents. Arthritis Rheum. 63:1812–22. DOI: 10.1002/art.30247. PMID: 21305513.
Article17. Phillips C, Zeringue AL, McDonald JR, Eisen SA, Ranganathan P. 2015; Tumor necrosis factor inhibition and head and neck cancer recurrence and death in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 10:e0143286. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143286. PMID: 26599370. PMCID: PMC4658068.
Article18. Pundole X, Zamora NV, Siddhanamatha H, Lin H, Tayar J, Leung CH, et al. 2020; Overall survival in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and solid malignancies receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 39:2943–50. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-020-05318-7. PMID: 32803571.
Article19. Silva-Fernández L, Lunt M, Kearsley-Fleet L, Watson KD, Dixon WG, Symmons DP, et al. 2016; The incidence of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a prior malignancy who receive TNF inhibitors or rituximab: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register-Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 55:2033–9. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew314. PMID: 27550304. PMCID: PMC5088627.
Article20. Pappas DA, Rebello S, Liu M, Schenfeld J, Li Y, Collier DH, et al. 2019; Therapy with biologic agents after diagnosis of solid malignancies: results from the Corrona registry. J Rheumatol. 46:1438–44. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.171457. PMID: 30936285.
Article21. Mamtani R, Clark AS, Scott FI, Brensinger CM, Boursi B, Chen L, et al. 2016; Association between breast cancer recurrence and immunosuppression in rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease: a cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:2403–11. DOI: 10.1002/art.39738. PMID: 27159030. PMCID: PMC5042817.
Article22. Pundole X, Zamora NV, Siddhanamatha H, Lin H, Tayar J, Hong LC, et al. 2020; Utilization of biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and cancer. Clin Rheumatol. 39:787–94. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-019-04874-x. PMID: 31853733.
Article23. Phan H, Weideman RA, Cipher DJ, Feagins LA. 2020; Safety of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor use in patients with concomitant malignancy. Intest Res. 18:282–8. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2019.09140. PMID: 32252501. PMCID: PMC7385568.
Article24. Ji J, Liu X, Sundquist K, Sundquist J. 2011; Survival of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a follow-up study in Sweden of patients hospitalized with rheumatoid arthritis 1 year before diagnosis of cancer. Rheumatology (Oxford). 50:1513–8. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker143. PMID: 21498553.
Article25. Nayak P, Luo R, Elting L, Zhao H, Suarez-Almazor ME. 2017; Impact of rheumatoid arthritis on the mortality of elderly patients who develop cancer: a population-based study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 69:75–83. DOI: 10.1002/acr.22997. PMID: 27483088.
Article26. Simard JF, Ekberg S, Johansson AL, Askling J. 2016; What is the impact of chronic systemic inflammation such as rheumatoid arthritis on mortality following cancer? Ann Rheum Dis. 75:862–6. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-207155. PMID: 25948597.
Article27. Baecklund E, Iliadou A, Askling J, Ekbom A, Backlin C, Granath F, et al. 2006; Association of chronic inflammation, not its treatment, with increased lymphoma risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 54:692–701. DOI: 10.1002/art.21675. PMID: 16508929.
Article28. Wilton KM, Matteson EL. 2017; Malignancy incidence, management, and prevention in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Ther. 4:333–47. DOI: 10.1007/s40744-017-0064-4. PMID: 28508282. PMCID: PMC5696277.
Article29. US Food and Drug Administration. c2021. Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR (tofacitinib): drug safety communication-initial safety trial results find increased risk of serious heart-related problems and cancer with arthritis and ulcerative colitis medicine [Internet]. US Food and Drug Administration;Silver Spring (MD): https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death. cited 2021 Sep 16.30. Naidoo J, Cappelli LC, Forde PM, Marrone KA, Lipson EJ, Hammers HJ, et al. 2017; Inflammatory arthritis: a newly recognized adverse event of immune checkpoint blockade. Oncologist. 22:627–30. DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0390. PMID: 28576858. PMCID: PMC5469592.
Article31. Belkhir R, Burel SL, Dunogeant L, Marabelle A, Hollebecque A, Besse B, et al. 2017; Rheumatoid arthritis and polymyalgia rheumatica occurring after immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:1747–50. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211216. PMID: 28600350.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Artritis
- Medical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (I): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and glucocorticoids
- Cementless Total Knee Arthroplasty and Effects of Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis