Korean J Leg Med.
2020 Feb;44(1):17-23. 10.7580/kjlm.2020.44.1.17.
Usefulness of Mast Cell Tryptase Analysis for Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjp@yuhs.ac
- 2Division of Forensic Medicine, National Forensic Service Daegu Institute, Chilgok, Korea.
- 3Division of Forensic Medicine, National Forensic Service Daejeon Institute, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2471740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2020.44.1.17
Abstract
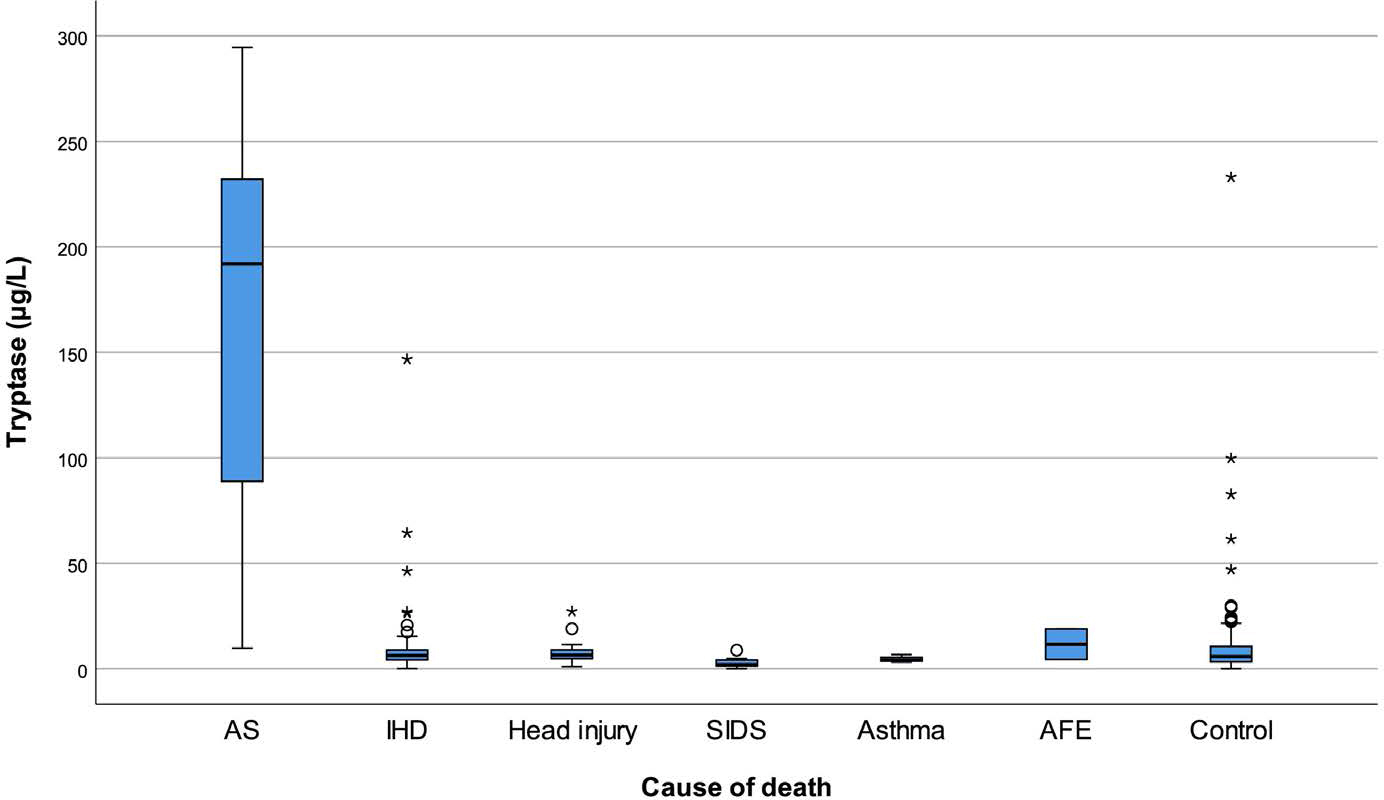
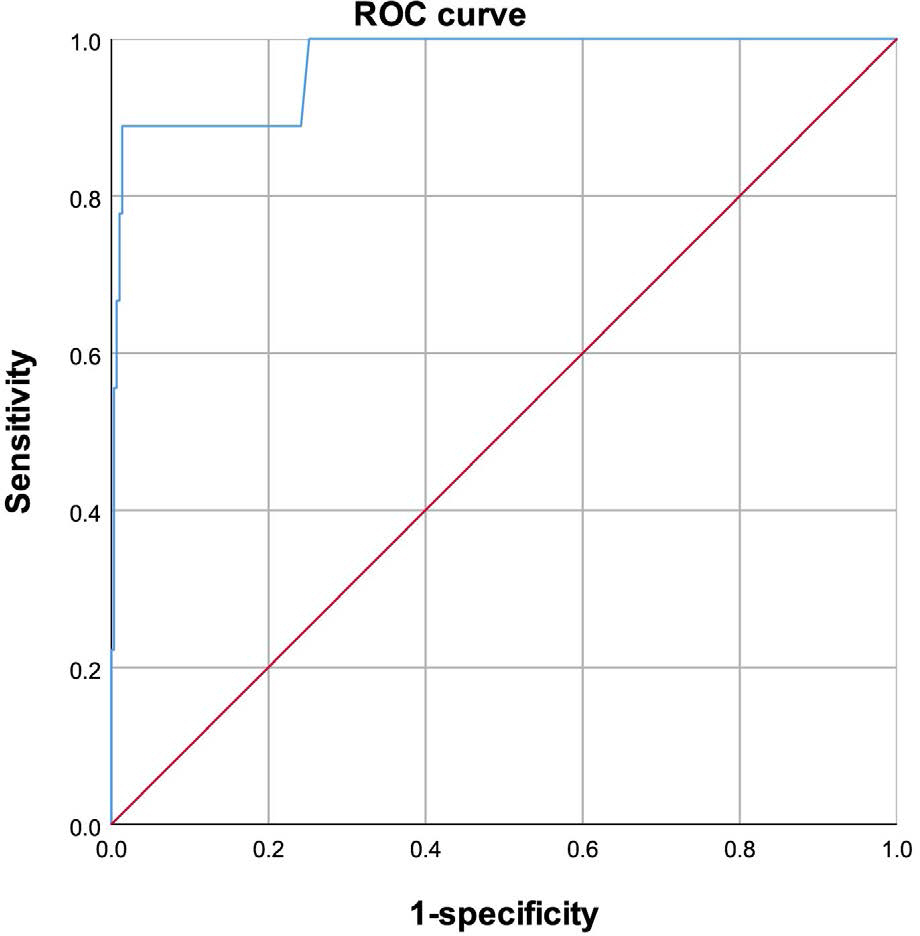
- Anaphylactic shock (AS) is a systemic and life-threatening type I hypersensitivity reaction and is often encountered at an autopsy. However, postmortem diagnosis of AS can be difficult due to non-specific autopsy findings. Clinically, the analysis of serum mast cell tryptase (MCT) is well known as a useful ancillary test for the diagnosis of AS. However, in order to apply this test to forensic autopsy, it is necessary to confirm its usefulness due to postmortem changes. We carried out serum MCT analysis in 299 autopsy cases including nine AS cases at National Forensic Service from January 2013 to May 2015 and analyzed the difference according to the cause of death and degree of postmortem change. As a result, the MCT level in AS was significantly increased compared to others, and the appropriate cutoff value for postmortem diagnosis of AS was 63.0 µg/L (sensitivity 88.9%, specificity 98.6%). Conclusively, serum MCT analysis is a useful test for postmortem diagnosis of AS and seems to be more appropriate for screening rather than confirmation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rutkowski K, Dua S, Nasser S. Anaphylaxis: current state of knowledge for the modern physician. Postgrad Med J. 2012; 88:458–64.
Article2. Da Broi U, Moreschi C. Postmortem diagnosis of anaphylaxis: a difficult task in forensic medicine. Forensic Sci Int. 2011; 204:1–5.
Article3. Byard RW. An analysis of possible mechanisms of unexpected death occurring in hydatid disease (echinococcosis). J Forensic Sci. 2009; 54:919–22.
Article4. Nara A, Aki T, Funakoshi T, et al. Death due to blood transfusion-induced anaphylactic shock: a case report. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2010; 12:148–50.
