Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2020 Feb;24(1):104-108. 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.1.104.
First experience of pancreaticoduodenectomy using Revo-i in a patient with insulinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. CMKANG@yuhs.ac
- 2Pancreatobiliary Cancer Center, Yonsei Cancer Center, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2471198
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.1.104
Abstract
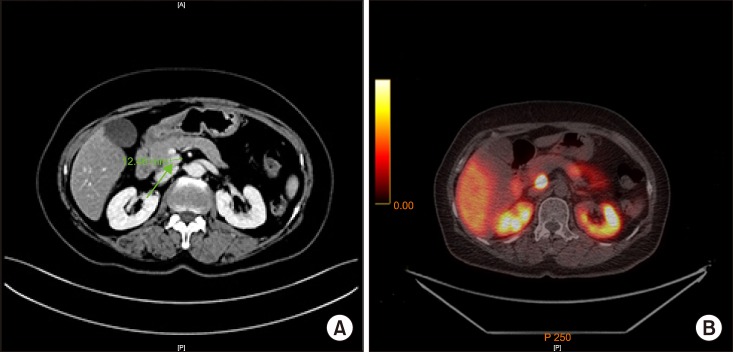
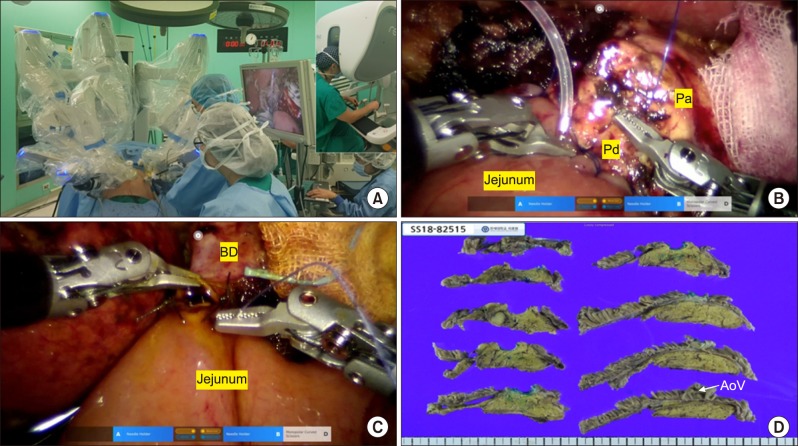
- Robotic surgery systems have been developed to overcome the limitations of laparoscopic surgery. Recently, Meerecompany Inc. in Korea successfully manufactured a robotic surgical system called Revo-i. A 65-year old woman was referred for a pancreatic head tumor, detected as an incidental finding during a routine check-up. Contrast abdominopelvic CT revealed a pancreatic uncinate tumor measuring around 13 mm in diameter, with no other focal lesions. The patient underwent a robot-assisted pancreaticoduodenectomy (laparoscopic resection and robotic reconstruction) using Revo-i. The patient's recovery was uneventful and discharged on postoperative day 7. Our case showed the technical feasibility of the Korean robotic surgical system Revo-i. Further experiences are mandatory to validate this finding.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Revo-i assisted robotic central pancreatectomy
Gayoon Ku, Incheon Kang, Woo Jung Lee, Chang Moo Kang
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2020;24(4):547-550. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.4.547.
Reference
-
1. Gagner M, Pomp A. Laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. Surg Endosc. 1994; 8:408–410. PMID: 7915434.
Article2. Kendrick ML, Cusati D. Total laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: feasibility and outcome in an early experience. Arch Surg. 2010; 145:19–23. PMID: 20083750.3. Boggi U, Amorese G, Vistoli F, Caniglia F, De Lio N, Perrone V, et al. Laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: a systematic literature review. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:9–23. PMID: 25125092.
Article4. Poves I, Burdío F, Morató O, Iglesias M, Radosevic A, Ilzarbe L, et al. Comparison of perioperative outcomes between laparoscopic and open approach for pancreatoduodenectomy: the PADULAP randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2018; 268:731–739. PMID: 30138162.5. Nagakawa Y, Nakamura Y, Honda G, Gotoh Y, Ohtsuka T, Ban D, et al. Learning curve and surgical factors influencing the surgical outcomes during the initial experience with laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2018; 25:498–507. PMID: 30291768.
Article6. Zhang T, Zhao ZM, Gao YX, Lau WY, Liu R. The learning curve for a surgeon in robot-assisted laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: a retrospective study in a high-volume pancreatic center. Surg Endosc. 2019; 33:2927–2933. PMID: 30483970.
Article7. Kang CM, Lee SH, Chung MJ, Hwang HK, Lee WJ. Laparoscopic pancreatic reconstruction technique following laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015; 22:202–210. PMID: 25546026.
Article8. Pratt WB, Maithel SK, Vanounou T, Huang ZS, Callery MP, Vollmer CM Jr. Clinical and economic validation of the International Study Group of Pancreatic Fistula (ISGPF) classification scheme. Ann Surg. 2007; 245:443–451. PMID: 17435552.
