Lab Med Online.
2021 Jul;11(3):199-202. 10.47429/lmo.2021.11.3.199.
Identification of a UGT1A1*37 Allele in a Korean Patient with Pancreatic Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526070
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2021.11.3.199
Abstract
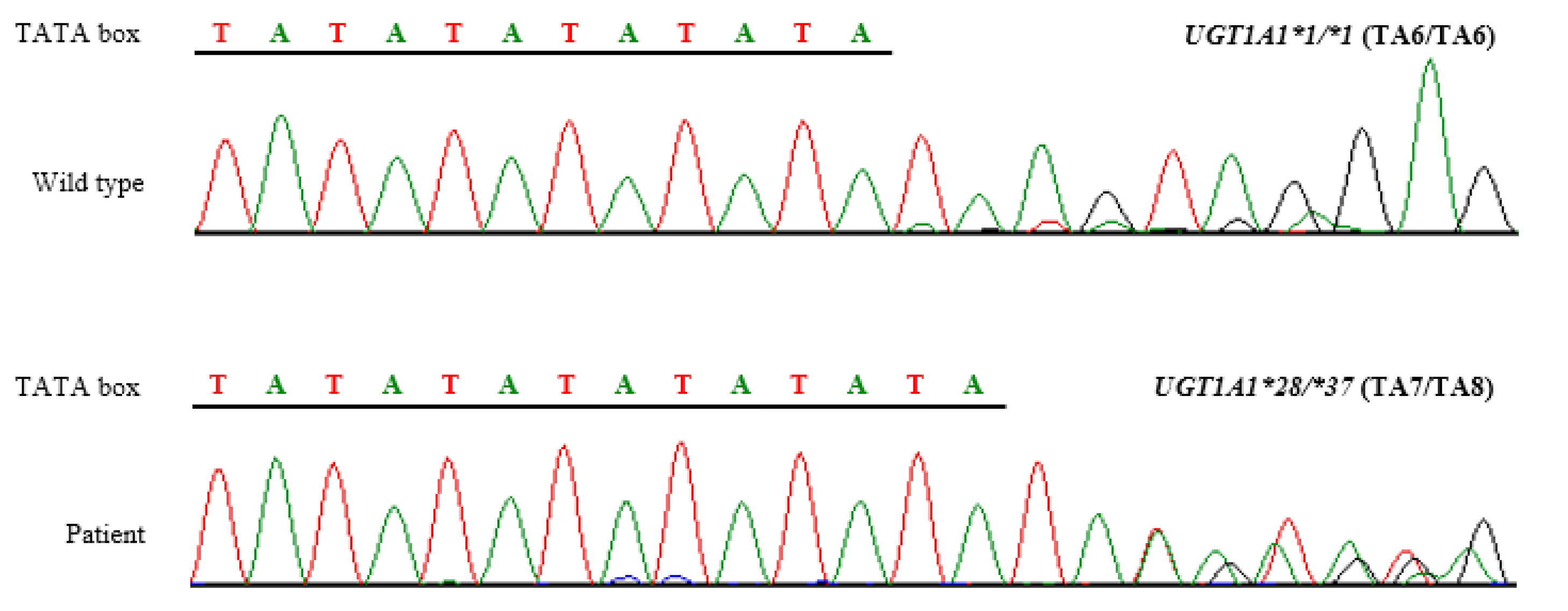
- UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) is an enzyme that catalyzes glucuronidation of substances, including bilirubin and other drug metabolites. Certain UGT1A1 polymorphisms reduce UGT1A1 activity, notably UGT1A1*28 contains thymine-adenine repeats in the TATA box of the promotor region. Irinotecan, a chemotherapy agent for solid cancers, is converted in the body to an active metabolite, SN-28, and then excreted, after being conjugated with glucuronide by UGT1A1. If UGT1A1 activity decreases (e.g. UGT1A1*28), the risk of irinotecan toxicity increases, which can develop into severe neutropenia and diarrhea. UGT1A1*37, a rare allele that has never been found in Asians, was previously reported to be associated with severe neutropenia by reducing UGT1A1 activity further than UGT1A1*28. In this study, we first detected UGT1A1*37 in a 69-year-old Korean woman diagnosed with pancreatic cancer and excluded irinotecan from her chemotherapy regimen, in consideration of the increased risk of toxicity, based on pre-treatment UGT1A1 genotyping.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barbarino JM, Haidar CE, Klein TE, Altman RB. 2014; PharmGKB summary: very important pharmacogene information for UGT1A1. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 24:177–83. DOI: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000024. PMID: 24492252. PMCID: PMC4091838.2. Kim JJ, Oh J, Kim Y, Lee KA. 2020; Genetic spectrum of UGT1A1 in Korean patients with unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Ann Lab Med. 40:281–3. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.3.281. PMID: 31858773. PMCID: PMC6933057.3. Marques SC, Ikediobi ON. 2010; The clinical application of UGT1A1 pharmacogenetic testing: gene-environment interactions. Hum Genomics. 4:238–49. DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-4-4-238. PMID: 20511137. PMCID: PMC3525209.
