Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Jun;36(3):647-660. 10.3803/EnM.2020.934.
Efficacy and Safety of the New Appetite Suppressant, Liraglutide: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 2Department of Biomedical Science and Engineering, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju, Korea
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea
- KMID: 2517655
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.934
Abstract
- Background
Obesity is a chronic disease associated with metabolic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved liraglutide as an anti-obesity drug for nondiabetic patients in 2014, it has been widely used for weight control in overweight and obese people. This study aimed to systematically analyze the effects of liraglutide on body weight and other cardiometabolic parameters.
Methods
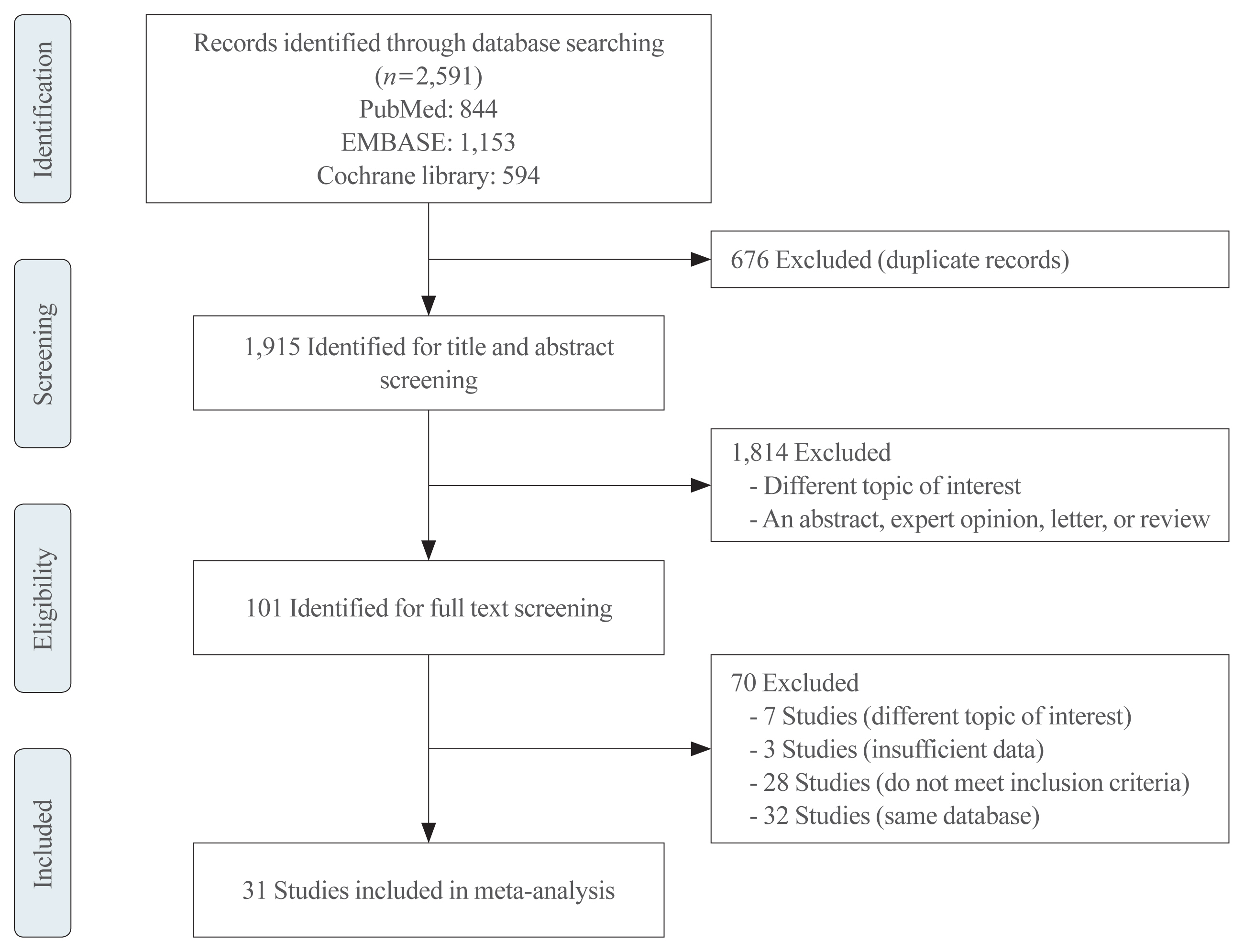
We investigated articles from PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library to search randomized clinical trials that examined body weight changes with liraglutide treatment.
