Korean J Gastroenterol.
2020 Dec;76(6):337-339. 10.4166/kjg.2020.149.
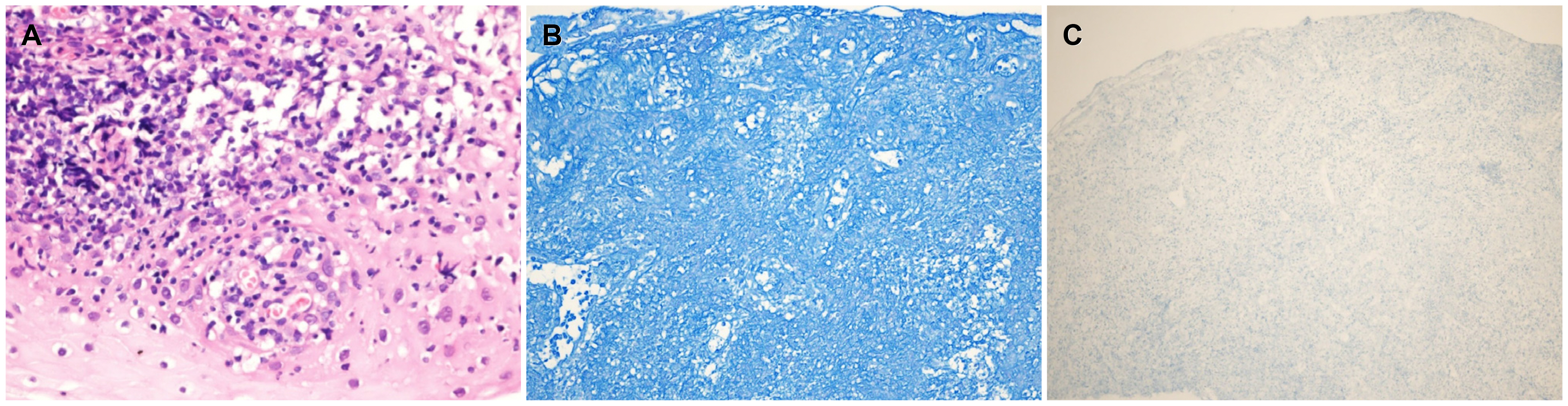
Esophageal Involvement of Behcet’s Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Departments of Pathology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2509712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.149
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davatchi F. 2012; Diagnosis/classification criteria for Behcet's disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012:607921. DOI: 10.1155/2012/607921. PMID: 21961081. PMCID: PMC3180812.
Article2. Yi SW, Cheon JH, Kim JH, et al. 2009; The prevalence and clinical characteristics of esophageal involvement in patients with Behçet's disease: a single center experience in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 24:52–56. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.52. PMID: 19270813. PMCID: PMC2650985.
Article3. Morimoto Y, Tanaka Y, Itoh T, Yamamoto S, Kurihara Y, Nishikawa K. 2005; Esophagobronchial fistula in a patient with Behçet's disease: report of a case. Surg Today. 35:671–676. DOI: 10.1007/s00595-004-2975-2. PMID: 16034549.
Article4. Houman MH, Ben Ghorbel I, Lamloum M, et al. 2002; Esophageal involvement in Behcet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 43:457–460. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2002.43.4.457. PMID: 12205734.5. Hatemi G, Christensen R, Bang D, et al. 2018; 2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 77:808–818. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213225. PMID: 29625968.
Article6. Jung YS, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH, Cheon JH. 2012; Long-term clinical outcomes and factors predictive of relapse after 5-aminosalicylate or sulfasalazine therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 46:e38–e45. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182431d56. PMID: 22298088.
Article7. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. 2012; Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for thiopurine maintenance therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 18:750–757. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.21757. PMID: 21618352.
Article8. Park YE, Cheon JH. 2018; Updated treatment strategies for intestinal Behçet's disease. Korean J Intern Med. 33:1–19. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2017.377. PMID: 29207867. PMCID: PMC5768550.
Article9. Hatemi I, Esatoglu SN, Hatemi G, Erzin Y, Yazici H, Celik AF. 2016; Characteristics, treatment, and long-term outcome of gastrointestinal involvement in Behcet's syndrome: a strobe-compliant observational study from a dedicated multidisciplinary center. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e3348. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003348. PMID: 27100417. PMCID: PMC4845821.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiological Findings of Esophageal and Intestinal Involvement in Behcet's Disease
- The Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Esophageal Involvement in Patients with Behcet's Disease: A Single Center Experience in Korea
- Esophageal Involvement in Behcet's Disease
- Clinical manifestations of Behcet's disease: an analysis of 2147 patients
- A Case of Multiple Esophageal Ulcerations in Behcet's Disease