Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2020 May;13(2):173-178. 10.21053/ceo.2019.01340.
Surgical Outcomes of Subtotal Parathyroidectomy for Renal Hyperparathyroidism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Departments of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Departments of Radiology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2500290
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2019.01340
Abstract
Objectives
. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of subtotal parathyroidectomy for patients with renal hyperparathyroidism.
Methods
. We studied 25 patients with renal hyperparathyroidism who underwent subtotal parathyroidectomy from October 2002 to October 2017. We analyzed serum intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), calcium, and inorganic phosphorus levels before and at multiple time points following surgery, and evaluated the surgical outcomes and complications.
Results
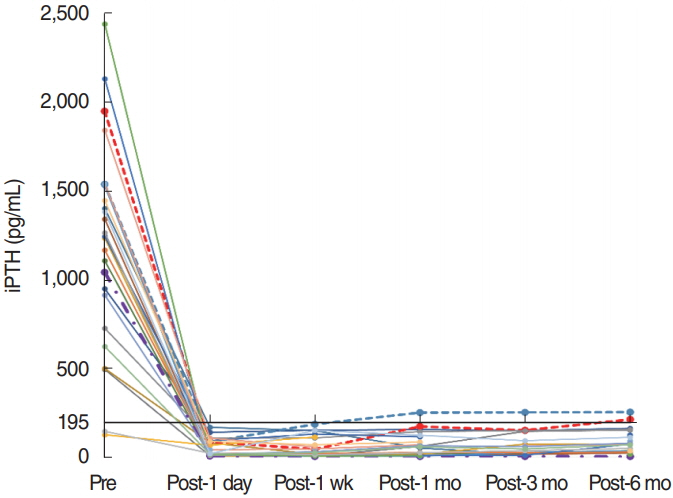
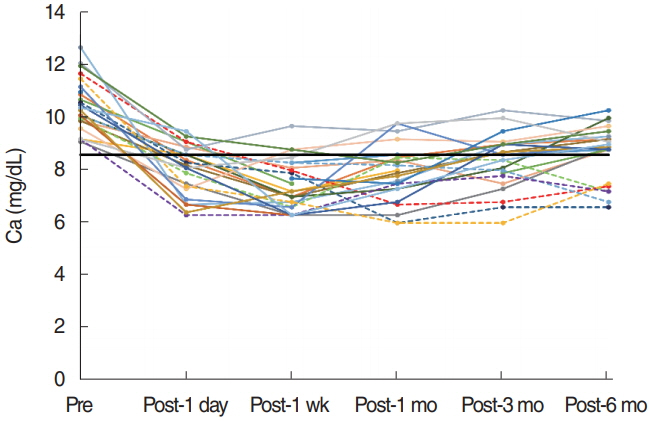
. Of the 25 patients, 13 (52%) were male and 12 (48%) were female, and the mean age was 53.4±9.3 years. The mean duration of dialysis before parathyroidectomy was 156.8±79.5 months. Mean preoperative serum iPTH and calcium levels were 1,199.0±571.3 pg/mL and 10.5±1.0 mg/dL, respectively. At 6 months postoperatively, the mean iPTH and calcium levels decreased to 49.2±47.6 pg/mL (P<0.01) and 8.0±1.0 mg/dL (P<0.01), respectively. Recurrent hyperparathyroidism occurred in two patients: one subsequently underwent kidney transplantation and the other continued hemodialysis and maintained normal calcium levels. One patient developed postoperative permanent hypoparathyroidism.
Conclusion
. Subtotal parathyroidectomy is a safe and effective surgical treatment for renal hyperparathyroidism.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recent Trends in the Surgical Treatment of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
Ho-Ryun Won, Bon Seok Koo
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;13(2):91-92. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2020.00493.
Reference
-
1. Madorin C, Owen RP, Fraser WD, Pellitteri PK, Radbill B, Rinaldo A, et al. The surgical management of renal hyperparathyroidism. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; Jun. 269(6):1565–76.
Article2. Cunningham J, Locatelli F, Rodriguez M. Secondary hyperparathyroidism: pathogenesis, disease progression, and therapeutic options. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; Apr. 6(4):913–21.
Article3. Saliba W, El-Haddad B. Secondary hyperparathyroidism: pathophysiology and treatment. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009; Sep-Oct. 22(5):574–81.
Article4. Jimenez Vibora E, Areste N, Salgueira M, del Toro N, Jimenez Garcia A, Villar JL, et al. Renal hyperparathyroidism’s control after subtotal parathyroidectomy. Nefrologia. 2005; 25(4):416–21.5. Konturek A, Barczynski M, Stopa M, Nowak W. Subtotal parathyroidectomy for secondary renal hyperparathyroidism: a 20-year surgical outcome study. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2016; Nov. 401(7):965–74.