Article4. Gammal RS, Court MH, Haidar CE, Iwuchukwu OF, Gaur AH, Alvarellos M, et al. 2016; Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium (CPIC) guideline for UGT1A1 and atazanavir prescribing. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 99:363–9. DOI: 10.1002/cpt.269. PMID: 26417955. PMCID: PMC4785051.5. Beutler E, Gelbart T, Demina A. 1998; Racial variability in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 (UGT1A1) promoter: a balanced polymorphism for regulation of bilirubin metabolism? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:8170–4. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8170. PMID: 9653159. PMCID: PMC20948.6. Guillemette C. 2003; Pharmacogenomics of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes. Pharmacogenomics J. 3:136–58. DOI: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500171. PMID: 12815363.
Article7. AlFadhli S, Al-Jafer H, Hadi M, Al-Mutairi M, Nizam R. 2013; The effect of UGT1A1 promoter polymorphism in the development of hyperbilirubinemia and cholelithiasis in hemoglobinopathy patients. PLoS One. 8:e77681. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077681. PMID: 24204915. PMCID: PMC3813713.8. Riera P, Salazar J, Virgili AC, Tobeña M, Sebio A, Gallano P, et al. 2018; Relevance of CYP3A4*20, UGT1A1*37 and UGT1A1*28 variants in irinotecan-induced severe toxicity. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 84:1389–92. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13574. PMID: 29504153. PMCID: PMC5980573.9. Rouits E, Boisdron-Celle M, Dumont A, Guérin O, Morel A, Gamelin E. 2004; Relevance of different UGT1A1 polymorphisms in irinotecan-induced toxicity: a molecular and clinical study of 75 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5151–9. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0548. PMID: 15297419.10. Strassburg CP. 2008; Pharmacogenetics of Gilbert's syndrome. Pharmacogenomics. 9:703–15. DOI: 10.2217/14622416.9.6.703. PMID: 18518849.
Article11. Hsieh TY, Shiu TY, Huang SM, Lin HH, Lee TC, Chen PJ, et al. 2007; Molecular pathogenesis of Gilbert's syndrome: decreased TATA-binding protein binding affinity of UGT1A1 gene promoter. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 17:229–36. DOI: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e328012d0da. PMID: 17496722.12. Bosma PJ, Chowdhury JR, Bakker C, Gantla S, de Boer A, Oostra BA, et al. 1995; The genetic basis of the reduced expression of bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 in Gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 333:1171–5. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199511023331802. PMID: 7565971.
Article13. Monaghan G, Ryan M, Seddon R, Hume R, Burchell B. 1996; Genetic variation in bilirubin UPD-glucuronosyltransferase gene promoter and Gilbert's syndrome. Lancet. 347:578–81. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)91273-8.14. Iyer L, Das S, Janisch L, Wen M, Ramírez J, Karrison T, et al. 2002; UGT1A1*28 polymorphism as a determinant of irinotecan disposition and toxicity. Pharmacogenomics J. 2:43–7. DOI: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500072. PMID: 11990381.
Article15. Innocenti F, Undevia SD, Iyer L, Chen PX, Das S, Kocherginsky M, et al. 2004; Genetic variants in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene predict the risk of severe neutropenia of irinotecan. J Clin Oncol. 22:1382–8. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2004.07.173. PMID: 15007088.16. de Man FM, Goey AKL, van Schaik RHN, Mathijssen RHJ, Bins S. 2018; Individualization of irinotecan treatment: a review of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacogenetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 57:1229–54. DOI: 10.1007/s40262-018-0644-7. PMID: 29520731. PMCID: PMC6132501.
Article17. Shirasu H, Todaka A, Omae K, Fujii H, Mizuno N, Ozaka M, et al. 2019; Impact of UGT1A1 genetic polymorphism on toxicity in unresectable pancreatic cancer patients undergoing FOLFIRINOX. Cancer Sci. 110:707–16. DOI: 10.1111/cas.13883. PMID: 30447099. PMCID: PMC6361560.18. Liu X, Cheng D, Kuang Q, Liu G, Xu W. 2014; Association of UGT1A1*28 polymorphisms with irinotecan-induced toxicities in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis in Caucasians. Pharmacogenomics J. 14:120–9. DOI: 10.1038/tpj.2013.10. PMID: 23529007. PMCID: PMC3992871.19. Palomaki GE, Bradley LA, Douglas MP, Kolor K, Dotson WD. 2009; Can UGT1A1 genotyping reduce morbidity and mortality in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with irinotecan? An evidence-based review. Genet Med. 11:21–34. DOI: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e31818efd77. PMID: 19125129. PMCID: PMC2743611.20. Hoskins JM, Goldberg RM, Qu P, Ibrahim JG, McLeod HL. 2007; UGT1A1*28 genotype and irinotecan-induced neutropenia: dose matters. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1290–5. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djm115. PMID: 17728214.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The UGT1A9*22 genotype identifies a high-risk group for irinotecan toxicity among gastric cancer patients
- Incidence of Atazanavir-associated Hyperbilirubinemia in Korean HIV Patients: 30 Months Follow-up Results in a Population with Low UDP-glucuronosyltransferase1A1*28 Allele Frequency
- Evaluation of a Fully Automated, Rapid Detection System for CYP2C19 and UGT1A1 Genotyping
- The Efficacy of UGT1A1 Polymorphism in Chemoradiation Therapy Using Irinotecan in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
- The Association of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia with UGT1A1 and CYP1A2 Gene Polymorphism in Korean Neonates