Clin Orthop Surg.
2020 Mar;12(1):49-54. 10.4055/cios.2020.12.1.49.
Long-term Follow-up of Patellar Nonresurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jhs@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University College of Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2470050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2020.12.1.49
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We aimed to confirm the long-term effect of patellar nonresurfacing (patellar decompression) in preventing anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and to investigate the possible complications.
METHODS
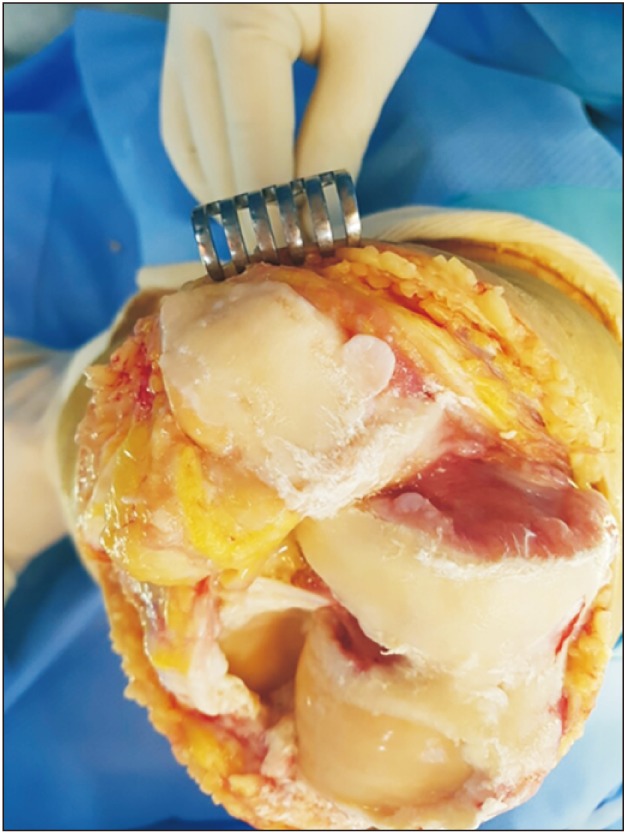
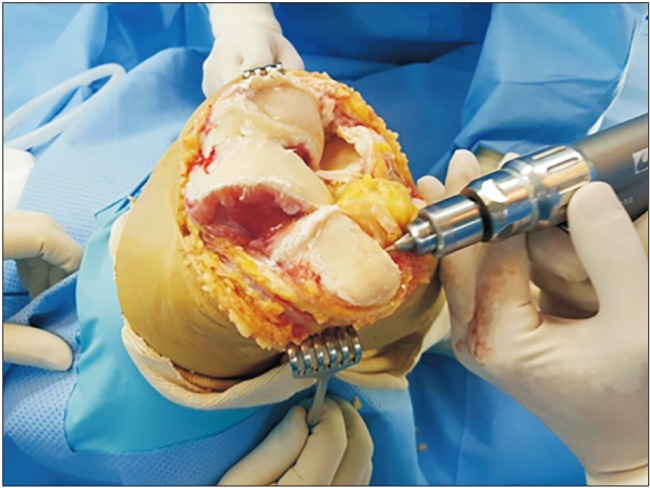
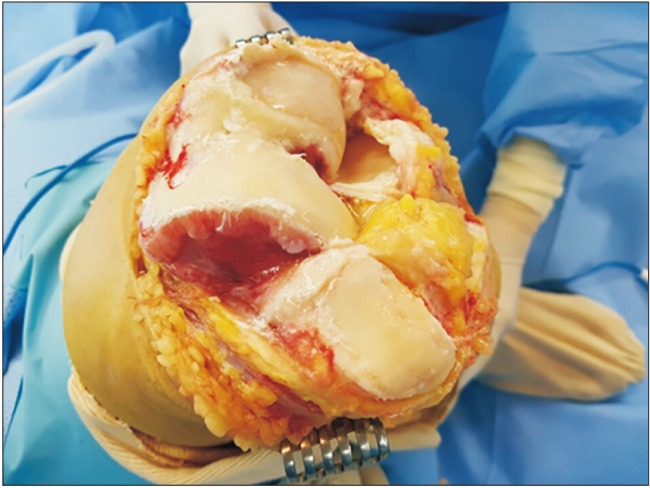
Among patients who underwent primary TKA after being diagnosed as having advanced osteoarthritis (Kellgren-Lawrence grade 4) at our institution from January 2004 to December 2010, 121 patients who were followed up for more than 7 years were included in this study. Patients who underwent TKA with and without patellar decompression were classified as the study group and control group, respectively. A clinical knee rating score was used to compare the postoperative clinical outcomes between groups. To identify complications after patellar decompression, simple radiographs (weight-bearing anteroposterior and lateral views, patella in 30° and 45° axial views, and whole scanogram) were taken during follow-up.
