Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2020 May;24(2):234-238. 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.2.234.
Seeking the unseen: Localization and surgery for an occult sporadic insulinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of HPB Surgery, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo
- 2The University Surgical Unit, The National Hospital of Sri Lanka
- 3Departments of Endocrinology and Diabetes, The National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka
- 4Departments of Interventional Radiology, The National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka
- KMID: 2500812
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.2.234
Abstract
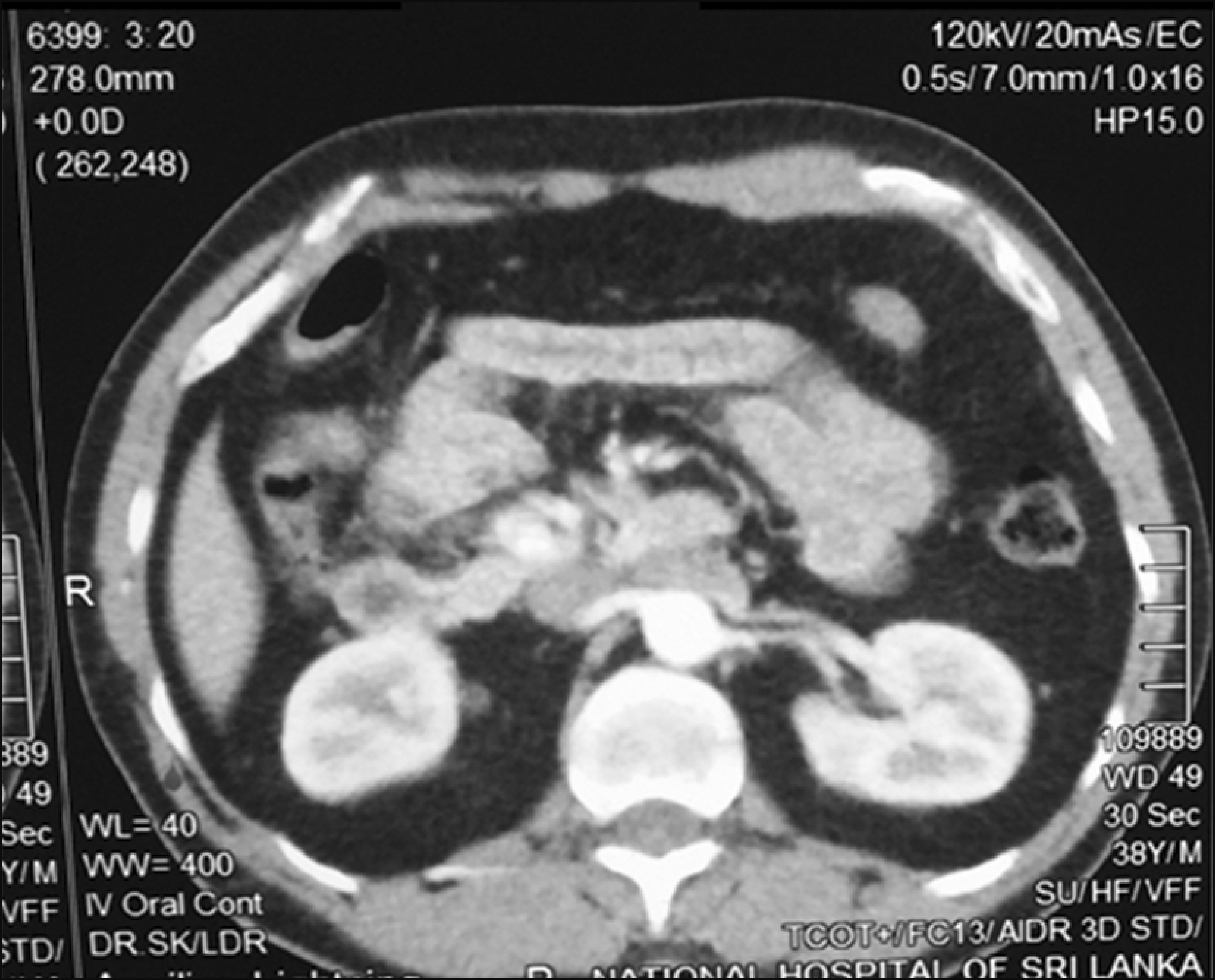
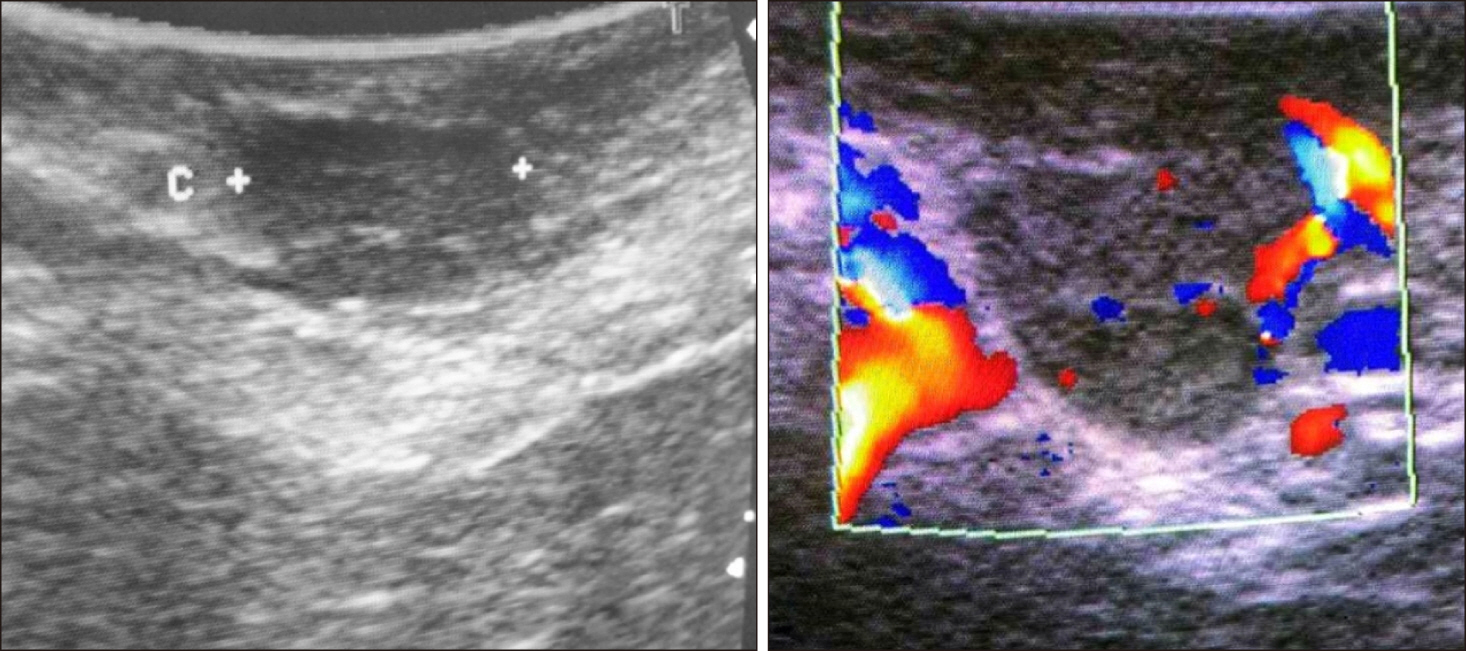
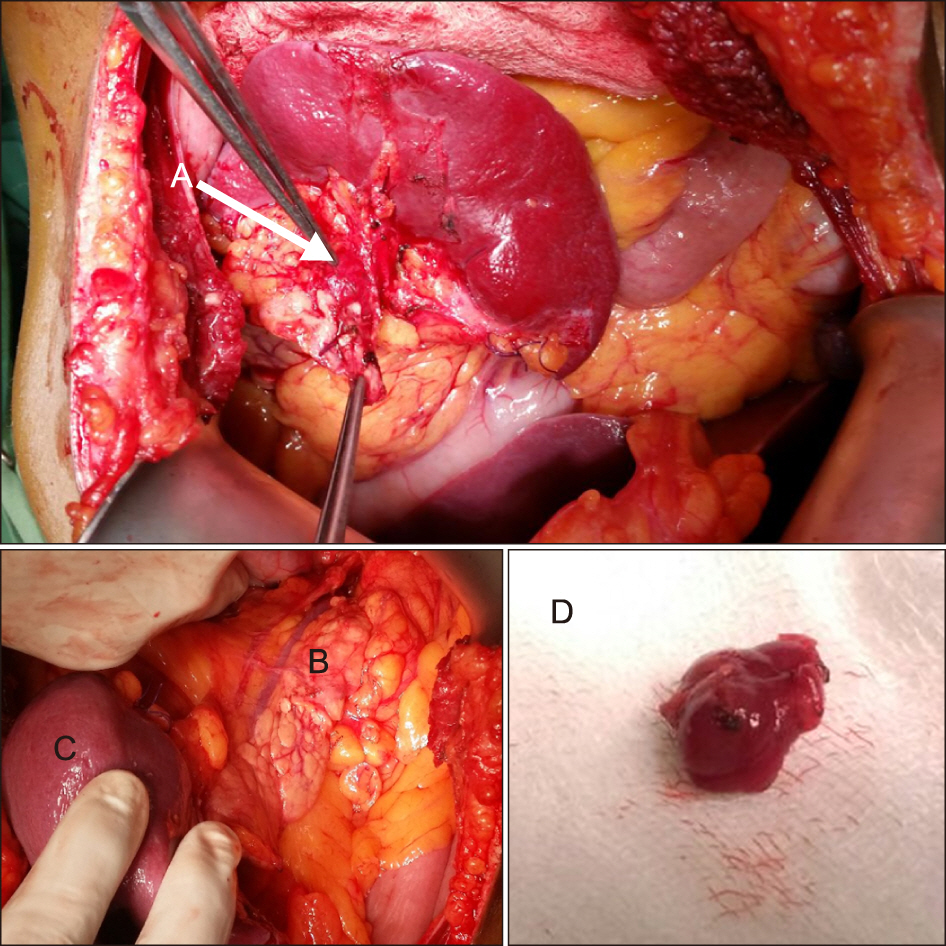
- Insulinomas are rare pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours and the commonest cause for endogenous hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycemia. Small