Ann Surg Treat Res.
2020 Jun;98(6):307-314. 10.4174/astr.2020.98.6.307.
Comparative study of bilateral axillo-breast approach endoscopic and robotic thyroidectomy: propensity score matching analysis of large multi-institutional data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Surgery, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 4Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 6Yeo-Kyu Youn Thyroid Clinic, St. Peter’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2502116
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2020.98.6.307
Abstract
- Purpose
The aim of this study was to compare the large multi-institutional data of surgical outcomes of bilateral axillo-breast approach (BABA) robotic (RT) and endoscopic thyroidectomy (ET) and to evaluate the merits of robotic thyroidectomy.
Methods
From 2004 to 2015, 1,029 patients underwent BABA ET, and from 2008 to 2015, 2003 patients underwent BABA RT in 3 large volume centers in Korea. Two groups were retrospectively compared in terms of clinicopathologic characteristics, complications, surgical completeness, and long-term outcomes using propensity score matching analysis.
Results
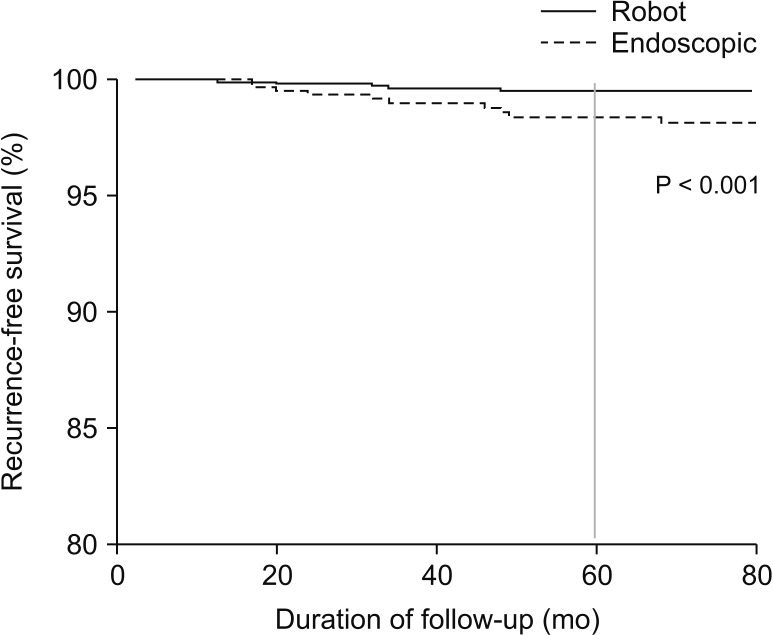
Both groups had similar demographic characteristics including age, sex, tumor size, pathologic stage, and hospital stay after matching. Each group had similar rate of transient hypoparathyroidism, however, ET showed significantly higher rate of permanent hypoparathyroidism (ET 5.2% vs. RT 2.3%, P = 0.05), and transient vocal cord palsy (ET 14.4% vs. RT 9.1%, P = 0.006). Total operation time was longer in the ET group irrespective of surgical extents, including lobectomy (P = 0.016), total thyroidectomy (P = 0.031), and total thyroidectomy with central lymph node dissection (P = 0.019). The rate of patients with off-Tg under 1.0 ng/mL after 1st ablation was significantly higher in RT than ET group (ET 64.6% vs. RT 92.7%, P < 0.001). In long-term follow-up of cancer patients, 1.4% experienced recurrence after ET (10 cases), while 0.3% cases experienced recurrence after RT (5 cases) (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Both ET and RT can be safe and effective methods to treat thyroid diseases. However, the application of robotic system may help to overcome the limitations of the instruments and surgeon’s skills.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gagner M. Endos copic subtot a l parathyroidectomy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Br J Surg. 1996; 83:875. PMID: 8696772.2. Ikeda Y, Takami H, Sasaki Y, Takayama J, Niimi M, Kan S. Comparative study of thyroidectomies. Endoscopic surgery versus conventional open surgery. Surg Endosc. 2002; 16:1741–1745. PMID: 12140635.3. Shimazu K, Shiba E, Tamaki Y, Takiguchi S, Taniguchi E, Ohashi S, et al. Endoscopic thyroid surgery through the axillo-bilateral-breast approach. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2003; 13:196–201. PMID: 12819505.4. Lombardi CP, Raffaelli M, Princi P, De Crea C, Bellantone R. Video-assisted thyroidectomy: report of a 7-year experience in Rome. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2006; 391:174–177. PMID: 16528568.5. Choe JH, Kim SW, Chung KW, Park KS, Han W, Noh DY, et al. Endoscopic thyroidectomy using a new bilateral axillo-breast approach. World J Surg. 2007; 31:601–606. PMID: 17308853.6. Lee KE, Kim E, Koo DH, Choi JY, Kim KH, Youn YK. Robotic thyroidectomy by bilateral axillo-breast approach: review of 1,026 cases and surgical completeness. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:2955–2962. PMID: 23436099.7. Kim WW, Kim JS, Hur SM, Kim SH, Lee SK, Choi JH, et al. Is robotic surgery super ior to endoscopic and open surgeries in thyroid cancer? World J Surg. 2011; 35:779–784. PMID: 21253726.8. Lee KE, Rao J, Youn YK. Endoscopic thyroidectomy with the da Vinci robot system using the bilateral axillary breast approach (BABA) technique: our initial experience. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2009; 19:e71–e75. PMID: 19542833.9. Chung YS, Choe JH, Kang KH, Kim SW, Chung KW, Park KS, et al. Endoscopic thyroidectomy for thyroid malignancies: comparison with conventional open thyroidectomy. World J Surg. 2007; 31:2302–2306. PMID: 17566819.10. Lee KE, Koo DH, Im HJ, Park SK, Choi JY, Paeng JC, et al. Surgical completeness of bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic thyroidectomy: comparison with conventional open thyroidectomy after propensity score matching. Surgery. 