Results
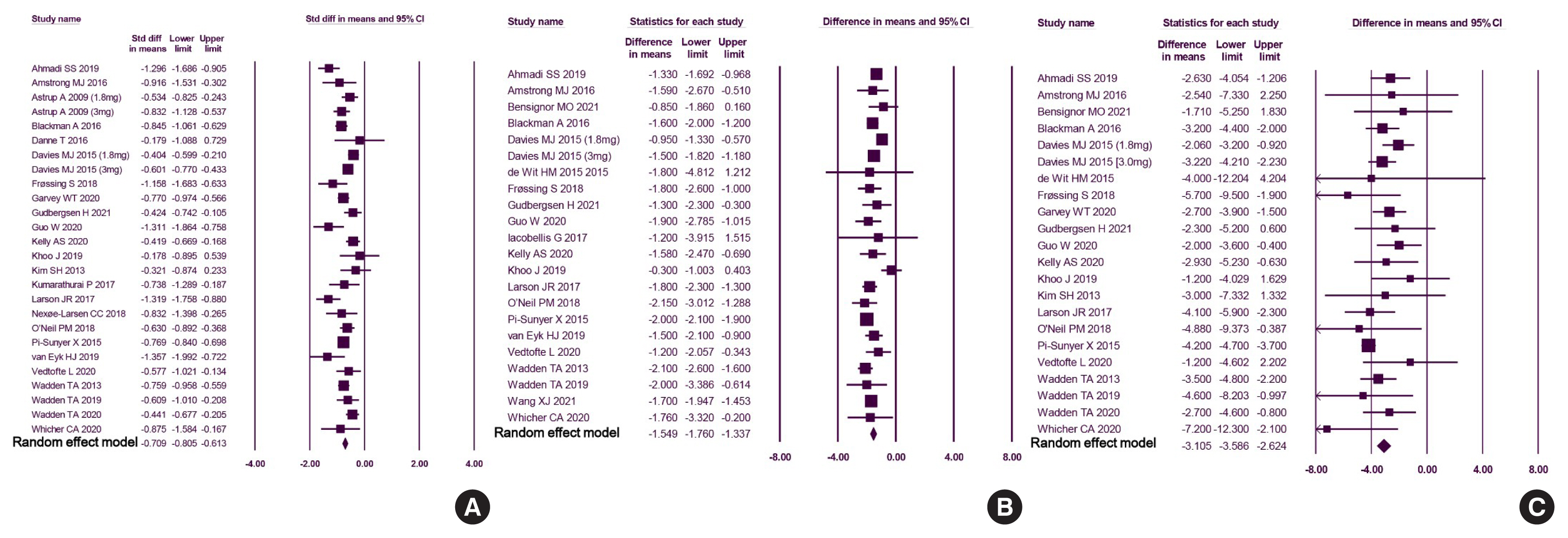
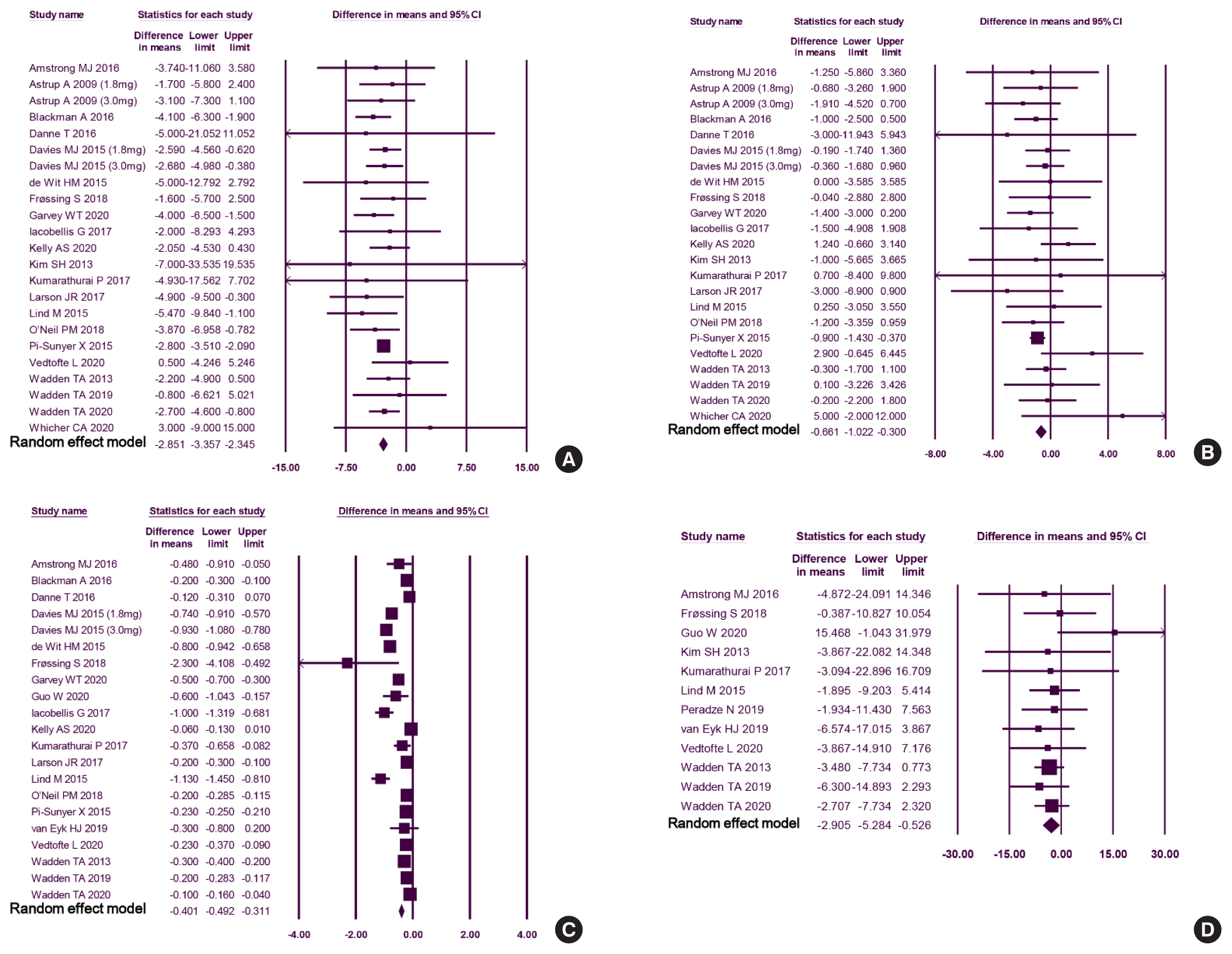
We included 31 studies with 8,060 participants for this meta-analysis. The mean difference (MD) between the liraglutide group and the placebo group was −4.19 kg (95% confidence interval [CI], −4.84 to −3.55), with a −4.16% change from the baseline (95% CI, −4.90 to −3.43). Liraglutide treatment correlated with a significantly reduced body mass index (MD: −1.55; 95% CI, −1.76 to −1.34) and waist circumference (MD: −3.11 cm; 95% CI, −3.59 to −2.62) and significantly decreased blood pressure (systolic blood pressure, MD: −2.85 mm Hg; 95% CI, −3.36 to −2.35; diastolic blood pressure, MD: −0.66 mm Hg; 95% CI, −1.02 to −0.30), glycated hemoglobin (MD: −0.40%; 95% CI, −0.49 to −0.31), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (MD: –2.91 mg/dL; 95% CI, −5.28 to −0.53; MD: −0.87% change from baseline; 95% CI, −1.17 to −0.56).
