Korean J Sports Med.
2020 Sep;38(3):137-142. 10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.3.137.
Incidence and Characteristics of Immediate Substitutions of Injured Players in Korean Professional Football League Matches
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Orthopedic Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 2Departments of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- KMID: 2506070
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.3.137
Abstract
- Purpose
To identify the incidence and characteristics of immediate substitutions of injured players that occurred during Korean professional football league matches.
Methods
This study included injuries that resulted in immediate substitutions of injured players during Korean professional football league matches. The match broadcasting records were used to check the date of the match, home-away matches, the team to which players belong, the position on the field of play, and the time of injury. The match recording videos were used to evaluate the injury mechanism and the injured area.
Results
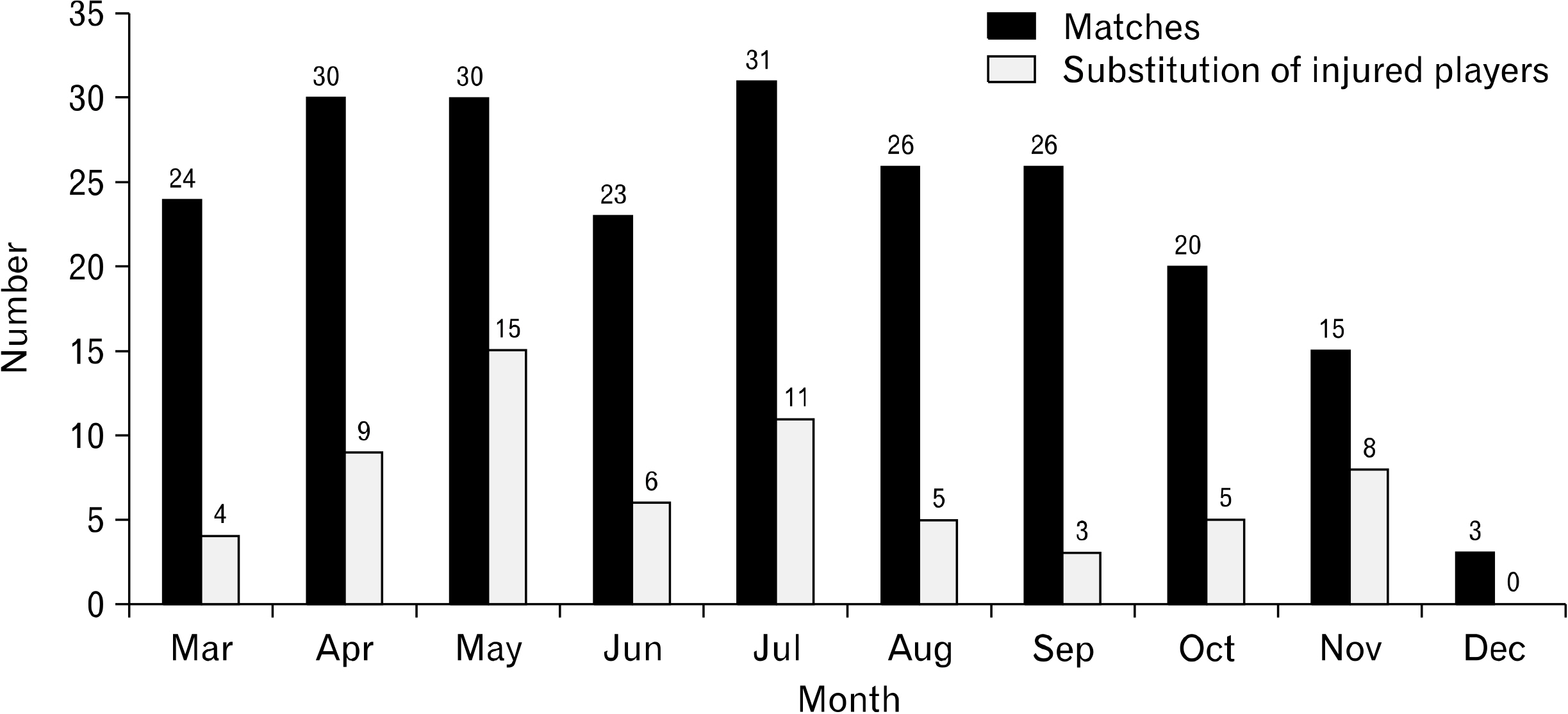
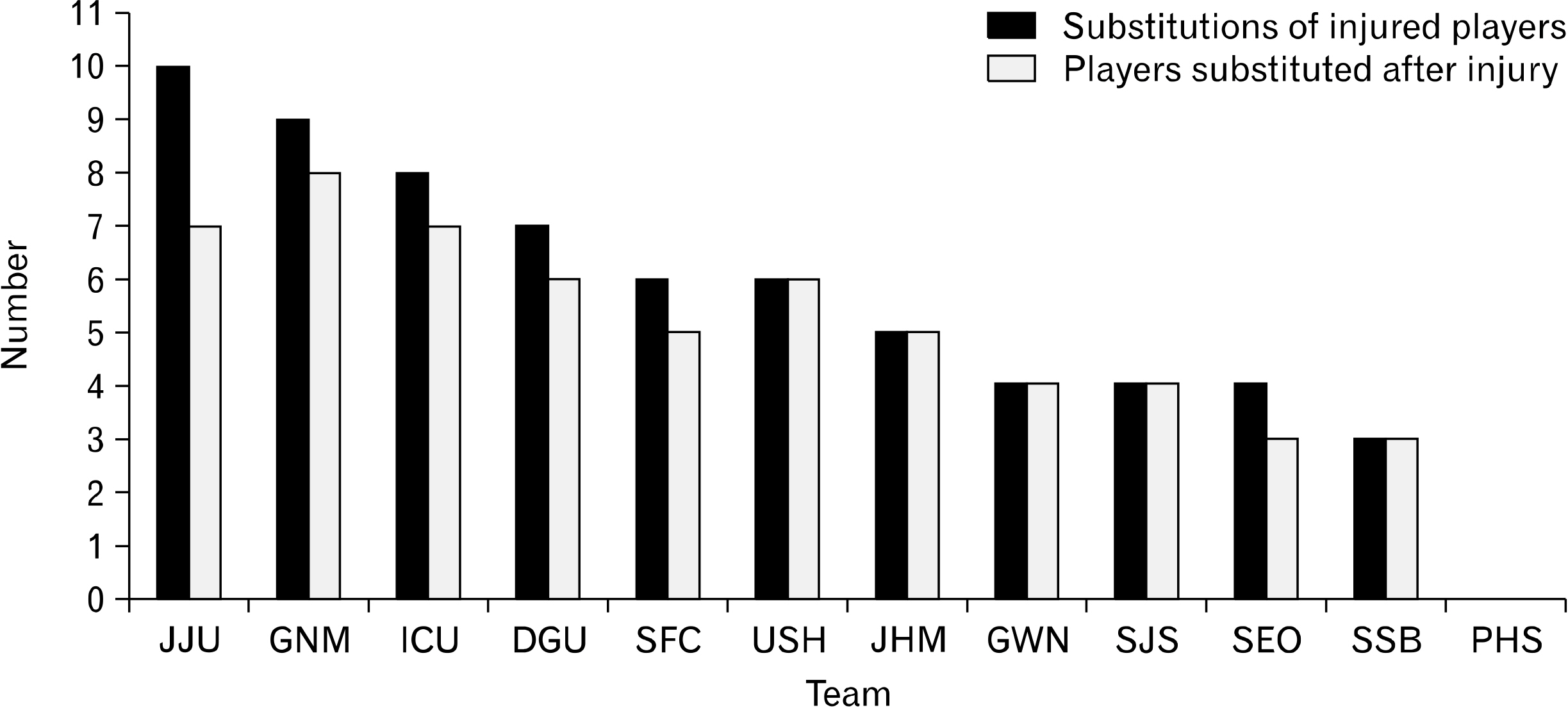
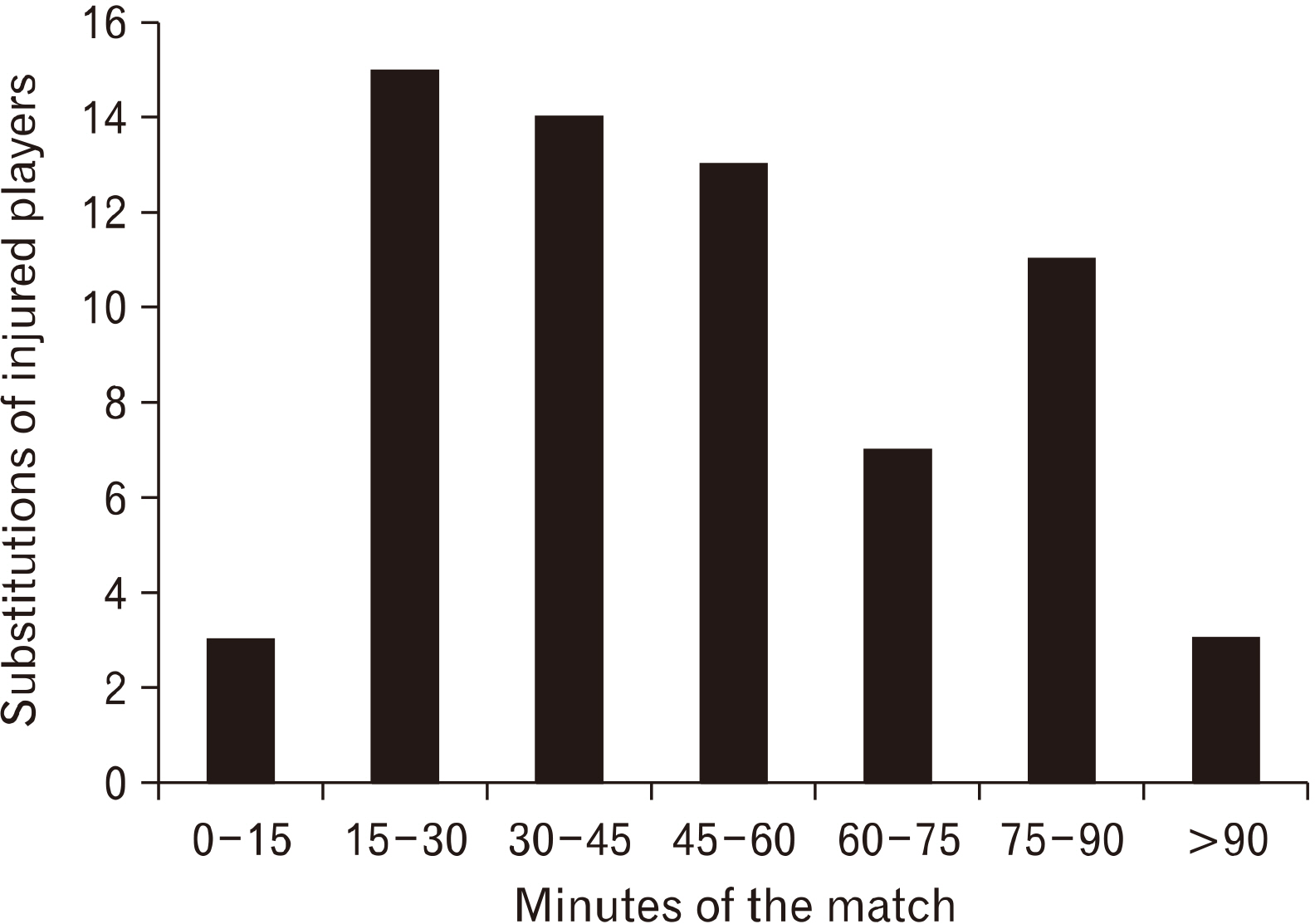
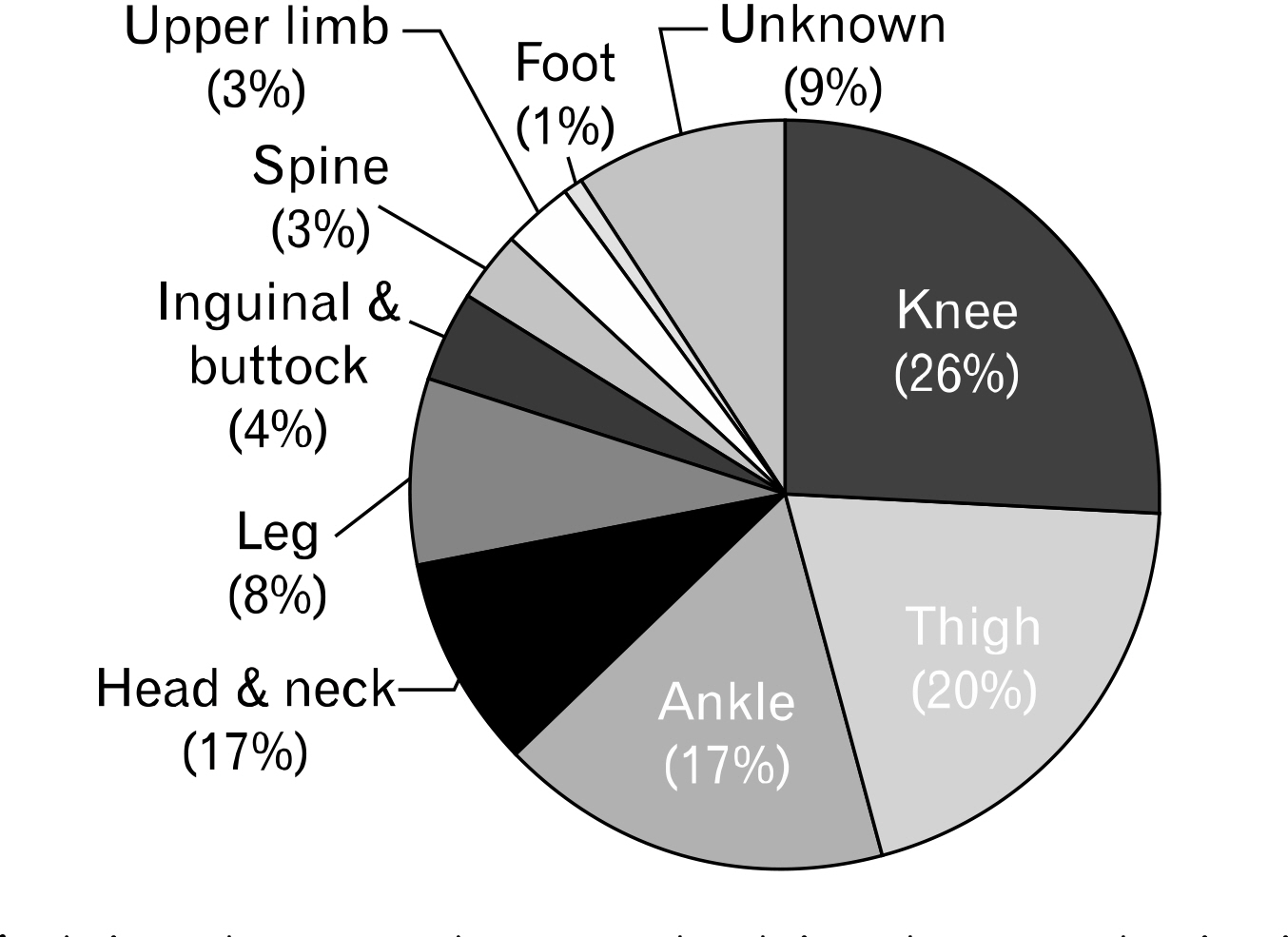
In 228 matches, 66 immediate substitutions of injured players occurred, with an incidence rate of 0.3 per match. Total number of substitutions due to injuries most frequently occurred in May, with 15 substitutions in 30 matches; however, after considering the number of substitutions per match in each month, November was the most severe month with 0.53 substitutions after injuries per match. Most frequently injured players were defenders (36.4%), followed by midfielders, forwards, and goalkeepers. Immediate substitutions of injured players took place 32 times in the first half and 34 times in the second half. 51.5% of all injuries were related to collisions, and injuries to the knee and thigh accounted for 45.5% of all injuries.
Conclusion
There were 66 immediate substitutions of injured players during a single season of the Korean professional football league, with 0.3 substitutions after injuries per match. To prevent and manage serious injuries that can occur during a football match, a thorough analysis of risk factors of injuries that lead to immediate substitution is required.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hwang-Bo K, Joo CH. 2019; Analysis of injury incidences in the Korea national men's soccer teams. J Exerc Rehabil. 15:861–6. DOI: 10.12965/jer.1938624.312. PMID: 31938710. PMCID: PMC6944875.
Article2. Stevenson MR, Hamer P, Finch CF, Elliot B, Kresnow M. 2000; Sport, age, and sex specific incidence of sports injuries in Western Australia. Br J Sports Med. 34:188–94. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.34.3.188. PMID: 10854018. PMCID: PMC1763272.
Article3. Wong P, Hong Y. 2005; Soccer injury in the lower extremities. Br J Sports Med. 39:473–82. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.2004.015511. PMID: 16046325. PMCID: PMC1725275.
Article4. Fuller CW, Ekstrand J, Junge A, Andersen TE, Bahr R, Dvorak J, et al. 2006; Consensus statement on injury definitions and data collection procedures in studies of football (soccer) injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 16:97–106. DOI: 10.1097/00042752-200603000-00003. PMID: 16603877.
Article5. Junge A, Dvorak J, Graf-Baumann T. 2004; Football injuries during the World Cup 2002. Am J Sports Med. 32(1 Suppl):23S–27S. DOI: 10.1177/0363546503261246. PMID: 14754856.
Article6. Morgan BE, Oberlander MA. 2001; An examination of injuries in major league soccer: the inaugural season. Am J Sports Med. 29:426–30. DOI: 10.1177/03635465010290040701. PMID: 11476380.7. Lee KT, Kim JS, Choi BO. 2006; Analysis of seasonal injuries in professional football player. J Korean Orthop Sports Med. 5:135–40.8. Ekstrand J, Hagglund M, Walden M. 2011; Injury incidence and injury patterns in professional football: the UEFA injury study. Br J Sports Med. 45:553–8. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.2009.060582. PMID: 19553225.
Article9. Junge A, Dvorak J. 2015; Football injuries during the 2014 FIFA World Cup. Br J Sports Med. 49:599–602. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2014-094469. PMID: 25878077. PMCID: PMC4413685.
Article10. Chomiak J, Junge A, Peterson L, Dvorak J. 2000; Severe injuries in football players. Influencing factors. Am J Sports Med. 28(5 Suppl):S58–68. DOI: 10.1177/28.suppl_5.s-58. PMID: 11032109.11. Sin DW, Yun YS. 2003; Incidence and pattern of injuries of Asian youth soccer players during match. Korean J Sports Med. 21:145–50.12. Lee KT, Song BY, Young KW, Kim NM, Kim CY, Park SR. 2000; Analysis of the injuries in professional soccer player. Korean J Sports Med. 18:176–80.13. Goga IE, Gongal P. 2003; Severe soccer injuries in amateurs. Br J Sports Med. 37:498–501. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.37.6.498. PMID: 14665587. PMCID: PMC1724720.
Article14. Fuller CW, Junge A, Dvorak J. 2005; A six year prospective study of the incidence and causes of head and neck injuries in international football. Br J Sports Med. 39 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i3–9. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.2005.018937. PMID: 16046353. PMCID: PMC1765312.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Video Analysis of Sports Injuries and Management in Korean Professional Football
- A Study on Dietary Behaviors, Nutrients Intake Status and Hematological Status of Middle School Football Players in Busan
- Acute Infrapatellar Fat Pad Injury after Non-contact, Hyperflexion Injury in a Professional Football Player: A Case Report
- Electrocardiographic Abnormalities following Syncope during Warm-up in a Professional Football Player: A Case Report
- Descriptive Epidemiology of Injuries in Professional Basketball Players during the 2020‒2021 Korean Basketball League Season