Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2020 Nov;24(4):526-532. 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.4.526.
Convalescent plasma therapy and remdesivir duo successfully salvaged an early liver transplant recipient with severe COVID-19 pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of HPB Surgery and Liver Transplantation, B. L. Kapoor Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, India
- 2Departments of Critical Care, B. L. Kapoor Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, India
- 3Departments of Transfusion Medicine, B. L. Kapoor Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, India
- 4Departments of Liver Transplant & HPB Anaesthesia, B. L. Kapoor Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, India
- KMID: 2508864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.4.526
Abstract
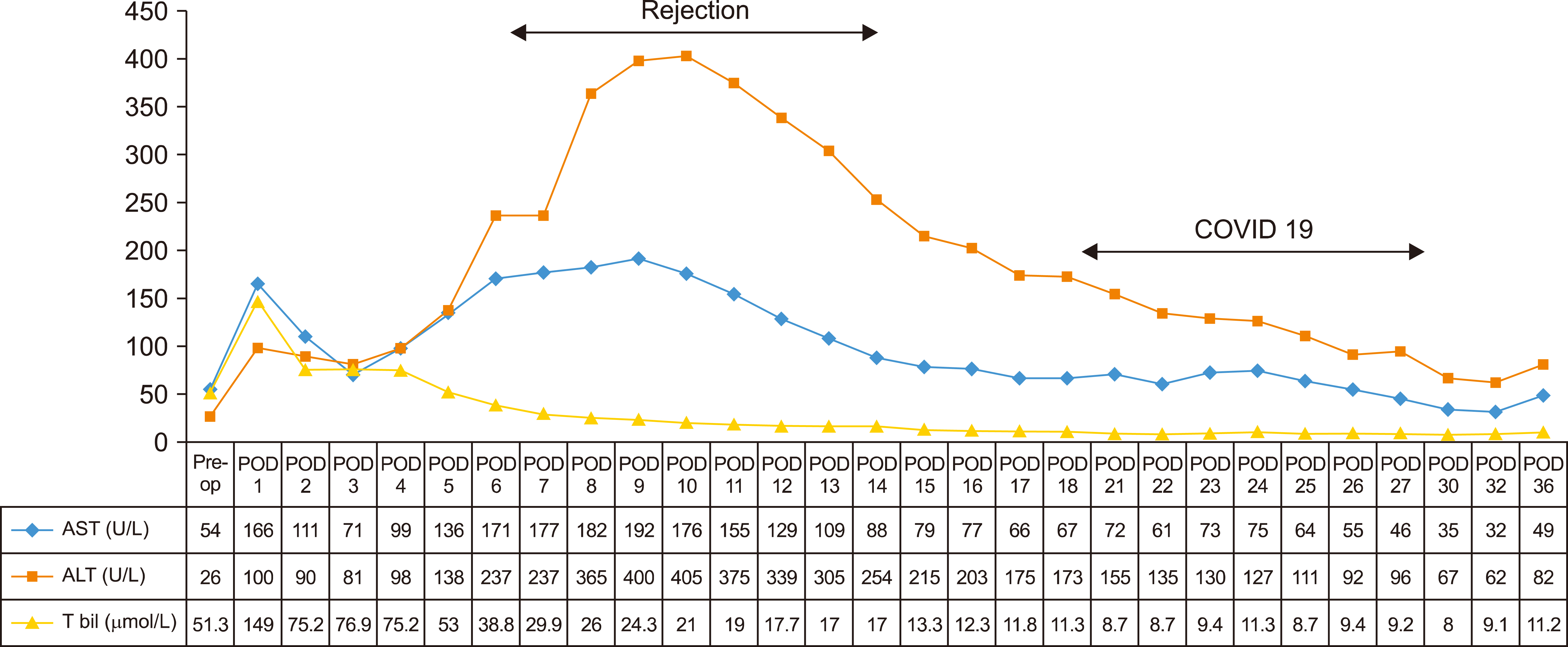
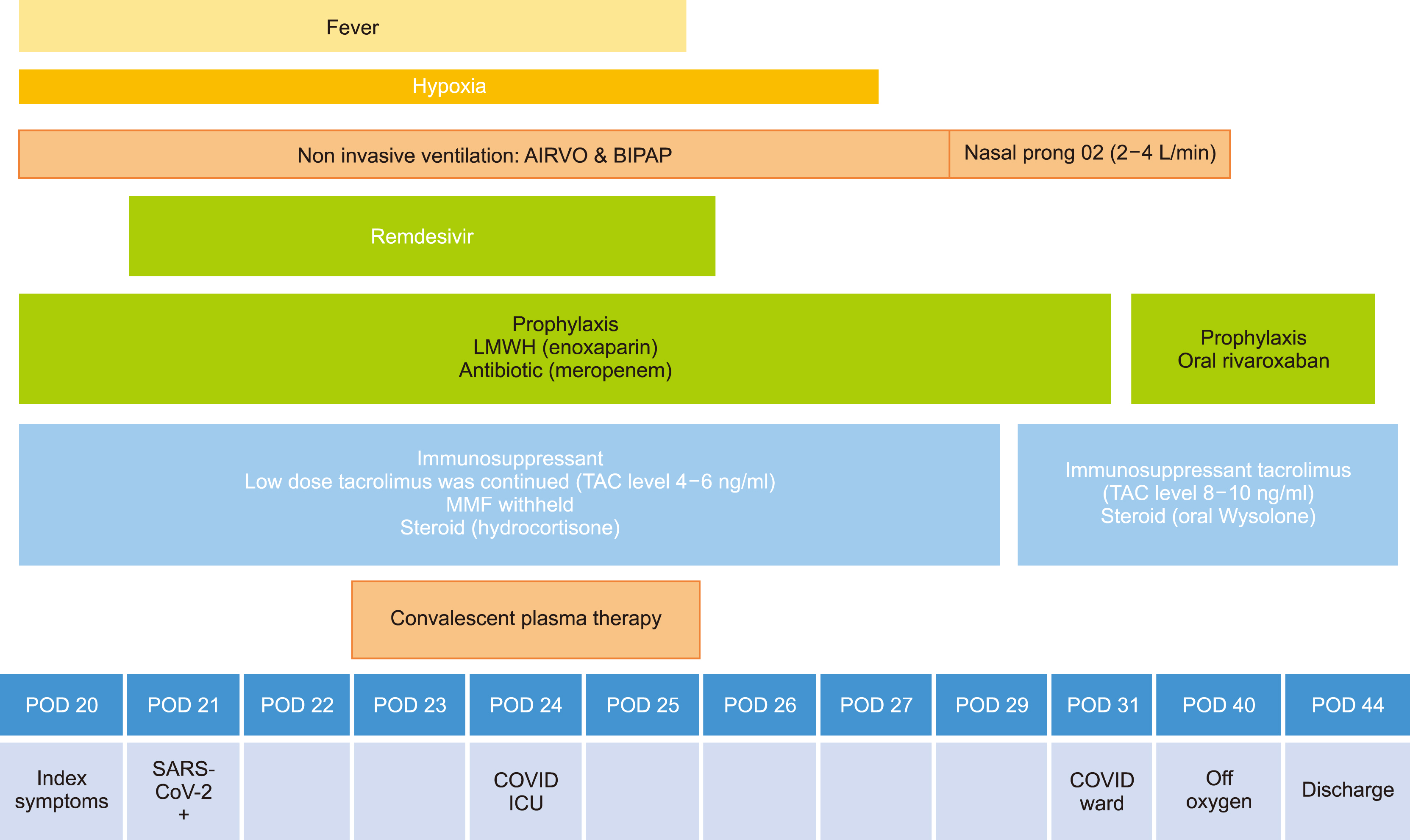
- The impact and clinical spectrum of COVID-19 infection in liver transplant recipients/solid organ transplants are being unveiled during this recent pandemic. The clinical experience of use of current antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are sparse in solid organ transplantation. We present the clinical course of a 49-year-old male recipient who underwent living donor liver transplant for recurrent gastrointestinal bleed and contracted severe COVID-19 pneumonia during the third postoperative week. Herein we report the successful management of severe COVID-19 pneumonia using convalescent plasma therapy and remdesivir. Recipient’s clinical deterioration was halted after three consecutive convalescent plasma transfusions with improvement in hypoxia and inflammatory markers (interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein). The use of convalescent plasma therapy along with remdesivir may be an ideal combination in the management of severe COVID-19 pneumonia in solid organ transplant recipients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization (WHO). 2020. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. WHO;Geneva: Available from: https://covid19.who.int/table. cited 2020 Jul 15.2. Saigal S, Gupta S, Sudhindran S, Goyal N, Rastogi A, Jacob M, et al. 2020; Liver transplantation and COVID-19 (Coronavirus) infection: guidelines of the liver transplant Society of India (LTSI). Hepatol Int. 14:429–431. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-020-10041-1. PMID: 32270388. PMCID: PMC7140588.
