Ann Lab Med.
2021 Jul;41(4):436-438. 10.3343/alm.2021.41.4.436.
First Identification of IMP-1 Metallo-β-Lactamase in Delftia tsuruhatensis Strain CRS1243 Isolated From a Clinical Specimen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2512726
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2021.41.4.436
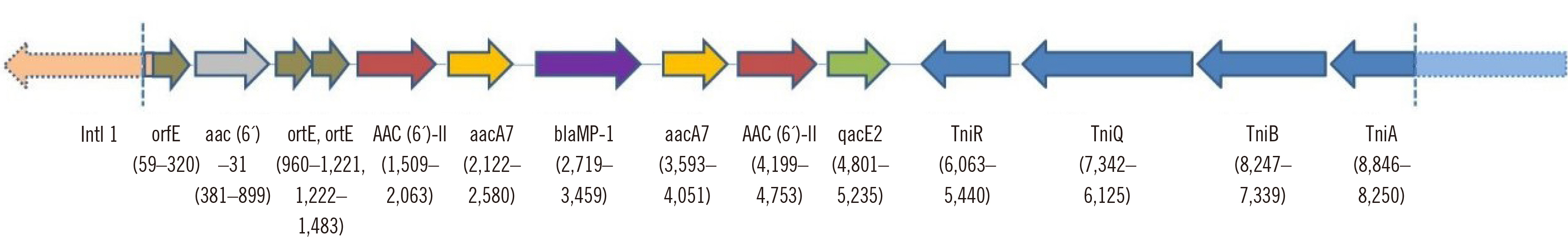
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shigematsu T, Yumihara K, Ueda Y, Numaguchi M, Morimura S, Kida K. 2003; Delftia tsuruhatensis sp. nov., a terephthalate-assimilating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 53:1479–83. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.02285-0. PMID: 13130036.2. Preiswerk B, Ullrich S, Speich R, Bloemberg GV, Hombach M. 2011; Case report human infection with Delftia tsuruhatensis isolated from a central venous catheter. J Med Microbiol. 60:246–8. DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.021238-0. PMID: 20965913.3. Jorgensen NO, Brandt KK, Nybroe O, Hansen M. 2009; Delftia lacustris sp. nov., a peptidoglycan-degrading bacterium from fresh water, and emended description of Delftia tsuruhatensis as a peptidoglycan-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 59:2195–9. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.008375-0. PMID: 19605727.4. Ranc A, Dubourg G, Fournier PE, Raoult D, Fenollar F. 2018; Delftia tsuruhatensis, an emergent opportunistic healthcare-associated pathogen. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:594–6. DOI: 10.3201/eid2403.160939. PMID: 29460754. PMCID: PMC5823324.5. CLSI. 2018. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; approved standard. CLSI M100-S28. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institut;Wayne, PA:6. CLSI. 2018. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard. CLSI M7-A11. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institut;Wayne, PA:7. Ellington MJ, Kistler J, Livermore DM, Woodford N. 2007; Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of genes encoding acquired metallo-beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 59:321–2. DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkl481. PMID: 17185300.8. Sandvang D, Aarestrup FM, Jensen LB. 1997; Characterisation of integrons and antibiotic resistance genes in Danish multiresistant Salmonella enterica Typhimurium DT104. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 157:177–81. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb12770.x. PMID: 9418253.9. Zhao WH, Hu ZQ. 2011; IMP-type metallo-β-lactamases in Gram-negative bacilli: distribution, phylogeny, and association with integrons. Crit Rev Microbiol. 37:214–26. DOI: 10.3109/1040841X.2011.559944. PMID: 21707466.
Article10. Jeong SH, Bae IK, Park KO, An YJ, Sohn SG, Jang SJ, Sung KH, Yang KS, Lee K, Young D, Lee SH. 2006; Outbreaks of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing carbapenemases in Korea. J Microbiol. 44:423–31.11. Chu YW, Afzal-Shah M, Houang ET, Palepou MI, Lyon DJ, Woodford N, Livermore DM. 2001; IMP-4, a novel metallo-beta-lactamase from nosocomial Acinetobacter spp. collected in Hong Kong between 1994 and 1998. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 45:710–4. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.3.710-714.2001. PMID: 11181348. PMCID: PMC90361.12. Xu H, Davies J, Miao V. 2007; Molecular characterization of class 3 integrons from Delftia spp. J Bacteriol. 189:6276–83. DOI: 10.1128/JB.00348-07. PMID: 17573473. PMCID: PMC1951913.13. Walsh TR, Weeks J, Livermore DM, Toleman MA. 2011; Dissemination of NDM-1 positive bacteria in the New Delhi environment and its implications for human health: an environmental point prevalence study. Lancet Infect Dis. 11:355–62. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70059-7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Emergence of Acinetobacter pittii Harboring New Delhi Metallo-beta-Lactamase Genes in Daejeon, Korea
- Metallo-beta-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas spp. in Korea: High Prevalence of Isolates with VIM-2 Type and Emergence of Isolates with IMP-1 Type
- Epidemiology and Characteristics of Metallo-beta-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Characterization of Class 1 Integrons in Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Dissemination of Carbapenem-Resistance among Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Genes, including the Novel bla(IMP-65) Gene in Thailand