Article9. Choe YM, Lee KY, Oh CA, Lee JB, Choi SK, Hur YS, et al. Risk factors affecting pancreatic fistulas after pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:6970–6974. PMID: 19058333.
Article10. McMillan MT, Malleo G, Bassi C, Sprys MH, Ecker BL, Drebin JA, et al. Pancreatic fistula risk for pancreatoduodenectomy: an international survey of surgeon perception. HPB (Oxford). 2017; 19:515–524. PMID: 28202218.
Article11. Satava RM. Surgical robotics: the early chronicles: a personal historical perspective. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2002; 12:6–16. PMID: 12008765.12. Del Chiaro M, Segersvärd R. The state of the art of robotic pancreatectomy. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:920492. PMID: 24982913.
Article13. Stafford AT, Walsh RM. Robotic surgery of the pancreas: the current state of the art. J Surg Oncol. 2015; 112:289–294. PMID: 26220683.
Article14. Nio D, Bemelman WA, Busch OR, Vrouenraets BC, Gouma DJ. Robot-assisted laparoscopic cholecystectomy versus conventional laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a comparative study. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:379–382. PMID: 14716538.
Article15. Cadière GB, Himpens J, Germay O, Izizaw R, Degueldre M, Vandromme J, et al. Feasibility of robotic laparoscopic surgery:146 cases. World J Surg. 2001; 25:1467–1477. PMID: 11760751.16. Fanfani F, Monterossi G, Fagotti A, Rossitto C, Gueli Alletti S, Costantini B, et al. The new robotic TELELAP ALF-X in gynecological surgery: single-center experience. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:215–221. PMID: 25840895.
Article17. Yi B, Wang G, Li J, Jiang J, Son Z, Su H, et al. The first clinical use of domestically produced Chinese minimally invasive surgical robot system “Micro Hand S”. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:2649–2655. PMID: 26293795.
Article18. Chang KD, Abdel Raheem A, Choi YD, Chung BH, Rha KH. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy using the Revo-i robotic surgical system: surgical technique and results of the first human trial. BJU Int. 2018; 122:441–448. PMID: 29645348.
Article19. Kang CM, Chong JU, Lim JH, Park DW, Park SJ, Gim S, et al. Robotic cholecystectomy using the newly developed Korean robotic surgical system, Revo-i: a preclinical experiment in a porcine model. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58:1075–1077. PMID: 28792158.
Article20. Park H, Kang I, Kang CM. Laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy with segmental resection of superior mesenteric vein-splenic vein-portal vein confluence in pancreatic head cancer: can it be a standard procedure? Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2018; 22:419–424. PMID: 30588536.
Article21. Peng L, Lin S, Li Y, Xiao W. Systematic review and meta-analysis of robotic versus open pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:3085–3097. PMID: 27928665.
Article22. Cole AP, Trinh QD, Sood A, Menon M. The rise of robotic surgery in the new millennium. J Urol. 2017; 197(2S):S213–S215. PMID: 28010986.
Article23. Boggi U, Signori S, De Lio N, Perrone VG, Vistoli F, Belluomini M, et al. Feasibility of robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. Br J Surg. 2013; 100:917–925. PMID: 23640668.
Article24. Liao CH, Wu YT, Liu YY, Wang SY, Kang SC, Yeh CN, et al. Systemic review of the feasibility and advantage of minimally invasive pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Surg. 2016; 40:1218–1225. PMID: 26830906.
Article25. Kornaropoulos M, Moris D, Beal EW, Makris MC, Mitrousias A, Petrou A, et al. Total robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy: a systematic review of the literature. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:4382–4392. PMID: 28389798.
Article26. Tedesco G, Faggiano FC, Leo E, Derrico P, Ritrovato M. A comparative cost analysis of robotic-assisted surgery versus laparoscopic surgery and open surgery: the necessity of investing knowledgeably. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:5044–5051. PMID: 26983435.
Article27. Conlon KC, de Rooij T, van Hilst J, Abu Hidal M, Fleshman J, Talamonti M, et al. Minimally invasive pancreatic resections: cost and value perspectives. HPB (Oxford). 2017; 19:225–233. PMID: 28268161.
Article28. Kim DK, Park DW, Rha KH. Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy with the REVO-I robot platform in porcine models. Eur Urol. 2016; 69:541–542. PMID: 26688371.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Revo-i Robotic Surgical System in Advanced Pancreatic Surgery: A Second Non-Randomized Clinical Trial and Comparative Analysis to the da VinciTM System
- Successful Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Alcohol Ablation of Sporadic Insulinoma Using Three-Dimensional Targeting (with Video)
- Anesthesia for an Insulinoma Case
- A Case of Surgically Treated Insulinoma in Pregnancy
- Robotic Cholecystectomy Using the Newly Developed Korean Robotic Surgical System, Revo-i: A Preclinical Experiment in a Porcine Model