Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2020 Mar;25(1):31-37. 10.6065/apem.2020.25.1.31.
Effect of -202 A/C IGFBP-3 polymorphisms on growth responses in children with idiopathic short stature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2501034
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2020.25.1.31
Abstract
- Purpose
This study evaluated the -202 A/C insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) promoter polymorphism as a predictor of serum IGFBP-3 concentration and growth velocity after recombinant growth hormone (rhGH) therapy in patients with idiopathic short stature (ISS).
Methods
Genotyping and serial measurement of clinical parameters were performed in 69 children with a confirmed diagnosis of ISS. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis was performed to determine the genotype at the -202 IGFBP-3 locus. Serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and IGFBP-3 levels were measured at baseline and after 1 year of rhGH treatment, as were height standard deviation score and growth velocity.
Results
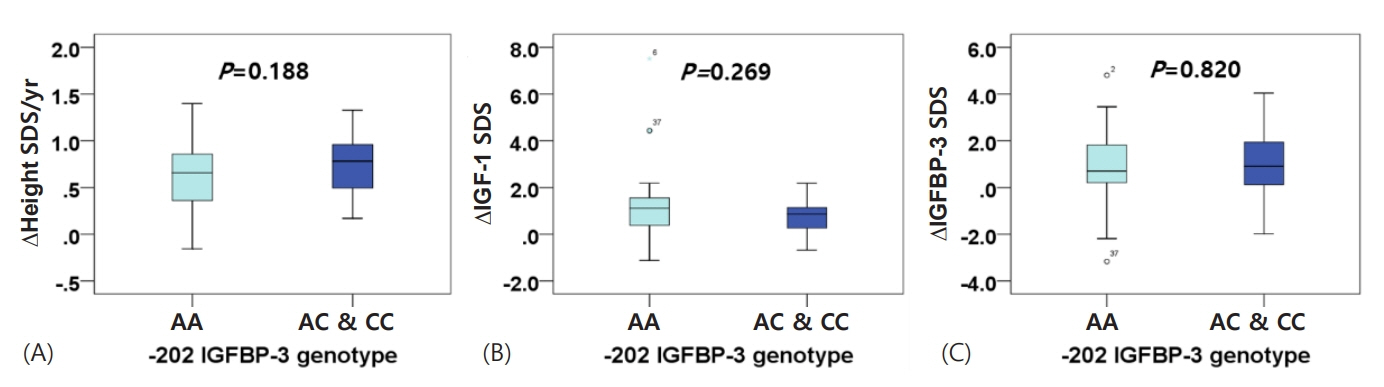
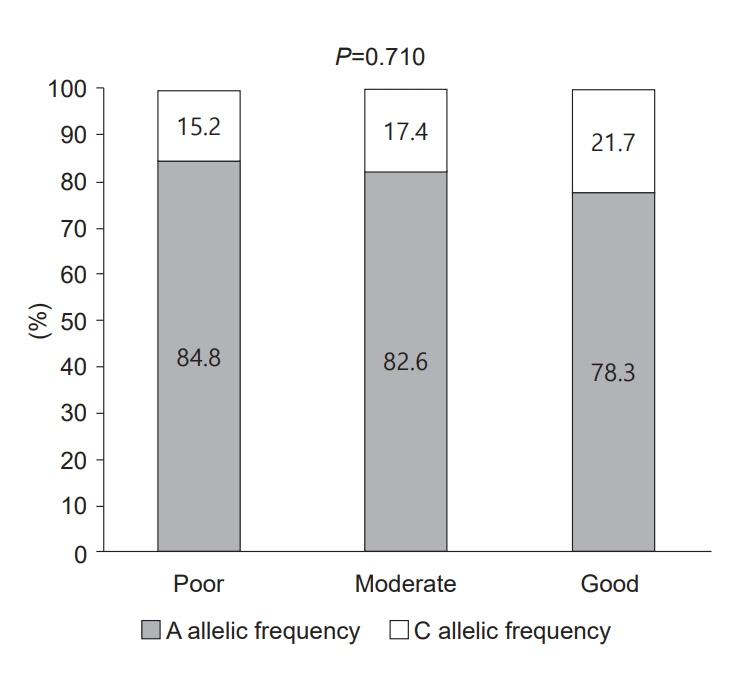
The -202 A/C IGFBP-3 genotype comprised 69.6% AA, 24.6% AC, and 5.8% CC. One year of treatment did not produce a meaningful difference in IGF-1 or IGFBP-3 levels between children in the AA group and those with at least one copy of the C allele (AC/CC group). Comparing the 2 groups after one year also revealed no significant difference in growth velocity (ΔHeight: 9.061±1.612 cm/yr in the AA group, 9.421±1.864 in the AC/CC group, P=0.419).