Conclusion
Liraglutide is effective for weight control and can be a promising drug for cardiovascular protection in overweight and obese people.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pi-Sunyer X. The medical risks of obesity. Postgrad Med. 2009; 121:21–33.
Article2. GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:13–27.
Article3. Wilson K. Obesity: lifestyle modification and behavior interventions. FP Essent. 2020; 492:19–24.4. Dalle Grave R, Calugi S, Centis E, Marzocchi R, El Ghoch M, Marchesini G. Lifestyle modification in the management of the metabolic syndrome: achievements and challenges. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2010; 3:373–85.5. Khera R, Murad MH, Chandar AK, Dulai PS, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, et al. Association of pharmacological treatments for obesity with weight loss and adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016; 315:2424–34.
Article6. Bode B. Liraglutide: a review of the first once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist. Am J Manag Care. 2011; 17(2 Suppl):S59–70.7. Mehta A, Marso SP, Neeland IJ. Liraglutide for weight management: a critical review of the evidence. Obes Sci Pract. 2017; 3:3–14.
Article8. Howell R, Wright AM, Clements JN. Clinical potential of liraglutide in cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes: evidence to date. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019; 12:505–12.9. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article10. Garvey WT, Birkenfeld AL, Dicker D, Mingrone G, Pedersen SD, Satylganova A, et al. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide 3.0 mg in individuals with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin: the SCALE insulin randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:1085–93.
Article11. Wadden TA, Tronieri JS, Sugimoto D, Lund MT, Auerbach P, Jensen C, et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg and intensive behavioral therapy (ibt) for obesity in primary care: the SCALE IBT randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2020; 28:529–36.
Article12. Kelly AS, Auerbach P, Barrientos-Perez M, Gies I, Hale PM, Marcus C, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of liraglutide for adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:2117–28.
Article13. Wadden TA, Walsh OA, Berkowitz RI, Chao AM, Alamuddin N, Gruber K, et al. Intensive behavioral therapy for obesity combined with liraglutide 3.0 mg: a randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019; 27:75–86.
Article14. van Eyk HJ, Blauw LL, Bizino MB, Wang Y, van Dijk KW, de Mutsert R, et al. Hepatic triglyceride content does not affect circulating CETP: lessons from a liraglutide intervention trial and a population-based cohort. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:9996.
Article15. Peradze N, Farr OM, Perakakis N, Lazaro I, Sala-Vila A, Mantzoros CS. Short-term treatment with high dose liraglutide improves lipid and lipoprotein profile and changes hormonal mediators of lipid metabolism in obese patients with no overt type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over, double-blind clinical trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:141.
Article16. Khoo J, Hsiang JC, Taneja R, Koo SH, Soon GH, Kam CJ, et al. Randomized trial comparing effects of weight loss by liraglutide with lifestyle modification in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2019; 39:941–9.
Article17. Ahmadi SS, Filipsson K, Dimenas H, Isaksson SS, Imberg H, Sjoberg S, et al. Effect of liraglutide on anthropometric measurements, sagittal abdominal diameter and adiponectin levels in people with type 2 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: evaluations from a randomized trial (MDI-liraglutide study 5). Obes Sci Pract. 2019; 5:130–40.