2011; 150:1266–1274. PMID: 22136850.11. He QQ, Zhu J, Zhuang DY, Fan ZY, Zheng LM, Zhou P, et al. Comparative study between robotic total thyroidectomy with central lymph node dissection via bilateral axillo-breast approach and conventional open procedure for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016; 129:2160–2166. PMID: 27625085.12. Choi JY, Lee KE, Chung KW, Kim SW, Choe JH, Koo DH, et al. Endoscopic thyroidectomy via bilateral axillo-breast approach (BABA): review of 512 cases in a single institute. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:948–955. PMID: 22052422.13. Kwon H, Koo do H, Choi JY, Kim E, Lee KE, Youn YK. Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic thyroidectomy for Graves' disease: an initial experience in a single institute. World J Surg. 2013; 37:1576–1581. PMID: 23558759.14. Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Byrd DR, Brookland RK, Washington MK, editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual (8th edition). Springer International Publishing: American Joint Commission on Cancer;2017.15. Mehra S, Tuttle RM, Milas M, Orloff L, Bergman D, Bernet V, et al. Database and registry research in thyroid cancer: striving for a new and improved national thyroid cancer database. Thyroid. 2015; 25:157–168. PMID: 25517683.16. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid. 2016; 26:1–133. PMID: 26462967.17. Miccoli P, Berti P, Bendinelli C, Conte M, Fasolini F, Martino E. Minimally invasive video-assisted surgery of the thyroid: a preliminary report. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2000; 385:261–264. PMID: 10958509.18. Shimizu K, Akira S, Jasmi AY, Kitamura Y, Kitagawa W, Akasu H, et al. Video-assisted neck surgery: endoscopic resection of thyroid tumors with a very minimal neck wound. J Am Coll Surg. 1999; 188:697–703. PMID: 10359365.19. Ohgami M, Ishii S, Arisawa Y, Ohmori T, Noga K, Furukawa T, et al. Scarless endoscopic thyroidectomy: breast approach for better cosmesis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2000; 10:1–4. PMID: 10872517.20. Yoon JH, Park CH, Chung WY. Gasless endoscopic thyroidectomy via an axillary approach: experience of 30 cases. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2006; 16:226–231. PMID: 16921301.21. Jackson NR, Yao L, Tufano RP, Kandil EH. Safety of robotic thyroidectomy approaches: meta-analysis and systematic review. Head Neck. 2014; 36:137–143. PMID: 23471784.22. Koo DH, Kim DM, Choi JY, Lee KE, Cho SH, Youn YK. In-depth survey of scarring and distress in patients undergoing bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic thyroidectomy or conventional open thyroidectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2015; 25:436–439. PMID: 26271022.23. Sherman SI. Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet. 2003; 361:501–511. PMID: 12583960.24. Kim SJ, Lee KE, Myong JP, Kwon MR, Youn YK. Recovery of sensation in the anterior chest area after bilateral axillo-breast approach endoscopic/robotic thyroidectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2011; 21:366–371. PMID: 22002276.25. Kim SJ, Lee KE, Myong JP, Koo DH, Lee J, Youn YK. Prospective study of sensation in anterior chest areas before and after a bilateral axillo-breast approach for endoscopic/robotic thyroid surgery. World J Surg. 2013; 37:1147–1153. PMID: 23397168.26. Kandil E, Hammad AY, Walvekar RR, Hu T, Masoodi H, Mohamed SE, et al. Robotic thyroidectomy versus nonrobotic approaches: a meta-analysis examining surgical outcomes. Surg Innov. 2016; 23:317–325. PMID: 26525401.27. Kim HY, Choi YJ, Yu HN, Yoon SZ. Optimal carbon dioxide insufflation pressure during robot-assisted thyroidectomy in patients with various benign and malignant thyroid diseases. World J Surg Oncol. 2012; 10:202. PMID: 23017080.28. Kim JA, Kim JS, Chang MS, Yoo YK, Kim DK. Influence of carbon dioxide insufflation of the neck on intraocular pressure during robot-assisted endoscopic thyroidectomy: a comparison with open thyroidectomy. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:1587–1593. PMID: 23073689.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic total thyroidectomy without isthmectomy: a case report
- Endoscopic Thyroidectomy via an Axillo-bilateral Breast Approach: 5 Years of Experience
- Robotic and Endoscopic Thyroid Surgery: Evolution and Advances
- Preliminary Study on Safety of Robotic or Endoscopic Thyroidectomy via Bilateral Axillo-breast Approach (BABA) without Drainage Procedure: Multicenter Trial
- Nationwide Multicenter Survey for Current Status of Endoscopic Thyroidectomy in Korea