J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2022 Apr;39(2):141-149. 10.12701/yujm.2021.01571.
Clinical implication of adjuvant chemotherapy according to mismatch repair status in patients with intermediate-risk stage II colon cancer: a retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology/Hematology, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Kyungpook National University Cancer Research Institute, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Surgery, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2529272
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01571
Abstract
- Background
The present study evaluated the clinical implications of adjuvant chemotherapy according to the mismatch repair (MMR) status and clinicopathologic features of patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage II colon cancer (CC).
Methods
This study retrospectively reviewed 5,774 patients who were diagnosed with CC and underwent curative surgical resection at Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital. The patients were enrolled according to the following criteria: (1) pathologically diagnosed with primary CC; (2) stage II CC classified based on the 7th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system; (3) intermediate- and high-risk features; and (4) available test results for MMR status. A total of 286 patients met these criteria and were included in the study.
Results
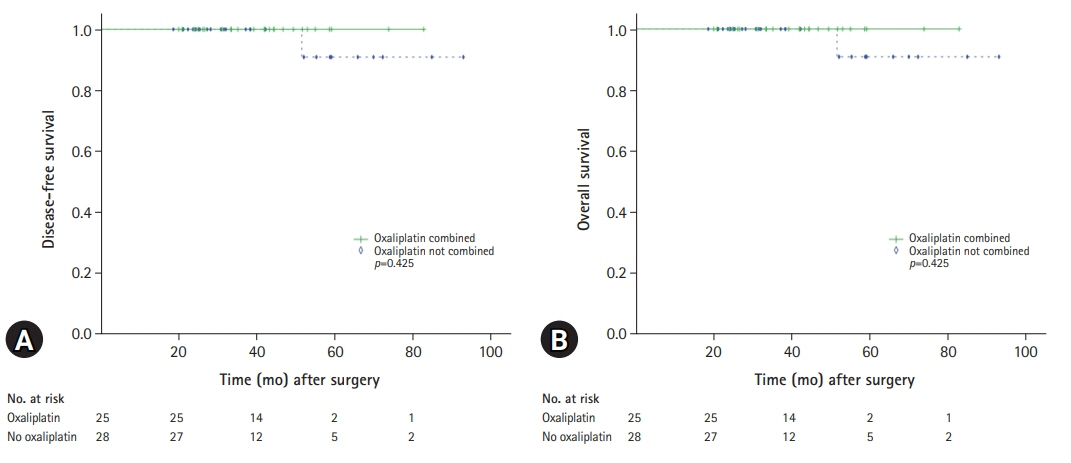
Among the 286 patients, 54 (18.9%) were identified as microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or deficient MMR (dMMR). Although all the patients identified as MSI-H/dMMR showed better survival outcomes, T4 tumors and adjuvant chemotherapy were identified as independent prognostic factors for survival. For the intermediate-risk patients identified as MSI-low (MSI-L)/microsatellite stable (MSS) or proficient MMR (pMMR), adjuvant chemotherapy exhibited a significantly better disease-free survival (DFS) but had no impact on overall survival (OS). Oxaliplatin-containing regimens showed no association with DFS or OS. Adjuvant chemotherapy was not associated with DFS in intermediate-risk patients identified as MSI-H/dMMR.