Article18. O’Neil PM, Birkenfeld AL, McGowan B, Mosenzon O, Pedersen SD, Wharton S, et al. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2018; 392:637–49.
Article19. Nexoe-Larsen CC, Sorensen PH, Hausner H, Agersnap M, Baekdal M, Bronden A, et al. Effects of liraglutide on gallbladder emptying: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in adults with overweight or obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:2557–64.
Article20. Frossing S, Nylander M, Kistorp C, Skouby SO, Faber J. Effect of liraglutide on atrial natriuretic peptide, adrenomedullin, and copeptin in PCOS. Endocr Connect. 2018; 7:115–23.
Article21. Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MS, Jespersen HR, Jakobsen MI, Svensson CK, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017; 74:719–28.
Article22. Kumarathurai P, Anholm C, Larsen BS, Olsen RH, Madsbad S, Kristiansen O, et al. Effects of liraglutide on heart rate and heart rate variability: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:117–24.
Article23. Iacobellis G, Mohseni M, Bianco SD, Banga PK. Liraglutide causes large and rapid epicardial fat reduction. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2017; 25:311–6.
Article24. Danne T, Biester T, Kapitzke K, Jacobsen SH, Jacobsen LV, Petri KC, et al. Liraglutide in an adolescent population with obesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 5-week trial to assess safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of liraglutide in adolescents aged 12–17 years. J Pediatr. 2017; 181:146–53.
Article25. Blackman A, Foster GD, Zammit G, Rosenberg R, Aronne L, Wadden T, et al. Effect of liraglutide 3.0 mg in individuals with obesity and moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea: the SCALE Sleep Apnea randomized clinical trial. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016; 40:1310–9.26. Lind M, Hirsch IB, Tuomilehto J, Dahlqvist S, Ahren B, Torffvit O, et al. Liraglutide in people treated for type 2 diabetes with multiple daily insulin injections: randomised clinical trial (MDI Liraglutide trial). BMJ. 2015; 351:h5364.
Article27. Davies MJ, Bergenstal R, Bode B, Kushner RF, Lewin A, Skjoth TV, et al. Efficacy of liraglutide for weight loss among patients with type 2 diabetes: the SCALE diabetes randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015; 314:687–99.
Article28. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, Greenway F, Halpern A, Krempf M, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:11–22.
Article29. de Wit HM, Vervoort GM, Jansen HJ, de Galan BE, Tack CJ. Durable efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and pronounced insulin-associated weight gain: 52-week results from the Effect of Liraglutide on insulin-associated wEight GAiN in patients with Type 2 diabetes’ (ELEGANT) randomized controlled trial. J Intern Med. 2016; 279:283–92.
Article30. Kim SH, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Liu A, Ariel D, Schaaf P, et al. Benefits of liraglutide treatment in overweight and obese older individuals with prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3276–82.
Article31. Astrup A, Rossner S, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, Niskanen L, Al Hakim M, et al. Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet. 2009; 374:1606–16.
Article32. Wadden TA, Hollander P, Klein S, Niswender K, Woo V, Hale PM, et al. Weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie-diet-induced weight loss: the SCALE Maintenance randomized study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013; 37:1443–51.
Article33. Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, Barton D, Hull D, Parker R, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. 2016; 387:679–90.
Article34. Whicher CA, Price HC, Phiri P, Rathod S, Barnard-Kelly K, Ngianga K, et al. The use of liraglutide 3.0 mg daily in the management of overweight and obesity in people with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and first episode psychosis: results of a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:1262–71.
Article35. Wang XJ, Gong P, Zhou C, Huang C, Lok UW, Tang S, et al. Liraglutide reduces attenuation coefficient as a measure of hepatic steatosis during 16 weeks’ treatment in nondiabetic obese patients: a pilot trial. JGH Open. 2020; 5:193–8.