tumours are not easily detected by conventional cross-sectional imaging making localization prior to surgical removal a challenge. Selective arterial calcium stimulation is an invaluable adjunct to localization in such circumstances. This is further supplemented by intraoperative ultrasonography. A 39-year-old male was referred with features of Whipple’s triad of 10 months duration. Clinical and biochemical evaluation including C-peptide and serum insulin levels during supervised hypoglycemia concluded endogenous hyperinsulinaemia as the underlying aetiology. Contrast CT and MRI of the abdomen failed to localize the tumour. Selective arterial calcium stimulation localized the lesion in distal pancreas. During the surgery, tumour was further localized to the tail of the pancreas using intraoperative ultrasonography and enucleated. Histology confirmed an insulinoma and patient made an unremarkable recovery and was well more than a year after the surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bilimoria KY, Talamonti MS, Tomlinson JS, Stewart AK, Winchester DP, Ko CY, et al. 2008; Prognostic score predicting survival after resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: analysis of 3851 patients. Ann Surg. 247:490–500. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815b9cae. PMID: 18376195.2. Abboud B, Boujaoude J. 2008; Occult sporadic insulinoma: localization and surgical strategy. World J Gastroenterol. 14:657–665. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.657. PMID: 18205253. PMCID: PMC2683990.
Article3. Barts Endocrinology. 2009. Barts endocrine e-protocols GI and pancreas [Internet]. Barts Endocrinology;London: Available from: http://bartsendocrinology.co.uk/resources/GI+AND+PANCREAS+and+NETS+PROTOCOLS+$5B final$5D.pdf. 2012 Oct 20.4. Sotoudehmanesh R, Hedayat A, Shirazian N, Shahraeeni S, Ainechi S, Zeinali F, et al. 2007; Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in the localization of insulinoma. Endocrine. 31:238–241. DOI: 10.1007/s12020-007-0045-4. PMID: 17906369.