Conclusion
The current study found that the use of adjuvant chemotherapy was correlated with better DFS in MSI-L/MSS or pMMR intermediate-risk stage II CC patients.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Des Guetz G, Uzzan B, Morere JF, Perret G, Nicolas P. Duration of adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with non-metastatic colorectal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (1):CD007046.2. André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2343–51.3. Benson AB 3rd, Schrag D, Somerfield MR, Cohen AM, Figueredo AT, Flynn PJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations on adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:3408–19.4. Compton CC, Fielding LP, Burgart LJ, Conley B, Cooper HS, Hamilton SR, et al. Prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. College of American Pathologists Consensus Statement 1999. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000; 124:979–94.5. André T, de Gramont A, Vernerey D, Chibaudel B, Bonnetain F, Tijeras-Raballand A, et al. Adjuvant fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin in stage II to III colon cancer: updated 10-year survival and outcomes according to BRAF mutation and mismatch repair status of the MOSAIC Study. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:4176–87.6. Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Arain MA, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, et al. Colon cancer, version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021; 19:329–59.7. Thibodeau SN, Bren G, Schaid D. Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science. 1993; 260:816–9.8. Markowitz SD, Bertagnolli MM. Molecular origins of cancer: molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2449–60.9. Sargent DJ, Marsoni S, Monges G, Thibodeau SN, Labianca R, Hamilton SR, et al. Defective mismatch repair as a predictive marker for lack of efficacy of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy in colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3219–26.10. Ribic CM, Sargent DJ, Moore MJ, Thibodeau SN, French AJ, Goldberg RM, et al. Tumor microsatellite-instability status as a predictor of benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:247–57.11. Klingbiel D, Saridaki Z, Roth AD, Bosman FT, Delorenzi M, Tejpar S. Prognosis of stage II and III colon cancer treated with adjuvant 5-fluorouracil or FOLFIRI in relation to microsatellite status: results of the PETACC-3 trial. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26:126–32.12. Argilés G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, et al. Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020; 31:1291–305.13. Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:1471–4.14. Twelves C, Wong A, Nowacki MP, Abt M, Burris H 3rd, Carrato A, et al. Capecitabine as adjuvant treatment for stage III colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:2696–704.15. Haller DG, Tabernero J, Maroun J, de Braud F, Price T, Van Cutsem E, et al. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil and folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:1465–71.16. Haller DG, Catalano PJ, Macdonald JS, O’Rourke MA, Frontiera MS, Jackson DV, et al. Phase III study of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and levamisole in high-risk stage II and III colon cancer: final report of Intergroup 0089. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8671–8.17. André T, Sargent D, Tabernero J, O’Connell M, Buyse M, Sobrero A, et al. Current issues in adjuvant treatment of stage II colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006; 13:887–98.18. de Gramont A, de Gramont A, Chibaudel B, Larsen AK, Tournigand C, André T, et al. The evolution of adjuvant therapy in the treatment of early-stage colon cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011; 10:218–26.19. Lindor NM, Burgart LJ, Leontovich O, Goldberg RM, Cunningham JM, Sargent DJ, et al. Immunohistochemistry versus microsatellite instability testing in phenotyping colorectal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:1043–8.20. Chakrabarti S, Peterson CY, Sriram D, Mahipal A. Early stage colon cancer: current treatment standards, evolving paradigms, and future directions. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020; 12:808–32.21. Dienstmann R, Salazar R, Tabernero J. Personalizing colon cancer adjuvant therapy: selecting optimal treatments for individual patients. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:1787–96.22. Varghese A. Chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2015; 28:256–61.23. Rebuzzi SE, Pesola G, Martelli V, Sobrero AF. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12:2584.24. Tournigand C, André T, Bonnetain F, Chibaudel B, Lledo G, Hickish T, et al. Adjuvant therapy with fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in stage II and elderly patients (between ages 70 and 75 years) with colon cancer: subgroup analyses of the Multicenter International Study of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in the Adjuvant Treatment of Colon Cancer trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:3353–60.25. Yothers G, O’Connell MJ, Allegra CJ, Kuebler JP, Colangelo LH, Petrelli NJ, et al. Oxaliplatin as adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: updated results of NSABP C-07 trial, including survival and subset analyses. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3768–74.26. Bertagnolli MM, Redston M, Compton CC, Niedzwiecki D, Mayer RJ, Goldberg RM, et al. Microsatellite instability and loss of heterozygosity at chromosomal location 18q: prospective evaluation of biomarkers for stages II and III colon cancer: a study of CALGB 9581 and 89803. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3153–62.27. Hutchins G, Southward K, Handley K, Magill L, Beaumont C, Stahlschmidt J, et al. Value of mismatch repair, KRAS, and BRAF mutations in predicting recurrence and benefits from chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:1261–70.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The efficacy of chemotherapy in the patients with stage II colon cancer associated with number of high-risk factors
- Effectiveness of oral fluoropyrimidine monotherapy as adjuvant chemotherapy for high-risk stage II colon cancer
- Adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage II high-risk and III colon cancer: Hindering factors to adherence and impact on long-term survival
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Colon Cancer
- Oncologic outcomes of early adjuvant chemotherapy initiation in patients with stage III colon cancer