Conclusion
rhGH treatment was effective and there were no significant differences in IGF-1, IGFBP-3, or growth velocity according to genotype. Thus, -202 IGFBP-3 genotype may not be a major factor affecting individual growth responses in Korean children with ISS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wit JM, Clayton PE, Rogol AD, Savage MO, Saenger PH, Cohen P. Idiopathic short stature: definition, epidemiology, and diagnostic evaluation. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008; 18:89–110.
Article2. Kim HS, Yang SW, Yoo HW, Suh BK, Ko CW, Chung WY, et al. Efficacy of short-term growth hormone treatment in prepubertal children with idiopathic short stature. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:53–60.
Article3. Ranke MB. Towards a consensus on the definition of idiopathic short stature. Horm Res. 1996; 45 Suppl 2:64–6.
Article4. Ayyar VS. History of growth hormone therapy. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 15 Suppl 3:S162–5.
Article5. Kim J, Suh BK, Ko CW, Lee KH, Shin CH, Hwang JS, et al. Recombinant growth hormone therapy for prepubertal children with idiopathic short stature in Korea: a phase III randomized trial. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018; 41:475–83.
Article6. Grimberg A, DiVall SA, Polychronakos C, Allen DB, Cohen LE, Quintos JB, et al. Guidelines for growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-i treatment in children and adolescents: growth hormone deficiency, idiopathic short stature, and primary insulin-like growth factor-I deficiency. Horm Res Paediatr. 2016; 86:361–97.
Article7. Deal C, Ma J, Wilkin F, Paquette J, Rozen F, Ge B, Hudson T, et al. Novel promoter polymorphism in insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3: correlation with serum levels and interaction with known regulators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:1274–80.
Article8. Al-Zahrani A, Sandhu MS, Luben RN, Thompson D, Baynes C, Pooley KA, et al. IGF1 and IGFBP3 tagging polymorphisms are associated with circulating levels of IGF1, IGFBP3 and risk of breast cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2006; 15:1–10.
Article9. Cheng I, DeLellis Henderson K, Haiman CA, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE, Freedman ML, et al. Genetic determinants of circulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein (BP)-1, and IGFBP-3 levels in a multiethnic population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:3660–6.
Article10. Jernström H, Deal C, Wilkin F, Chu W, Tao Y, Majeed N, et al. Genetic and nongenetic factors associated with variation of plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in healthy premenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001; 10:377–84.11. Morimoto LM, Newcomb PA, White E, Bigler J, Potter JD. Variation in plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3: genetic factors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005; 14:1394–401.
Article12. Ren Z, Cai Q, Shu XO, Cai H, Li C, Yu H, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in the IGFBP3 gene: association with breast cancer risk and blood IGFBP-3 protein levels among Chinese women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004; 13:1290–5.13. Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ, Blouin MJ, Pollak MN. Polymorphic variation at the -202 locus in IGFBP3: Influence on serum levels of insulin-like growth factors, interaction with plasma retinol and vitamin D and breast cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2003; 107:60–4.14. Slattery ML, Baumgartner KB, Byers T, Guiliano A, Sweeney C, Herrick J, et al. Genetic, anthropometric, and lifestyle factors associated with IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women. Cancer Causes Control. 2005; 16:1147–57.
Article15. Costalonga EF, Antonini SR, Guerra-Junior G, Mendonca BB, Arnhold IJ, Jorge AA. The -202 A allele of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP3) promoter polymorphism is associated with higher IGFBP-3 serum levels and better growth response to growth hormone treatment in patients with severe growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:588–95.16. Braz AF, Costalonga EF, Montenegro LR, Trarbach EB, Antonini SR, Malaquias AC, et al. The interactive effect of GHR-exon 3 and -202 A/C IGFBP3 polymorphisms on rhGH responsiveness and treatment outcomes in patients with Turner syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:E671–7.17. Hyun SE, Lee BC, Suh BK, Chung SC, Ko CW, Kim HS, et al. Reference values for serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in Korean children and adolescents. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:16–21.