Article5. McAuley G, Delaney H, Colville J, Lyburn I, Worsley D, Govender P, et al. 2005; Multimodality preoperative imaging of pancreatic insulinomas. Clin Radiol. 60:1039–1050. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2005.06.005. PMID: 16179163.
Article6. Ardengh JC, Rosenbaum P, Ganc AJ, Goldenberg A, Lobo EJ, Malheiros CA, et al. 2000; Role of EUS in the preoperative localization of insulinomas compared with spiral CT. Gastrointest Endosc. 51:552–555. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(00)70288-4. PMID: 10805840.
Article7. Schumacher B, Lübke HJ, Frieling T, Strohmeyer G, Starke AA. 1996; Prospective study on the detection of insulinomas by endoscopic ultrasonography. Endoscopy. 28:273–276. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1005452. PMID: 8781789.
Article8. Doppman JL, Miller DL, Chang R, Shawker TH, Gorden P, Norton JA. 1991; Insulinomas: localization with selective intraarterial injection of calcium. Radiology. 178:237–241. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.178.1.1984311. PMID: 1984311.
Article9. Brändle M, Pfammatter T, Spinas GA, Lehmann R, Schmid C. 2001; Assessment of selective arterial calcium stimulation and hepatic venous sampling to localize insulin-secreting tumours. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 55:357–362. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2001.01335.x. PMID: 11589679.
Article10. Guettier JM, Kam A, Chang R, Skarulis MC, Cochran C, Alexander HR, et al. 2009; Localization of insulinomas to regions of the pancreas by intraarterial calcium stimulation: the NIH experience. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:1074–1080. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2008-1986. PMID: 19190102. PMCID: PMC2682461.
Article11. Thompson SM, Vella A, Service FJ, Grant CS, Thompson GB, Andrews JC. 2015; Impact of variant pancreatic arterial anatomy and overlap in regional perfusion on the interpretation of selective arterial calcium stimulation with hepatic venous sampling for preoperative localization of occult insulinoma. Surgery. 158:162–172. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.03.004. PMID: 25873534. PMCID: PMC4461470.12. Placzkowski KA, Vella A, Thompson GB, Grant CS, Reading CC, Charboneau JW, et al. 2009; Secular trends in the presentation and management of functioning insulinoma at the Mayo Clinic, 1987-2007. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:1069–1073. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2008-2031. PMID: 19141587.
Article13. Doppman JL, Miller DL, Chang R, Gorden P, Eastman RC, Norton JA. 1993; Intraarterial calcium stimulation test for detection of insulinomas. World J Surg. 17:439–443. DOI: 10.1007/BF01655101. PMID: 8362527.
Article14. Doppman JL, Chang R, Fraker DL, Norton JA, Alexander HR, Miller DL, et al. 1995; Localization of insulinomas to regions of the pancreas by intra-arterial stimulation with calcium. Ann Intern Med. 123:269–273. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-123-4-199508150-00004. PMID: 7611592.
Article15. Mehrabi A, Fischer L, Hafezi M, Dirlewanger A, Grenacher L, Diener MK, et al. 2014; A systematic review of localization, surgical treatment options, and outcome of insulinoma. Pancreas. 43:675–686. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000110. PMID: 24921202.
Article16. Shin JJ, Gorden P, Libutti SK. 2010; Insulinoma: pathophysiology, localization and management. Future Oncol. 6:229–237. DOI: 10.2217/fon.09.165. PMID: 20146582. PMCID: PMC3498768.
Article17. Service FJ, McMahon MM, O'Brien PC, Ballard DJ. 1991; Functioning insulinoma--incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival of patients: a 60-year study. Mayo Clin Proc. 66:711–719. DOI: 10.1016/S0025-6196(12)62083-7. PMID: 1677058.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Alcohol Ablation of Sporadic Insulinoma Using Three-Dimensional Targeting (with Video)
- Localization of an Insulinoma by Endoscopic Ultrasonography
- A Case of Insulinoma Localized by Percutaneous Tracshepatic Portal Catheterization with Insulin Hormone Assay
- Experiences of Endoscopic Ultrasonography in the 5 cases with Pancreatic Insulinoma
- Radioguided Surgery in Insulinoma Using 68Ga Labeled Exendin-4: a Case Report