Article5. Belton AL, Chira T. Fatal anaphylactic reaction to hair dye. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1997; 18:290–2.
Article6. Pumphrey RS, Roberts IS. Postmortem findings after fatal anaphylactic reactions. J Clin Pathol. 2000; 53:273–6.
Article7. Beck SC, Wilding T, Buka RJ, et al. Biomarkers in human anaphylaxis: a critical appraisal of current evidence and perspectives. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:494.
Article8. Edston E, van Hage-Hamsten M. beta-Tryptase measurements postmortem in anaphylactic deaths and in controls. Forensic Sci Int. 1998; 93:135–42.9. Mayer DE, Krauskopf A, Hemmer W, et al. Usefulness of post mortem determination of serum tryptase, histamine and diamine oxidase in the diagnosis of fatal anaphylaxis. Forensic Sci Int. 2011; 212:96–101.
Article10. Scarpelli MP, Keller S, Tran L, et al. Postmortem serum levels of IgE and mast cell tryptase in fatal asthma. Forensic Sci Int. 2016; 269:113–8.
Article11. Tamura N, Farhana M, Oda T, et al. Amniotic fluid embolism: pathophysiology from the perspective of pathology. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2017; 43:627–32.
Article12. Xiao N, Li DR, Wang Q, et al. Postmortem serum tryptase levels with special regard to acute cardiac deaths. J Forensic Sci. 2017; 62:1336–8.
Article13. Sun KJ, He JT, Huang HY, et al. Diagnostic role of serum tryptase in anaphylactic deaths in forensic medicine: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2018; 14:209–15.
Article14. Tse R, Wong CX, Kesha K, et al. Post mortem tryptase cutoff level for anaphylactic death. Forensic Sci Int. 2018; 284:5–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of Serum Mast Cell Tryptase Analysis in Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock
- Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock by Histopathological Examination of Mast Cell
- Anaphylactic Shock by Hemocoagulase with Increased Concentration of Mast Cell Tryptase: A case report
- Expression of Mast Cell Tryptase in the Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion
- Involvement of MITF-A, an alternative isoform of mi transcription factor, on the expression of tryptase gene in human mast cells