J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Jun;37(24):e197. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e197.
MicroRNA Expression in Plasma of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Convergence Medical Sciences, Pusan National University Graduate School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2530508
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e197
Abstract
- Background
Patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) have a poor prognosis and there are no effective clinical biomarkers. Recently, stable microRNAs detected in the blood have been suggested as potential biomarkers in various cancers. Therefore, we investigated whether plasma microRNAs could be feasible biomarkers for ESCC.
Methods
Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 16 healthy volunteers and 66 ESCC patients before treatment between May 2016 and April 2021. Plasma miR-18b, miR-21, miR-31, and miR-375 expression levels were measured using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Results
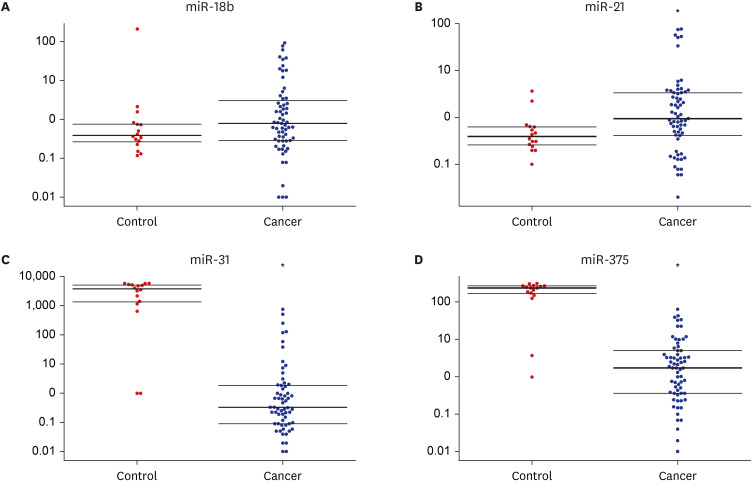
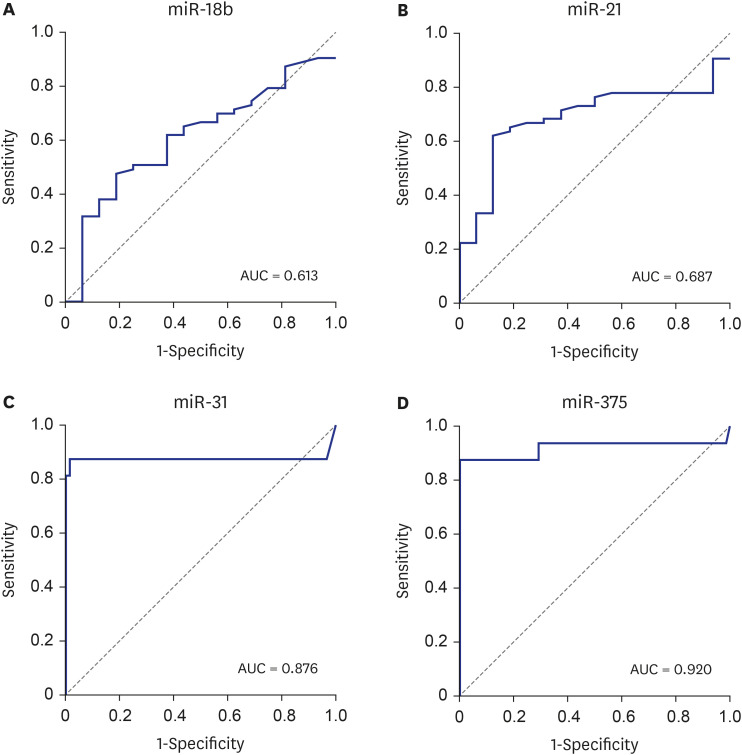
Compared with those in healthy controls, the expression levels of plasma miR-21 were significantly higher (P = 0.022) and those of plasma miR-31 and miR-375 were significantly lower in ESCC patients (both P < 0.001). Plasma miR-18b expression levels increased in ESCC patients, but the difference was not significant (P = 0.164). The sensitivities and specificities of miR-21, miR-31, and miR-375 for differentiating ESCC patients from healthy controls were 87.5% and 61.9%, 87.5% and 98.4%, and 87.5% and 100%, respectively. There was no difference in expression levels of plasma miR-21, miR-31, and miR-375 according to clinicopathological characteristics of sex, age, tumor size and location, histologic grade, and tumor-node-metastasis stage.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that plasma miR-21, miR-31, and miR-375 could be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of ESCC. Particularly, plasma miR-31 and miR-375 showed high sensitivity and specificity for differentiating ESCC patients from healthy controls.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71(3):209–249. PMID: 33538338.
