Ann Clin Microbiol.
2021 Jun;24(2):61-65. 10.5145/ACM.2021.24.2.4.
First Report of Roseomonas aerofrigidensis Isolated from the Peritoneal Fluid of a Gastric Cancer Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Sprayberry High School, Marietta, USA
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Brain Korea 21 plus Program for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516724
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2021.24.2.4
Abstract
- Roseomonas aerofrigidensis is a gram-negative, strictly aerobic, non-motile bacterium, which was first isolated in 2017 in South Korea. We present the first report of the isolation of R.aerofrigidensis from the peritoneal fluid of a 38-year-old woman with a history of metastatic gastric cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis. The isolate was resistant to cotrimoxazole. Further research on clinical and microbiological responses to several antibiotics are warranted.
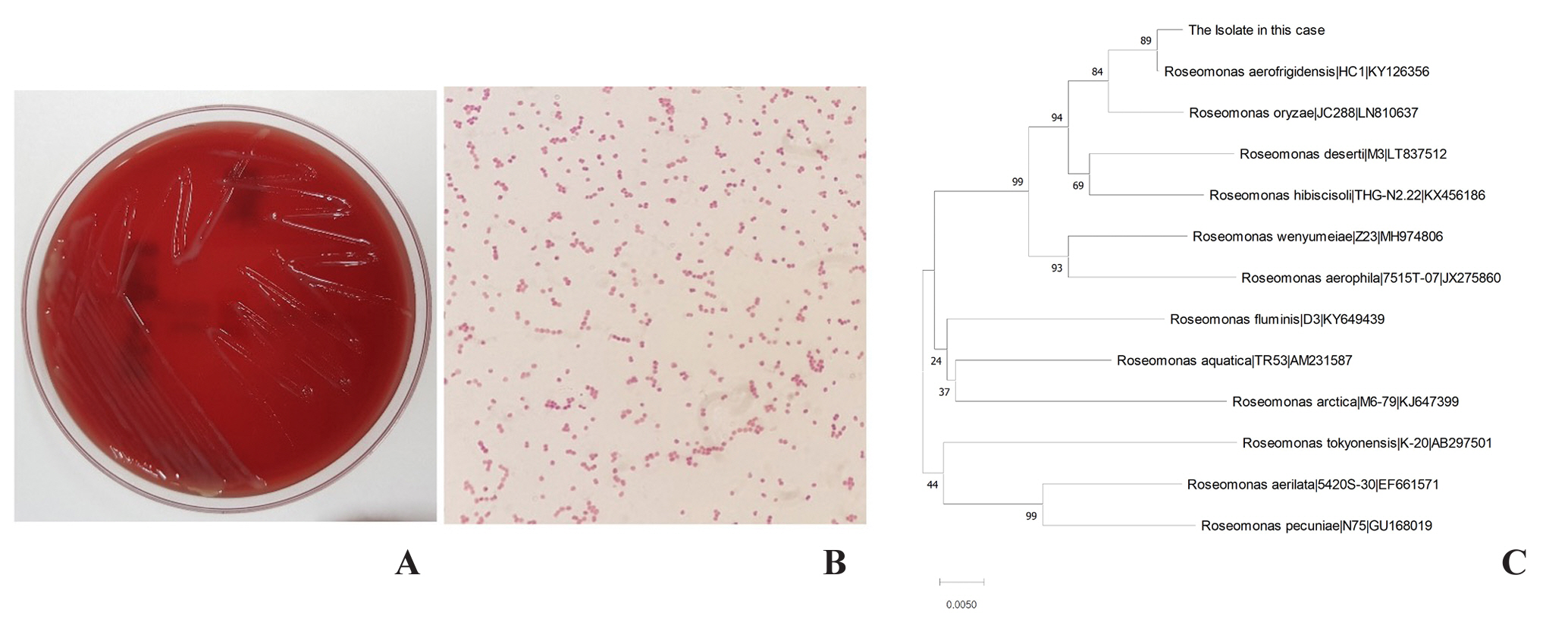
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hyeon JW and Jeon CO. Roseomonas aerofrigidensis sp. nov., isolated from an air conditioner. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2017;67:4039-44.2. Kim SJ, Weon HY, Ahn JH, Hong SB, Seok SJ, Whang KS, et al. Roseomonas aerophila sp. nov., isolated from air. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2013;63:2334-7.3. Furuhata K, Ishizaki N, Edagawa A, Fukuyama M. Roseomonas tokyonensis sp. nov. isolated from a biofilm sample obtained from a cooling tower in Tokyo, Japan. Biocontrol Sci 2013;18:205-9.4. Kim YK, Moon JS, Song KE, Lee WK. Two cases of bacteremia due to Roseomonas mucosa. Ann Lab Med 2016;36:367-70.5. Dé I, Rolston KV, Han XY. Clinical significance of Roseomonas species isolated from catheter and blood samples: analysis of 36 cases in patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis 2004;38:1579-84.6. Kim KY, Hur J, Jo W, Hong J, Cho OH, Kang DH, et al. Infectious spondylitis with bacteremia caused by Roseomonas mucosa in an immunocompetent patient. Infect Chemother 2015;47:194-6.7. Bibashi E, Sofianou D, Kontopoulou K, Mitsopoulos E, Kokolina E. Peritonitis due to Roseomonas fauriae in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:456-7.8. Struthers M, Wong J, Janda JM. An initial appraisal of the clinical significance of Roseomonas species associated with human infections. Clin Infect Dis 1996;23:729-33.9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by targeted DNA sequencing; approved guideline MM18-ED2. Wayne; PA:2018.10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; approved guideline M100-ED30. Wayne; PA:2019. .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infectious Spondylitis with Bacteremia Caused by Roseomonas mucosa in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Two Cases of Bacteremia Due to Roseomonas mucosa
- A Case of Roseomonas Infection in Korea
- Prognostic Value of CEA and CA19 - 9 in Serum and Peritoneal Washing Fluid in Gastric Carcinoma
- Gastric Cancer with Peritoneal Tuberculosis: Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment