Clin Endosc.
2020 May;53(3):374-376. 10.5946/ce.2019.192.
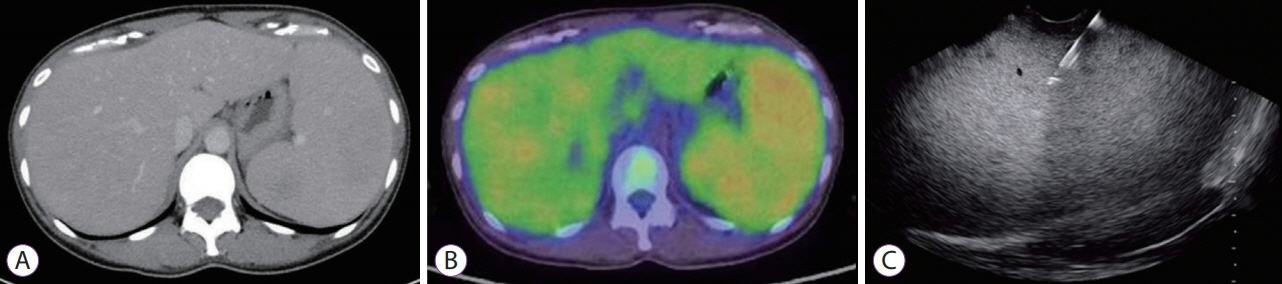
Hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Tama-Hokubu Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan
- 2Division of Hematology, Tama-Hokubu Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan
- 3Division of Pathology, Tama-Hokubu Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan
- KMID: 2502775
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.192
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eloubeidi MA, Varadarajulu S, Eltoum I, Jhala D, Chhieng DC, Jhala NC. Transgastric endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy and flow cytometry of suspected lymphoma of the spleen. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:617–620.
Article2. Iwashita T, Yasuda I, Tsurumi H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy for splenic tumor: a case series. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:179–182.
Article3. Saab S, Challita Y, Holloman D, Hathaway K, Kahaleh M, Nieto J. Case series review of the safety and efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided splenic mass core biopsy. Clin Endosc. 2018; 51:600–601.
Article4. Thai A, Prindiville T. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma and inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2010; 4:511–522.
Article5. Deepak P, Sifuentes H, Sherid M, Stobaugh D, Sadozai Y, Ehrenpreis ED. T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas reported to the FDA AERS with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors: results of the REFURBISH study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:99–105.6. Macon WR, Levy NB, Kurtin PJ, et al. Hepatosplenic alphabeta T-cell lymphomas: a report of 14 cases and comparison with hepatosplenic gammadelta T-cell lymphomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001; 25:285–296.7. Yabe M, Miranda RN, Medeiros LJ. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma: a review of clinicopathologic features, pathogenesis, and prognostic factors. Hum Pathol. 2018; 74:5–16.
Article8. Kudo T, Kawakami H, Hayashi T, et al. High and low negative pressure suction techniques in EUS-guided fine-needle tissue acquisition by using 25-gauge needles: a multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:1030–1037. e1.
Article9. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Chang KJ, et al. Slow pull versus suction in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of pancreatic solid masses. Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59:1578–1585.
Article10. Gerke H, Rizk MK, Vanderheyden AD, Jensen CS. Randomized study comparing endoscopic ultrasound-guided Trucut biopsy and fine needle aspiration with high suction. Cytopathology. 2010; 21:44–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration versus Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subepithelial Tumors
- Procore and Flexible 19 Gauge Needle Can Replace Trucut Biopsy Needle?
- Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Gallbladder Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy
- Role of Repeated Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Inconclusive Initial Cytology Result