Article2. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136(5):E359–E386. PMID: 25220842.
Article3. Jung HK. Epidemiology of and risk factors for esophageal cancer in Korea. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2019; 19(3):145–148.
Article4. Pennathur A, Farkas A, Krasinskas AM, Ferson PF, Gooding WE, Gibson MK, et al. Esophagectomy for T1 esophageal cancer: outcomes in 100 patients and implications for endoscopic therapy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009; 87(4):1048–1054. PMID: 19324126.
Article5. Kim GH. Diagnosis and clinical management of esophageal squamous dysplasia. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2021; 21(1):4–9.
Article6. Chiam KH, Shin SH, Choi KC, Leiria F, Militz M, Singh R. Current status of mucosal imaging with narrow-band imaging in the esophagus. Gut Liver. 2021; 15(4):492–499. PMID: 32307976.
Article7. Lee MW, Kim GH, Jeon HK, Park SJ. Clinical application of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer. Gut Liver. 2019; 13(4):394–401. PMID: 30970448.
Article8. Mroczko B, Kozłowski M, Groblewska M, Łukaszewicz M, Nikliński J, Jelski W, et al. The diagnostic value of the measurement of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), squamous cell cancer antigen (SCC) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in the sera of esophageal cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2008; 389(1-2):61–66. PMID: 18155162.
Article9. Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005; 120(1):15–20. PMID: 15652477.
Article10. Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008; 9(2):102–114. PMID: 18197166.
Article11. Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita F, Matsuki Y, Ochiya T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285(23):17442–17452. PMID: 20353945.
Article12. Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J. Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009; 19(2):43–51. PMID: 19144520.
Article13. Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(30):10513–10518. PMID: 18663219.
Article14. Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ, Bushell M. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13(6):e249–e258. PMID: 22652233.
Article15. He Y, Lin J, Kong D, Huang M, Xu C, Kim TK, et al. Current state of circulating microRNAs as cancer biomarkers. Clin Chem. 2015; 61(9):1138–1155. PMID: 26319452.
Article16. Liu F, Tian T, Xia LL, Ding Y, Cormier RT, He Y. Circulating miRNAs as novel potential biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis: a meta-analysis update. Dis Esophagus. 2017; 30(2):1–9.
Article17. Wan J, Wu W, Che Y, Kang N, Zhang R. Insights into the potential use of microRNAs as a novel class of biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2016; 29(5):412–420. PMID: 25789723.
Article18. Gao S, Zhao ZY, Zhang ZY, Zhang Y, Wu R. Prognostic value of microRNAs in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018; 9(11):203. PMID: 30420592.
Article19. Hirajima S, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Konishi H, Shiozaki A, et al. Clinical impact of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013; 108(9):1822–1829. PMID: 23579215.
Article20. Wang LL, Li HX, Yang YY, Su YL, Lian JS, Li T, et al. MiR-31 is a potential biomarker for diagnosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018; 11(9):4339–4345. PMID: 31949830.21. Wu C, Li M, Hu C, Duan H. Clinical significance of serum miR-223, miR-25 and miR-375 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2014; 41(3):1257–1266. PMID: 24390317.
Article22. Wang P, Xu L, Li L, Ren S, Tang J, Zhang M, et al. The microRNA-375 as a potentially promising biomarker to predict the prognosis of patients with head and neck or esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 276(4):957–968. PMID: 30747316.
Article23. Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Byrd DR, Brookland RK, Washington MK, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY, USA: Springer;2017.24. Choi MK, Kim GH, I H, Park SJ, Lee MW, Lee BE, et al. Circulating tumor cells detected using fluid-assisted separation technique in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 34(3):552–560. PMID: 30426559.
Article25. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 2001; 25(4):402–408. PMID: 11846609.
Article26. Yao C, Liu HN, Wu H, Chen YJ, Li Y, Fang Y, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating microRNAs for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer. 2018; 9(16):2876–2884. PMID: 30123356.
Article27. Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007; 9(6):654–659. PMID: 17486113.
Article28. Zhou X, Wen W, Zhu J, Huang Z, Zhang L, Zhang H, et al. A six-microRNA signature in plasma was identified as a potential biomarker in diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(21):34468–34480. PMID: 28380431.
Article29. Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008; 18(10):997–1006. PMID: 18766170.
Article30. Egeland NG, Jonsdottir K, Aure MR, Sahlberg K, Kristensen VN, Cronin-Fenton D, et al. MiR-18a and miR-18b are expressed in the stroma of oestrogen receptor alpha negative breast cancers. BMC Cancer. 2020; 20(1):377. PMID: 32370743.