Article3. Fix OK, Hameed B, Fontana RJ, Kwok RM, McGuire BM, Mulligan DC, et al. 2020; Clinical best practice advice for hepatology and liver transplant providers during the COVID-19 pandemic: AASLD expert panel consensus statement. Hepatology. 72:287–304. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31281. PMID: 32298473. PMCID: PMC7262242.
Article4. Qin J, Wang H, Qin X, Zhang P, Zhu L, Cai J, et al. 2020; Perioperative presentation of COVID-19 disease in a liver transplant recipient. Hepatology. doi: 10.1002/hep.31257. [in press]. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31257. PMID: 32220017.5. Pereira MR, Mohan S, Cohen DJ, Husain SA, Dube GK, Ratner LE, et al. 2020; COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: initial report from the US epicenter. Am J Transplant. 20:1800–1808. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15941. PMID: 32330343. PMCID: PMC7264777.
Article6. Hammami MB, Garibaldi B, Shah P, Liu G, Jain T, Chen PH, et al. 2020; Clinical course of COVID-19 in a liver transplant recipient on hemodialysis and response to tocilizumab therapy: a case report. Am J Transplant. 20:2254–2259. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15985. PMID: 32359210. PMCID: PMC7267667.
Article7. Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, et al. 2020; Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA. 323:1582–1589. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.4783. PMID: 32219428. PMCID: PMC7101507.
Article8. Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M, Bell JL, et al. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. 2020; Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 - preliminary report. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436. [in press]. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436. PMID: 32678530. PMCID: PMC7383595.
Article9. Tanaka Y, Sato Y, Sasaki T. 2013; Suppression of coronavirus replication by cyclophilin inhibitors. Viruses. 5:1250–1260. DOI: 10.3390/v5051250. PMID: 23698397. PMCID: PMC3712306.
Article10. Bikdeli B, Madhavan MV, Jimenez D, Chuich T, Dreyfus I, Driggin E, et al. 2020; COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow-up: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 75:2950–2973. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.031. PMID: 32311448. PMCID: PMC7164881.11. Grein J, Ohmagari N, Shin D, Diaz G, Asperges E, Castagna A, et al. 2020; Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 382:2327–2336. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007016. PMID: 32275812. PMCID: PMC7169476.12. Genentech Medical. 2019. Serious risk with use of ACTEMRA® (tocilizumab). Genentech;South San Francisco: Available from: https://www.gene.com/download/pdf/. cited 2020 Jul 15.13. Schmidt-Arras D, Rose-John S. 2016; IL-6 pathway in the liver: from physiopathology to therapy. J Hepatol. 64:1403–1415. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.004. PMID: 26867490.
Article14. Liu B, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Shi H, Zeng F, Chen Z. 2020; Successful treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia in a liver transplant recipient. Am J Transplant. 20:1891–1895. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15901. PMID: 32243673.
Article15. Psaltopoulou T, Sergentanis TN, Pappa V, Politou M, Terpos E, Tsiodras S, et al. 2020; The emerging role of convalescent plasma in the treatment of COVID-19. Hemasphere. 4:e409. DOI: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000409. PMID: 32647807. PMCID: PMC7306310.
Article16. Salazar E, Perez KK, Ashraf M, Chen J, Castillo B, Christensen PA, et al. 2020; Treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients with convalescent plasma. Am J Pathol. 190:1680–1690. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.05.014. PMID: 32473109. PMCID: PMC7251400.17. Ye M, Fu D, Ren Y, Wang F, Wang D, Zhang F, et al. 2020; Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25882. [in press]. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25882. PMID: 32293713. PMCID: PMC7262027.
Article18. Jiang J, Miao Y, Zhao Y, Lu X, Zhou P, Zhou X, et al. 2020; Convalescent plasma therapy: helpful treatment of COVID-19 in a kidney transplant recipient presenting with serve clinical manifestation and complex complications. Clin Transplant. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14025. [in press]. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.14025. PMCID: PMC7361058. PMID: 32602952.19. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. 2020; Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19 - final report. N Engl J Med . doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764. [in press]. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764. PMID: 32445440. PMCID: PMC7262788.
Article20. Wölfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Müller MA, et al. 2020; Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature. 581:465–469. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x. PMID: 32235945.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report for Severe COVID-19 in a 9-Year-Old Child Treated with Remdesivir and Dexamethasone
- Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Practical Considerations in Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Delayed exacerbation of COVID-19 pneumonia in vaccinated kidney transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressants: a case series
- COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Korea