RESULTS
There were no complications such as patellar fracture, osteonecrosis, and subluxation. At 2 years after surgery, the prevalence of anterior knee pain was 12.7% and 18.0% in the study group and control group, respectively (p = 0.42), and the number of patients with patellofemoral osteoarthritis grade II or over was lower in the study group (p = 0.03). At 7 years after surgery, the prevalence of anterior knee pain was 18.3% and 24.0% in the study group and control group, respectively (p = 0.45), and there was no statistically significant intergroup difference in the number of patients with patellofemoral osteoarthritis grade II or over (p = 0.11).
CONCLUSIONS
Patellar nonresurfacing TKA reduces anterior knee pain in the early postoperative period. The procedure can be considered a relatively safe option with fewer complications; however, its effectiveness appears to decrease over time.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sensi L, Buzzi R, Giron F, De Luca L, Aglietti P. Patellofemoral function after total knee arthroplasty: gender-related differences. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26(8):1475–1480. PMID: 21498038.2. Ghomrawi HM, Schackman BR, Mushlin AI. Appropriateness criteria and elective procedures--total joint arthroplasty. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367(26):2467–2469. PMID: 23268663.3. Scott RD. The evolving incidence and reasons for re-operation after fixed-bearing PCL retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94(11 Suppl A):134–136.
Article4. Richmond JC. Surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2013; 39(1):203–211. PMID: 23312417.
Article5. Fehring TK, Odum S, Griffin WL, Mason JB, Nadaud M. Early failures in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (392):315–318. PMID: 11716402.
Article6. Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (356):144–153.
Article7. Eisenhuth SA, Saleh KJ, Cui Q, Clark CR, Brown TE. Patellofemoral instability after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 446:149–160. PMID: 16672884.
Article8. Petersen W, Rembitzki IV, Bruggemann GP, et al. Anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty: a narrative review. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(2):319–328. PMID: 24057656.
Article9. Lee GW, Lee SM, Jang SJ, Son JH. The efficacy of patellar decompression for improving anterior knee pain following total knee arthroplasty without patellar resurfacing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133(4):561–567. PMID: 23435648.
Article10. Kim YM, Joo YB. Patellofemoral osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012; 24(4):193–200. PMID: 23269956.
Article11. Dye SF. Patellofemoral pain current concepts: an overview. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2001; 9(4):262–272.
Article12. Arnoldi CC, Lemperg K, Linderholm H. Intraosseous hypertension and pain in the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975; 57(3):360–363. PMID: 1158947.
Article13. Wood DJ, Smith AJ, Collopy D, White B, Brankov B, Bulsara MK. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(2):187–193. PMID: 11861723.14. Waters TS, Bentley G. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(2):212–217. PMID: 12571296.15. Burnett RS, Haydon CM, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Patella resurfacing versus nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial at a minimum of 10 years' followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (428):12–25.16. Schneider U, Breusch SJ, Thomsen M, Wenz W, Graf J, Niethard FU. A new concept in the treatment of anterior knee pain: patellar hypertension syndrome. Orthopedics. 2000; 23(6):581–586. PMID: 10875419.
Article17. Heyse TJ, Becher C, Kron N, et al. Patellofemoral pressure after TKA in vitro: highly conforming vs. posterior stabilized inlays. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010; 130(2):191–196. PMID: 19578863.
Article18. Barrack RL, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Waldman DA, Milicic M, Myers L. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study with five to seven years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83(9):1376–1381. PMID: 11568201.19. Park SJ, Jung YB, Jeong HJ, et al. Long-term results of primary total knee arthroplasty with and without patellar resurfacing. Acta Med Okayama. 2010; 64(5):331–338. PMID: 20975767.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Patellar Nonresurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Functional and Radiological Outcomes of Patella Retaining Total Knee Arthroplasty: Minimun 5-Year Follow-up Results
- Results of Total Knee Arthroplasty with Patella-Friendly ADVANTIM(R) Total Knee System
- Patellar Nonresurfacing Versus Patellar Resurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- The Mid to Long Term Results of PCL Substitution Type Total Knee Arthroplasty with Using a Scorpio(R) system (Comparison with or without Patella Resurfacing)