Article18. Schildkraut JM, Demark-Wahnefried W, Wenham RM, Grubber J, Jeffreys AS, Grambow SC, et al. IGF1 (CA)19 repeat and IGFBP3 -202 A/C genotypes and the risk of prostate cancer in Black and White men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005; 14:403–8.19. Yi MJ, Park TY, Hwang IT, Yang S. Influence of The -202 A/C insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 promoter polymorphism on individual variation in height in Korean girls. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 22:36–42.
Article20. Miletta MC, Scheidegger UA, Giordano M, Bozzola M, Pagani S, Bona G, et al. Association of the (CA)n repeat polymorphism of insulin-like growth factor-I and -202 A/C IGF-binding protein-3 promoter polymorphism with adult height in patients with severe growth hormone deficiency. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2012; 76:683–90.21. Hendriks AE, Brown MR, Boot AM, Oostra BA, de Jong FH, Drop SL, et al. Common polymorphisms in the GH/IGF-1 axis contribute to growth in extremely tall subjects. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2011; 21:318–24.
Article22. Wang L, Habuchi T, Tsuchiya N, Mitsumori K, Ohyama C, Sato K, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 gene -202 A/C polymorphism is correlated with advanced disease status in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:4407–11.23. Xiang H, Liu L, Chu GD, Wei S, Liu JP, Xu YH, et al. Association between two functional polymorphisms of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese population. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2009; 72:706–11.
Article24. van der Kaay DC, Hendriks AE, Ester WA, Leunissen RW, Willemsen RH, de Kort SW, et al. Genetic and epigenetic variability in the gene for IGFBP-3 (IGFBP3): correlation with serum IGFBP-3 levels and growth in short children born small for gestational age. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009; 19:198–205.
Article25. Ranke MB, Lindberg A, Chatelain P, Wilton P, Cutfield W, Albertsson-Wikland K, et al. Derivation and validation of a mathematical model for predicting the response to exogenous recombinant human growth hormone (GH) in prepubertal children with idiopathic GH deficiency. KIGS International Board. Kabi Pharmacia International Growth Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999; 84:1174–83.26. de Ridder MA, Stijnen T, Hokken-Koelega AC. Prediction of adult height in growth-hormone-treated children with growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:925–31.
Article27. Jorge AA, Marchisotti FG, Montenegro LR, Carvalho LR, Mendonca BB, Arnhold IJ. Growth hormone (GH) pharmacogenetics: influence of GH receptor exon 3 retention or deletion on first-year growth response and final height in patients with severe GH deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:1076–80.
Article28. Goddard AD, Covello R, Luoh SM, Clackson T, Attie KM, Gesundheit N, et al. Mutations of the growth hormone receptor in children with idiopathic short stature. The Growth Hormone Insensitivity Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1093–8.
Article29. Meyer S, Ipek M, Keth A, Minnemann T, von Mach MA, Weise A, et al. Short stature and decreased insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)/growth hormone (GH)-ratio in an adult GH-deficient patient pointing to additional partial GH insensitivity due to a R179C mutation of the growth hormone receptor. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007; 17:307–14.
Article30. Ferry RJ Jr, Cerri RW, Cohen P. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: new proteins, new functions. Horm Res. 1999; 51:53–67.
Article31. Hopwood NJ, Hintz RL, Gertner JM, Attie KM, Johanson AJ, Baptista J, et al. Growth response of children with nongrowth-hormone deficiency and marked short stature during three years of growth hormone therapy. J Pediatr. 1993; 123:215–22.
Article32. Wit JM, Reiter EO, Ross JL, Saenger PH, Savage MO, Rogol AD, et al. Idiopathic short stature: management and growth hormone treatment. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008; 18:111–35.
Article33. Wudy SA, Hagemann S, Dempfle A, Ringler G, Blum WF, Berthold LD, et al. Children with idiopathic short stature are poor eaters and have decreased body mass index. Pediatrics. 2005; 116:e52. –7.
Article34. Roman R, Iniguez G, Lammoglia JJ, Avila A, Salazar T, Cassorla F. The IGF-I response to growth hormone is related to body mass index in short children with normal weight. Horm Res. 2009; 72:10–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Children with Idiopathic Short Stature
- Effects of Growth Hormone Therapy in Children with Idiopathic Short Stature
- Overnight Growth Hormone Secretions and Sleep Patterns in Idiopathic Short Stature Children
- Effects of Supraphysiological Growth Hormone on Body Composition in Children with Idiopathic Short Stature
- Usefulness of Serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 Levels in Children with Short Stature