Article31. He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature. 2005; 435(7043):828–833. PMID: 15944707.
Article32. Han X, Zhang Y, Wang D, Fu X, Li M, Wang A. Upregulation of microRNA-18b induces phosphatase and tensin homolog to accelerate the migration and invasion abilities of ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017; 14(5):5631–5637. PMID: 29142608.
Article33. Zhu L, Xu X, Tang Y, Zhu X. TRIP6 functions as a potential oncogene and facilitated proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer. Biologics. 2019; 13:101–110. PMID: 31354238.34. Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005; 65(14):6029–6033. PMID: 16024602.
Article35. Guraya S. Prognostic significance of circulating microRNA-21 expression in esophageal, pancreatic and colorectal cancers; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018; 60:41–47. PMID: 30336280.
Article36. Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Tsujiura M, Morimura R, Nagata H, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2011; 105(1):104–111. PMID: 21673684.
Article37. Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M, Tanaka Y, Kinoshita K, Saito S, et al. Serum microRNA-21 is a novel biomarker in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2012; 106(2):188–192. PMID: 22354855.
Article38. Cai EH, Gao YX, Wei ZZ, Chen WY, Yu P, Li K. Serum miR-21 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012; 13(4):1563–1567. PMID: 22799367.
Article39. Dong Y, Wu WK, Wu CW, Sung JJ, Yu J, Ng SS. MicroRNA dysregulation in colorectal cancer: a clinical perspective. Br J Cancer. 2011; 104(6):893–898. PMID: 21364594.
Article40. Lajer CB, Nielsen FC, Friis-Hansen L, Norrild B, Borup R, Garnæs E, et al. Different miRNA signatures of oral and pharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: a prospective translational study. Br J Cancer. 2011; 104(5):830–840. PMID: 21326242.
Article41. Liu X, Sempere LF, Ouyang H, Memoli VA, Andrew AS, Luo Y, et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J Clin Invest. 2010; 120(4):1298–1309. PMID: 20237410.
Article42. Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, Smerdova T, Knoflickova D, Bednarikova M, et al. Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2007; 72(5-6):397–402. PMID: 18196926.
Article43. Zhang Y, Guo J, Li D, Xiao B, Miao Y, Jiang Z, et al. Down-regulation of miR-31 expression in gastric cancer tissues and its clinical significance. Med Oncol. 2010; 27(3):685–689. PMID: 19598010.
Article44. Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, et al. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008; 14(11):2348–2360. PMID: 18812439.
Article45. Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2010; 126(5):1166–1176. PMID: 19676045.
Article46. Creighton CJ, Fountain MD, Yu Z, Nagaraja AK, Zhu H, Khan M, et al. Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for microRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and other cancers. Cancer Res. 2010; 70(5):1906–1915. PMID: 20179198.
Article47. Zhang T, Wang Q, Zhao D, Cui Y, Cao B, Guo L, et al. The oncogenetic role of microRNA-31 as a potential biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011; 121(10):437–447. PMID: 21658006.
Article48. Yan JW, Lin JS, He XX. The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer. Int J Cancer. 2014; 135(5):1011–1018. PMID: 24166096.
Article49. Avissar M, Christensen BC, Kelsey KT, Marsit CJ. MicroRNA expression ratio is predictive of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15(8):2850–2855. PMID: 19351747.
Article50. Mathé EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y, Budhu A, Schetter AJ, et al. MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15(19):6192–6200. PMID: 19789312.
Article51. Kong KL, Kwong DL, Chan TH, Law SY, Chen L, Li Y, et al. MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through repressing insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Gut. 2012; 61(1):33–42. PMID: 21813472.
Article52. Liu L, Wang S, Cao X, Liu J. Diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs for gastric cancer in Asian populations: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35(12):11995–12004. PMID: 25159040.
Article53. Liu L, Wang S, Cao X, Liu J. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers for breast cancer detection: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35(12):12245–12253. PMID: 25195131.
Article54. Xin H, Li X, Yang B, Zhang L, Han Z, Han C. Blood-based multiple-microRNA assay displays a better diagnostic performance than single-microRNA assay in the diagnosis of breast tumor. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35(12):12635–12643. PMID: 25213696.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cutaneous Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mimicking Benign Soft Tissue Tumor
- Expression of Minichromosome Maintenance Protein 7 and Smad 4 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus
- Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Esophageal Squamous Dysplasia
- Adjuvant Therapy for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia Mimicking Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Patient with Lye-induced Esophageal Stricture