Article36. Bensignor MO, Bomberg EM, Bramante CT, Divyalasya TV, Hale PM, Ramesh CK, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on body mass index and weight parameters in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes: post hoc analysis of the ellipse trial. Pediatr Obes. 2021. Feb. 25. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.12778 .
Article37. Gudbergsen H, Overgaard A, Henriksen M, Waehrens EE, Bliddal H, Christensen R, et al. Liraglutide after diet-induced weight loss for pain and weight control in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021; 113:314–23.
Article38. Guo W, Tian W, Lin L, Xu X. Liraglutide or insulin glargine treatments improves hepatic fat in obese patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in twenty-six weeks: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020; 170:108487.
Article39. Vedtofte L, Bahne E, Foghsgaard S, Bagger JI, Andreasen C, Strandberg C, et al. One year’s treatment with the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist liraglutide decreases hepatic fat content in women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and prior gestational diabetes mellitus in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:3213.
Article40. Tronieri JS, Wadden TA, Walsh O, Berkowitz RI, Alamuddin N, Gruber K, et al. Effects of liraglutide on appetite, food preoccupation, and food liking: results of a randomized controlled trial. Int J Obes (Lond). 2020; 44:353–61.
Article41. Davies MJ, Aronne LJ, Caterson ID, Thomsen AB, Jacobsen PB, Marso SP, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in adults with overweight or obesity: a post hoc analysis from SCALE randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:734–9.
Article42. Frison V, Simioni N, Marangoni A, Balzano S, Vinci C, Zenari L, et al. Clinical impact of 5 years of liraglutide treatment on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a real-life setting in Italy: an observational study. Diabetes Ther. 2018; 9:2201–8.
Article43. Verma S, Poulter NR, Bhatt DL, Bain SC, Buse JB, Leiter LA, et al. Effects of liraglutide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with or without history of myocardial infarction or stroke. Circulation. 2018; 138:2884–94.
Article44. Marso SP, Baeres FM, Bain SC, Goldman B, Husain M, Nauck MA, et al. Effects of liraglutide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with diabetes with or without heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 75:1128–41.45. Jackson SH, Martin TS, Jones JD, Seal D, Emanuel F. Liraglutide (victoza): the first once-daily incretin mimetic injection for type-2 diabetes. P&T. 2010; 35:498–529.46. Sheahan KH, Wahlberg EA, Gilbert MP. An overview of GLP-1 agonists and recent cardiovascular outcomes trials. Postgrad Med J. 2020; 96:156–61.
Article47. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:311–22.
Article48. Carlsson Petri KC, Ingwersen SH, Flint A, Zacho J, Overgaard RV. Semaglutide s.c. once-weekly in type 2 diabetes: a population pharmacokinetic analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2018; 9:1533–47.
Article49. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1834–44.
Article50. Lingvay I, Leiter LA. Use of GLP-1 RAs in cardiovascular disease prevention: a practical guide. Circulation. 2018; 137:2200–2.
Article51. Drucker DJ. The cardiovascular biology of glucagon-like peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2016; 24:15–30.
Article52. Hasegawa Y, Hori M, Nakagami T, Harada-Shiba M, Uchigata Y. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists reduced the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with statins. J Clin Lipidol. 2018; 12:62–9.
Article53. Yao Y, Li Q, Wang W, Zhang J, Gao P, Xu Y. Glucagon-like peptide-1 modulates cholesterol homeostasis by suppressing the miR-19b-induced downregulation of ABCA1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 50:679–93.
Article54. Mulvihill EE. Regulation of intestinal lipid and lipoprotein metabolism by the proglucagon-derived peptides glucagon like peptide 1 and glucagon like peptide 2. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2018; 29:95–103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prophylactic efficacy of probiotics on travelers' diarrhea: an adaptive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage related to Phentermine as an Appetite Suppressant
- Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplements in Prevention of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Meta-analysis for Efficacy and Safety of Propofol during Dental Sedation
- A Case of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Phendimetrazine as an Appetite Suppressant