Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, Soongsil University, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2530181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0106
Abstract
- Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults.
Methods
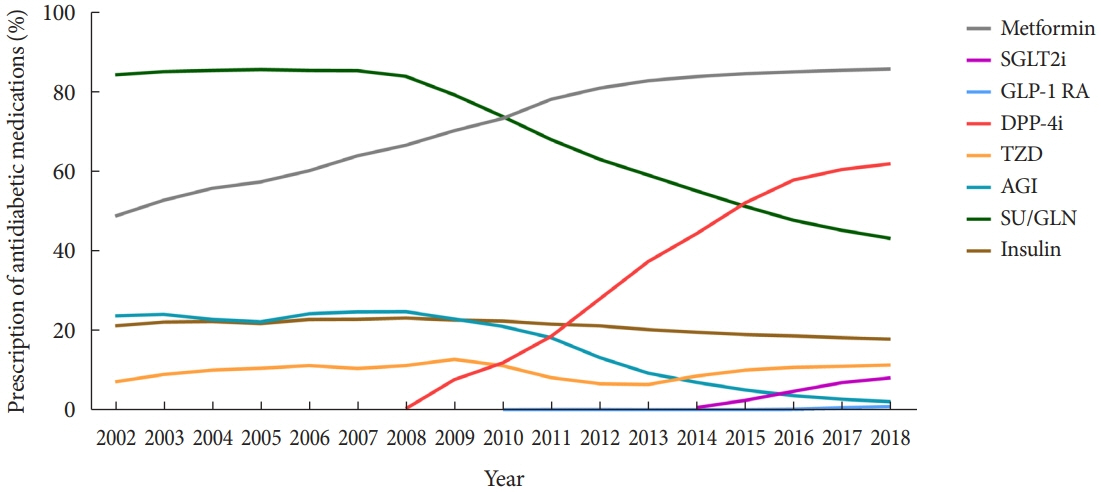
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to assess the prevalence, treatment, risk factors, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors of diabetes mellitus from 2019 to 2020. We also analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service to evaluate the use of antidiabetic medications in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
Results
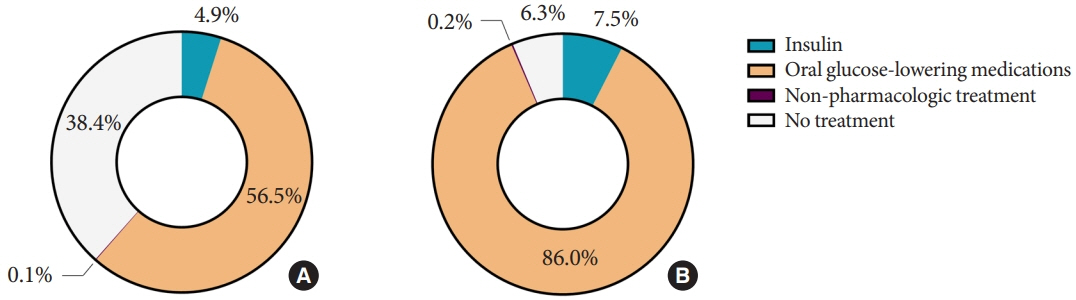
Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. From 2019 through 2020, 65.8% of adults with diabetes mellitus were aware of the disease and treated with antidiabetic medications. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) <6.5% was 24.5% despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications. We found that adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure (BP) <140/85 mm Hg, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL were 9.7%. The percentage of self-management behaviors was lower in men than women. Excess energy intake was observed in 16.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics and a national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care are needed.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 40 articles
-
Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovasc Prev Pharmacother. 2022;4(3):106-113. doi: 10.36011/cpp.2022.4.e13.Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):552-563. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0193.Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):667-674. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0215.Education for Insulin Injection in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Gi Yeon Lee
J Korean Diabetes. 2022;23(3):201-205. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2022.23.3.201.Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):827-828. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0372.Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):819-826. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0364.Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):10-26. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0420.Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0448.Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):307-314. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0386.Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):347-355. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0444.Exercise Frequency Reduction Is Associated With Higher Risk of Infection in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study
Yohwan Lim, Hye Jun Kim, Sung Soo Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Hyewon Park, Sun Jae Park, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(23):e176. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e176.Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
J Korean Diabetes. 2023;24(2):59-65. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2023.24.2.59.Refined Diagnostic Protocol for Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Paving the Way for Timely Detection
Byung-Mo Oh
Ann Rehabil Med. 2023;47(4):234-236. doi: 10.5535/arm.23122.Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):525-537. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1765.The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):522-524. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.502.Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extension
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):808-817. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0387.Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):279-289. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0225.Management of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jin Hwa Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2024;25(1):4-8. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2024.25.1.4.Holistic and Personalized Strategies for Managing in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(4):531-545. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0310.Why Are Doctors Not Interested in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Remission?