Article6. de Francisco AL, Fresnedo GF, Rodrigo E, Pinera C, Amado JA, Arias M. Parathyroidectomy in dialysis patients. Kidney Int Suppl. 2002; May. (80):161–6.
Article7. Moe S, Drueke T, Cunningham J, Goodman W, Martin K, Olgaard K, et al. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2006; Jun. 69(11):1945–53.
Article8. Stracke S, Keller F, Steinbach G, Henne-Bruns D, Wuerl P. Long-term outcome after total parathyroidectomy for the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Nephron Clin Pract. 2009; 111(2):c102–9.
Article9. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; Oct. 42(4 Suppl 3):S1–201.10. Guideline Working Group; Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. Clinical practice guideline for the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic dialysis patients. Ther Apher Dial. 2008; Dec. 12(6):514–25.11. Lim CT, Kalaiselvam T, Kitan N, Goh BL. Clinical course after parathyroidectomy in adults with end-stage renal disease on maintenance dialysis. Clin Kidney J. 2018; Apr. 11(2):265–9.
Article12. Liang Y, Sun Y, Ren L, Qi XW, Li Y, Zhang F. Short-term efficacy of surgical treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; Oct. 19(20):3904–9.13. Liu ME, Qiu NC, Zha SL, Du ZP, Wang YF, Wang Q, et al. To assess the effects of parathyroidectomy (TPTX versus TPTX+AT) for secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2017; Aug. 44:353–362.
Article14. Bellorin-Font E, Ambrosoni P, Carlini RG, Carvalho AB, Correa-Rotter R, Cueto-Manzano A, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of mineral and bone disorders in chronic kidney disease (CKD-MBD) in adults. Nefrologia. 2013; 33 Suppl 1:1–28.15. Xu D, Yin Y, Hou L, Dai W. Surgical management of secondary hyperparathyroidism: how to effectively reduce recurrence at the time of primary surgery. J Endocrinol Invest. 2016; May. 39(5):509–14.
Article16. Tominaga Y, Uchida K, Haba T, Katayama A, Sato T, Hibi Y, et al. More than 1,000 cases of total parathyroidectomy with forearm autograft for renal hyperparathyroidism. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; Oct. 38(4 Suppl 1):S168–71.
Article17. Lorenz K, Bartsch DK, Sancho JJ, Guigard S, Triponez F. Surgical management of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease: a consensus report of the European Society of Endocrine Surgeons. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2015; Dec. 400(8):907–27.18. Dotzenrath C, Cupisti K, Goretzki E, Mondry A, Vossough A, Grabensee B, et al. Operative treatment of renal autonomous hyperparathyroidism: cause of persistent or recurrent disease in 304 patients. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2003; Jan. 387(9-10):348–54.
Article19. Rajeev P, Lee KY, Tang XJ, Goo TT, Tan WB, Ngiam KY. Outcomes of parathyroidectomy in renal hyperparathyroidism in patients with No access to renal transplantation in Singapore. Int J Surg. 2016; Jan. 25:64–8.
Article20. Schneider R, Slater EP, Karakas E, Bartsch DK, Schlosser K. Initial parathyroid surgery in 606 patients with renal hyperparathyroidism. World J Surg. 2012; Feb. 36(2):318–26.
Article21. Alkhalili E, Tasci Y, Aksoy E, Aliyev S, Soundararajan S, Taskin E, et al. The utility of neck ultrasound and sestamibi scans in patients with secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism. World J Surg. 2015; Mar. 39(3):701–5.
Article22. Wimmer G, Profanter C, Kovacs P, Sieb M, Gabriel M, Putzer D, et al. CT-MIBI-SPECT image fusion predicts multiglandular disease in hyperparathyroidism. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010; Jan. 395(1):73–80.
Article23. Sakman G, Parsak CK, Balal M, Seydaoglu G, Eray IC, Saritas G, et al. Outcomes of total parathyroidectomy with autotransplantation versus subtotal parathyroidectomy with routine addition of thymectomy to both groups: single center experience of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Balkan Med J. 2014; Mar. 31(1):77–82.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subtotal Parathyroidectomy for Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism: a Case Report and Literature Review
- 2 Cases of Surgical Experience of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
- Efficacy of Subtotal Parathyroidectomy in Secondary Renal Hyperparathyroidism: Long-Term Follow-Up Result
- A Case of Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism Combined with Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma
- Disease of Parathyroid and Surgical Strategy