Ann Surg Treat Res.
2020 Feb;98(2):57-61. 10.4174/astr.2020.98.2.57.
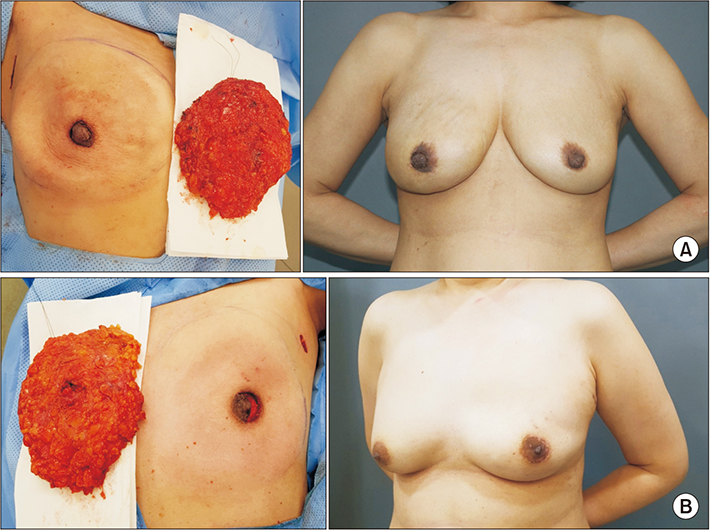
Nipple-sparing mastectomy through periareolar incision with immediate reconstruction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. limw@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2469104
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2020.98.2.57
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) has become increasingly popular due to improved cosmesis without compromising oncologic safety. Radial and inframammary incisions are usually used to achieve NSM, with periareolar incisions usually being avoided because of the risk to nipple-areola complex viability. In an attempt to maximize esthetic effects, we performed NSM through periareolar incision with immediate reconstruction. We report our initial experience.
METHODS
This case series consisted of all consecutive patients (n = 34) who underwent NSM through a periareolar incision in our institution between August 2017 and December 2018. All patients underwent NSM through periareolar incision followed by immediate reconstruction with an implant or deep inferior epigastric perforator flap. Patient demographics, tumor and treatment characteristics, and short-term postoperative outcomes were reviewed.
RESULTS
The mean patient age was 46.74 ± 6.69 years (range, 38-62 years), and the mean operation time was 96.68 ± 28.00 minutes. Indications included in situ cancer in 12 cases and invasive cancer in 22 cases. There was 1 major complication (postoperative hematoma) requiring operative reintervention. No other complications including fistula, implant exposure, or reconstruction failure was observed. At the time of writing, no case of local recurrence has been observed.
CONCLUSION
Our initial report shows that NSM with immediate reconstruction may successfully be performed through periareolar incision. This method maximizes esthetic effects and may be an appropriate surgical option for NSM.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Freeman BS. Subcutaneous mastectomy for benign breast lesions with immediate or delayed prosthetic replacement. Plast Reconstr Surg Transplant Bull. 1962; 30:676–682.
Article2. Freeman BS. Complications of subcutaneous mastectomy with prosthetic replacement, immediate or delayed. South Med J. 1967; 60:1277–1280.
Article3. Rawlani V, Fiuk J, Johnson SA, Buck DW 2nd, Hirsch E, Hansen N, et al. The effect of incision choice on outcomes of nipple-sparing mastectomy reconstruction. Can J Plast Surg. 2011; 19:129–133.
Article4. Paepke S, Schmid R, Fleckner S, Paepke D, Niemeyer M, Schmalfeldt B, et al. Subcutaneous mastectomy with conservation of the nipple-areola skin: broadening the indications. Ann Surg. 2009; 250:288–292.5. Gerber B, Krause A, Dieterich M, Kundt G, Reimer T. The oncological safety of skin sparing mastectomy with conservation of the nipple-areola complex and autologous reconstruction: an extended follow-up study. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:461–468.
Article6. Orzalesi L, Casella D, Santi C, Cecconi L, Murgo R, Rinaldi S, et al. Nipple sparing mastectomy: surgical and oncological outcomes from a national multicentric registry with 913 patients (1006 cases) over a six year period. Breast. 2016; 25:75–81.
Article7. Blechman KM, Karp NS, Levovitz C, Guth AA, Axelrod DM, Shapiro RL, et al. The lateral inframammary fold incision for nipple-sparing mastectomy: outcomes from over 50 immediate implant-based breast reconstructions. Breast J. 2013; 19:31–40.
Article8. Cavalcante FP, Lima MVA. Nipple-sparing mastectomy with periareolar incision and two-stage reconstruction: initial analysis of 31 cases. Breast J. 2018; 24:940–943.
Article9. Frey JD, Salibian AA, Levine JP, Karp NS, Choi M. Incision choices in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a comparative analysis of outcomes and evolution of a clinical algorithm. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018; 142:826e–835e.10. El Hage Chehade H, Headon H, Wazir U, Carmaichael AR, Choy C, Kasem A, et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy using a hemi-periareolar incision with or without minimal medial-lateral extensions; clinical outcome and patient satisfaction: a single centre prospective observational study. Am J Surg. 2017; 213:1116–1124.
Article11. Vaughn CJ, Peled AW, Esserman LJ, Foster RD. Feasibility of performing total skin-sparing mastectomy in patients with prior circumareolar mastopexy or reduction mammoplasty incisions. Ann Plast Surg. 2013; 06. 19. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182977904. [Epub].
Article12. Algaithy ZK, Petit JY, Lohsiriwat V, Maisonneuve P, Rey PC, Baros N, et al. Nipple sparing mastectomy: can we predict the factors predisposing to necrosis? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012; 38:125–129.
Article13. Munhoz AM, Aldrighi CM, Montag E, Arruda EG, Aldrighi JM, Gemperli R, et al. Clinical outcomes following nipple-areola-sparing mastectomy with immediate implant-based breast reconstruction: a 12-year experience with an analysis of patient and breast-related factors for complications. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 140:545–555.
Article14. Regolo L, Ballardini B, Gallarotti E, Scoccia E, Zanini V. Nipple sparing mastectomy: an innovative skin incision for an alternative approach. Breast. 2008; 17:8–11.
Article15. Pek WS, Tan BK, Ru Ng YY, Kiak Mien Tan V, Rasheed MZ, Kiat Tee Tan B, et al. Immediate breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy in an Asian population: aesthetic outcomes and mitigating nipple-areolar complex necrosis. Arch Plast Surg. 2018; 45:229–238.
Article16. Gougoutas AJ, Anderson BO. One-stage versus two-stage breast reconstruction: prudence in surgical decision-making. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:166–167.
Article17. Galimberti V, Vicini E, Corso G, Morigi C, Fontana S, Sacchini V, et al. Nipple-sparing and skin-sparing mastectomy: review of aims, oncological safety and contraindications. Breast. 2017; 34 Suppl 1:S82–S84.
Article18. Mota BS, Riera R, Ricci MD, Barrett J, de Castria TB, Atallah AN, et al. Nipple- and areola-sparing mastectomy for the treatment of breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 11:CD008932.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immediate Breast Reconstruction with TRAM Flap after Nipple-Areolar Sparing Mastectomy
- One-stage nipple and breast reconstruction using a deep inferior epigastric perforator flap after a skin-sparing mastectomy
- Skin - sparing Mastectomy with Circumareolar Incision and Immediate TRAM & One - stage Star Flap Nipple - areolar Complex Reconstruction
- Skin-Sparing Mastectomy with Circumareolar Incision and Immediate Reconstruction in Breast Cancer
- Skin-sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Nipple Graft for Large, Ptotic Breast