Heung Yong Jin, Tae Sun Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(4):709-712. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0312.2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management in Korea: Full Version Recommendation of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jun Sung Moon, Shinae Kang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, Yoon Ju Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae Jin Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Jung Hae Ko, Nam Hoon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Jeeyun Ahn, Tae Jung Oh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Eugene Han, Sang-Man Jin, Jaehyun Bae, Eonju Jeon, Ji Min Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Jung Hwan Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Bong-Soo Cha, Min Kyong Moon, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(4):546-708. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0249.Korean National Burden of Disease: The Importance of Diabetes Management
Chung-Nyun Kim, Yoon-Sun Jung, Young-Eun Kim, Minsu Ock, Seok-Jun Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(4):518-530. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0087.Financial Benefits of Renal Dose-Adjusted Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Hun Jee Choe, Yeh-Hee Ko, Sun Joon Moon, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Hyeongsuk Lee, Jae Hyun Bae, Hyung Joon Joo, Hyejin Lee, Jang Wook Son, Dae Jung Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Kwangsoo Kim, Young Min Cho
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(4):622-631. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.1965.Paradigm shift from glucocentric to organ protection for the management of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jie-Eun Lee, Jong Chul Won
Cardiovasc Prev Pharmacother. 2024;6(4):116-122. doi: 10.36011/cpp.2024.6.e15.Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
Ji-Yeon Park, Joonyub Lee, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soo Lim, Young-Hyun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Mook Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(5):915-928. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0259.Efficacy and Safety of IDegAsp in a Real-World Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Shinae Kang, Yu-Bae Ahn, Tae Keun Oh, Won-Young Lee, Sung Wan Chun, Boram Bae, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Sungeun Jung, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(5):929-936. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0297.Pioglitazone as Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Dapagliflozin and Metformin: Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Ji Hye Heo, Kyung Ah Han, Jun Hwa Hong, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jae Myung Yu, Hye Seung Jung, Bong-Soo Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(5):937-948. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0314.Management Strategies for Older Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Won Jun Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2024;25(3):157-164. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2024.25.3.157.Management Strategies for Obese Diabetes
Mi-Sook Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
J Korean Diabetes. 2024;25(3):165-171. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2024.25.3.165.Diabetes and Dietary Proteins-Protein Supplement Intake
Dasom Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2024;25(3):177-183. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2024.25.3.177.The Effects of Music Therapy on Self-Management, Depression, and Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jung-Hwa Lee, In-Kyung Jeong, Ga-Young Han, Heakyung Moon
J Korean Diabetes. 2024;25(3):189-198. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2024.25.3.189.Insulin Resistance and Impaired Insulin Secretion Predict Incident Diabetes: A Statistical Matching Application to the Two Korean Nationwide, Population-Representative Cohorts
Hyemin Jo, Soyeon Ahn, Jung Hun Ohn, Cheol Min Shin, Eunjeong Ji, Donggil Kim, Sung Jae Jung, Joongyub Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(5):711-721. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.1986.Cardiovascular Disease & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2010 to 2019
Jin Hwa Kim, Junyeop Lee, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Taek Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(6):1084-1092. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0275.Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea 2024
Se Eun Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ji Yoon Kim, Kyuho Kim, Joon Ho Moon, Nam Hoon Kim, Kyung Do Han, Sung Hee Choi, Bong Soo Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):24-33. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0818.Big Data Research for Diabetes-Related Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Kyung-Soo Kim, Bongseong Kim, Kyungdo Han
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):13-21. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0780.Evolving Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in East Asia
Joonyub Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinol Metab. 2025;40(1):57-63. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2193.Carnitine Metabolite as a Potential Circulating Biomarker for Sarcopenia in Men
Je Hyun Seo, Jung-Min Koh, Han Jin Cho, Hanjun Kim, Young‑Sun Lee, Su Jung Kim, Pil Whan Yoon, Won Kim, Sung Jin Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Seung Hun Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2025;40(1):93-102. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2117.Study Design and Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Enavogliflozin to Evaluate Cardiorenal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes (ENVELOP)
Nam Hoon Kim, Soo Lim, In-Kyung Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jun Sung Moon, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Chul Won, Sang Soo Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Bon Jeong Ku, Heung Yong Jin, Sin Gon Kim, Bong-Soo Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(2):225-234. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0238.Prevalence, Incidence, and Metabolic Characteristics of Young Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in South Korea (2010–2020)
Ji Yoon Kim, Jiyoon Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Se Eun Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung Hee Choi, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(2):172-182. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0826.Older Adults with Diabetes in Korea: Latest Clinical and Epidemiologic Trends
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Kyuna Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung Hee Choi, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(2):183-193. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0836.
Reference
-
1. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020; 396:1204–22.2. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: IDF;2021.3. Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018; 14:88–98.
Article4. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2018. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2018.5. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2020. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2020.6. Kim YE, Park H, Jo MW, Oh IH, Go DS, Jung J, et al. Trends and patterns of burden of disease and injuries in Korea using disability-adjusted life years. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34(Suppl 1):e75.
Article7. Kim J, Yoon SJ, Jo MW. Estimating the disease burden of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients considering its complications. PLoS One. 2021; 16:e0246635.
Article8. Lim S, Bae JH, Kwon HS, Nauck MA. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021; 17:11–30.
Article9. Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020; 584:430–6.
