Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2021 Oct;38(4):361-365. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00885.
Safety and effectiveness of early cardiac rehabilitation in a stroke patient with heart failure and atrial fibrillation: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Cardiac Rehabilitation Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- KMID: 2521717
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00885
Abstract
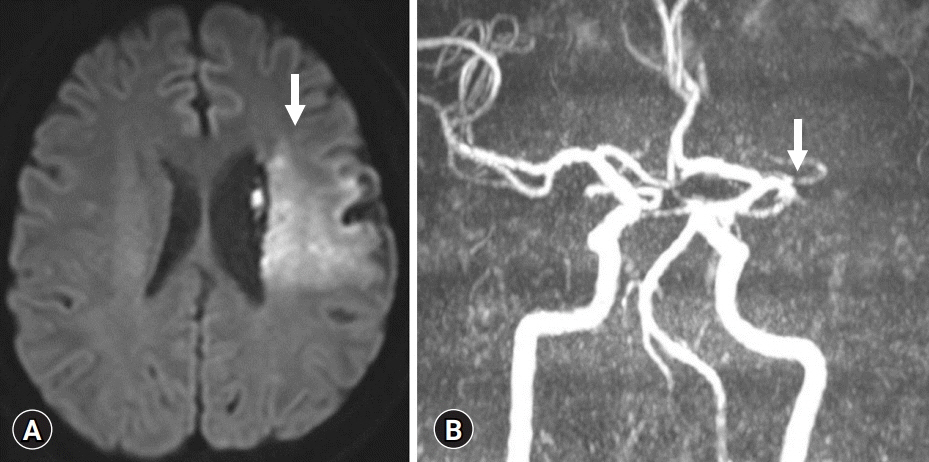
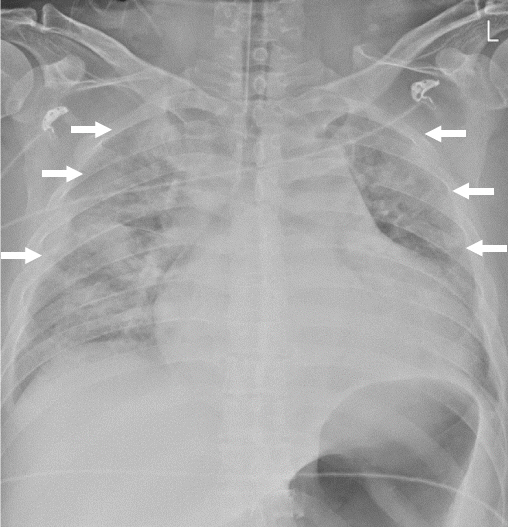
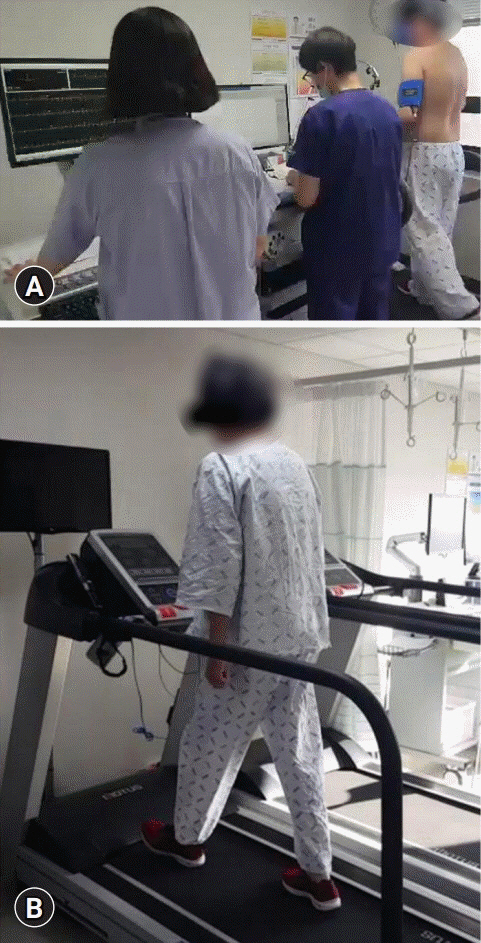
- Stroke patients have reduced aerobic capacity. Therefore, intensive structured exercise programs are needed. We report the case of a patient with stroke and cardiac disease who underwent early inpatient cardiac rehabilitation (CR). A 38-year-old male patient with atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and cerebral infarction underwent a symptom-limited exercise tolerance test (ETT) without any problems on day 45 after admission. He completed a 2-week inpatient program and an 8-week home-based CR program. Follow-up ETT showed increased exercise capacity. The present case might be the first to report a safely performed CR program in a patient with stroke and cardiac comorbidity in Korea. Systematic guidance is needed for post-stroke patients to receive safe and effective CR for the secondary prevention of stroke and cardiovascular risk.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Marzolini S. Integrating individuals with stroke into cardiac rehabilitation following traditional stroke rehabilitation: promoting a continuum of care. Can J Cardiol. 2018; 34(10 Suppl 2):S240–6.
Article2. Mackay-Lyons MJ, Makrides L. Exercise capacity early after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 83:1697–702.
Article3. Tang A, Closson V, Marzolini S, Oh P, McIlroy W, Brooks D. Cardiac rehabilitation after stroke-need and opportunity. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2009; 29:97–104.
Article4. Kesarwani M, Perez A, Lopez VA, Wong ND, Franklin SS. Cardiovascular comorbidities and blood pressure control in stroke survivors. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:1056–63.
Article5. Myers J, Kaminsky LA, Lima R, Christle JW, Ashley E, Arena R. A reference equation for normal standards for VO2 max: analysis from the fitness registry and the importance of exercise national database (FRIEND Registry). Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2017; 60:21–9.6. Song MJ, Lee JH, Shin WS. Minimal Clinically Important Difference of Berg Balance Scale scores in people with acute stroke. Phys Ther Rehabil Sci. 2018; 7:102–8.
Article7. Hong I, Lim Y, Han H, Hay CC, Woo HS. Application of the Korean version of the modified Barthel index: development of a keyform for use in clinical practice. Hong Kong J Occup Ther. 2017; 29:39–46.
Article8. American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Guidelines for cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention programs. Leeds: Human Kinetics;2004.9. Prior PL, Hachinski V, Unsworth K, Chan R, Mytka S, O'Callaghan C, et al. Comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation for secondary prevention after transient ischemic attack or mild stroke: I: feasibility and risk factors. Stroke. 2011; 42:3207–13.
Article10. Billinger SA, Mattlage AE, Ashenden AL, Lentz AA, Harter G, Rippee MA. Aerobic exercise in subacute stroke improves cardiovascular health and physical performance. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2012; 36:159–65.
Article11. Kim C, Sung J, Lee JH, Kim WS, Lee GJ, Jee S, et al. Clinical practice guideline for cardiac rehabilitation in Korea: recommendations for cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention after acute coronary syndrome. Korean Circ J. 2019; 49:1066–111.
Article12. Kim C, Kim DY, Lee DW. The impact of early regular cardiac rehabilitation program on myocardial function after acute myocardial infarction. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:535–40.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-medication Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
- Ventricular Fibrillation in a Patient with Tachycardia-Induced Cardiomyopathy after Liver Transplantation
- The Mechanism of and Preventive Therapy for Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- How and When to Screen for Atrial Fibrillation after Stroke: Insights from Insertable Cardiac Monitoring Devices
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction in Young Woman with Graves' Disease and Atrial Fibrillation