Article10. Barron E, Bakhai C, Kar P, Weaver A, Bradley D, Ismail H, et al. Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:813–22.
Article11. Moon SJ, Rhee EJ, Jung JH, Han KD, Kim SR, Lee WY, et al. Independent impact of diabetes on the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 in 5,307 patients in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44:737–46.
Article12. Muller JA, Gross R, Conzelmann C, Kruger J, Merle U, Steinhart J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Nat Metab. 2021; 3:149–65.
Article13. Reiterer M, Rajan M, Gomez-Banoy N, Lau JD, Gomez-Escobar LG, Ma L, et al. Hyperglycemia in acute COVID-19 is characterized by insulin resistance and adipose tissue infectivity by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Metab. 2021; 33:2174–88.
Article14. Carr MJ, Wright AK, Leelarathna L, Thabit H, Milne N, Kanumilli N, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on diagnoses, monitoring, and mortality in people with type 2 diabetes in the UK. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021; 9:413–5.
Article15. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, Brown FM, et al. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S125–43.16. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:461–81.
Article17. Jung CH, Son JW, Kang S, Kim WJ, Kim HS, Kim HS, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2020: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:1–10.
Article18. Oh K, Kim Y, Kweon S, Kim S, Yun S, Park S, et al. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol Health. 2021; 43:e2021025.
Article19. Choi EK. Cardiovascular research using the Korean National Health Information Database. Korean Circ J. 2020; 50:754–72.
Article20. Ministry of Health and Welfare; Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Korea Health Statistics 2020: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VIII-2). Seoul: KDCA;2022.21. Kim BY, Kang SM, Kang JH, Kang SY, Kim KK, Kim KB, et al. 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021; 30:81–92.
Article22. Ministry of Health and Welfare; The Korean Nutritional Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015. Seoul: KNS;2015.23. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. 2021 Obesity fact sheet. Seoul: KSSO;2021.24. Park JH, Ha KH, Kim BY, Lee JH, Kim DJ. Trends in cardiovascular complications and mortality among patients with diabetes in South Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:120–4.
Article25. Choi HH, Choi G, Yoon H, Ha KH, Kim DJ. Rising incidence of diabetes in young adults in South Korea: a national cohort study. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; Jan. 11. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0236.
Article26. Yang YS, Han K, Sohn TS, Kim NH. Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need. Korean J Intern Med. 2021; 36:1049–58.
Article27. Montefusco L, Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Loretelli C, Rossi A, Pastore I, et al. Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Metab. 2021; 3:774–85.
Article28. Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022; 10:311–21.
Article29. Ministry of Health and Welfare: Coronavirus (COVID-19), Republic of Korea. Available from: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/ (cited 2022 Apr 28).30. Fang M, Wang D, Coresh J, Selvin E. Trends in diabetes treatment and control in U.S. adults, 1999-2018. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:2219–28.
Article31. Wright AK, Suarez-Ortegon MF, Read SH, Kontopantelis E, Buchan I, Emsley R, et al. Risk factor control and cardiovascular event risk in people with type 2 diabetes in primary and secondary prevention settings. Circulation. 2020; 142:1925–36.
Article32. Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzen S, Sattar N, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, et al. Risk factors, mortality, and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:633–44.
Article33. Lingvay I, Sumithran P, Cohen RV, le Roux CW. Obesity management as a primary treatment goal for type 2 diabetes: time to reframe the conversation. Lancet. 2022; 399:394–405.
Article34. Yabe D, Seino Y. Type 2 diabetes via β-cell dysfunction in east Asian people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016; 4:2–3.
Article35. Yoshinari M, Hirakawa Y, Hata J, Higashioka M, Honda T, Yoshida D, et al. Comparison of the contributions of impaired beta cell function and insulin resistance to the development of type 2 diabetes in a Japanese community: the Hisayama Study. Diabetologia. 2021; 64:1775–84.
Article36. Jang H, Im J, Park K. Adherence to dietary guidelines among diabetes patients: comparison between elderly and non-elderly groups. Clin Nutr Res. 2021; 10:14–23.
Article37. Powers MA, Bardsley JK, Cypress M, Funnell MM, Harms D, Hess-Fischl A, et al. Diabetes self-management education and support in adults with type 2 diabetes: a consensus report of the American Diabetes Association, the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of PAs, the American Association of Nurse Practitioners, and the American Pharmacists Association. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:1636–49.
Article38. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, et al. 5. Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S60–82.39. Hill-Briggs F, Adler NE, Berkowitz SA, Chin MH, Gary-Webb TL, Navas-Acien A, et al. Social determinants of health and diabetes: a scientific review. Diabetes Care. 2020; 44:258–79.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and Current Status of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets 2024
- Prevalence and Current Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets
- Obesity Fact Sheet in Korea, 2021: Trends in Obesity Prevalence and Obesity-Related Comorbidity Incidence Stratified by Age from 2009 to 2019
- Dementia Epidemiology Fact Sheet 2022
- 2023 Obesity Fact Sheet: Prevalence of Obesity and Abdominal Obesity in Adults, Adolescents, and Children in Korea from 2012 to 2021