Anat Biol Anthropol.
2019 Dec;32(4):159-165. 10.11637/aba.2019.32.4.159.
Anatomical Characteristics of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament in Ankle Joint of Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Korea.
- 2Division in Biomedical Art, Incheon Catholic University Graduate School, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University of Medicine, Korea. hohotoy@nate.com
- KMID: 2467469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11637/aba.2019.32.4.159
Abstract
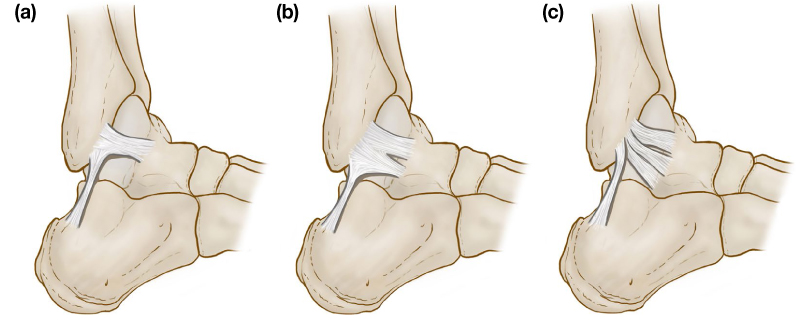
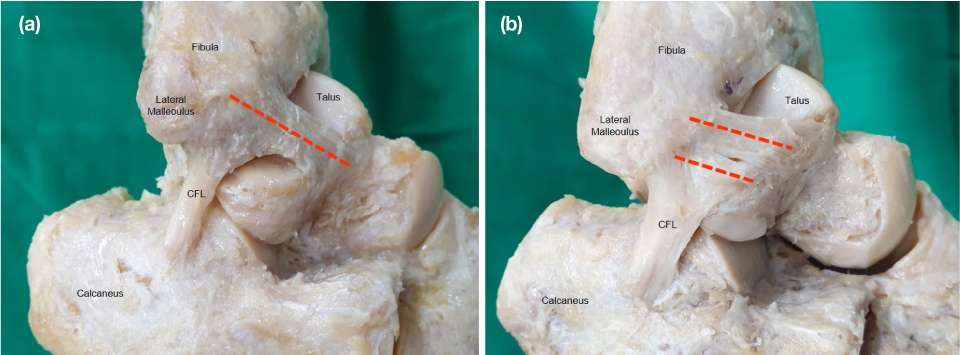
- The anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) plays a role to stabilize ankle joint and prevent ankle sprain by limiting the motion range of ankle joint. The aim of this study was to classify the shapes of the ATFL according to the shape and type of bands. For this study, formalin-fixed 42 Korean cadavers were used and 74 feet were dissected (49 males and 25 females / 38 right, 36 left). The average age was 77 years old. The number of bands in the ATFL was counted according to Kakegawa et al. The location of the attachment area of ATFL was determined. It's length and width were also measured. All of them were measured in prone position, and in neutral position of ankle. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 21.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL). Descriptive statistics were used to determine the mean and standard deviation, and independent T-tests were used to identify differences according to gender, left and right, and type of ATFL. As a result, type 1 and type 2 in the ATFL accounted for 48.6% and 51.4% of feet respectively. The length of the ATFL was 20.6±2.4 mm, the width of the proximal attachment was 13.7±3.4 mm, the mid-point was 12.9±3.5 mm, and the distal attachment was 13.0±3.4 mm. Type 2 was wider than type 1 (p<.001), type 1 was longer than type 2 (p<.05), and male ATFL was longer than female (p<.05). In conclusion, the morphological characteristics of ATFL in Koreans were different from other ethnic group. The continuous accumulation of morphological data on ATFL will offer the basic data of Korean anthropological characteristics, and it will be helpful for understanding the anatomical structure of the ankle, as well as for the diagnosis and treatment of ankle disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. van den Bekerom MP, Oostra RJ, Golanó P, van Dijk CN. The anatomy in relation to injury of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle: a current concepts review. Clin Anat. 2008; 21:619–626.
Article2. Khawaji B, Soames R. The anterior talofibular ligament: A detailed morphological study. Foot (Edinb). 2015; 25:141–147.
Article3. Kobayashi T, Gamada K. Lateral Ankle Sprain and Chronic Ankle Instability: A Critical Review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014; 7:298–326.4. Waterman BR, Owens BD, Davey S, Zacchilli MA, Belmont PJ Jr. The epidemiology of ankle sprains in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:2279–2284.
Article5. Kumai T, Takakura Y, Rufai A, Milz S, Benjamin M. The functional anatomy of the human anterior talofibular ligament in relation to ankle sprains. J Anat. 2002; 200:457–465.
Article6. Broström L. Sprained ankles. V. Treatment and prognosis in recent ligament ruptures. Acta Chir Scand. 1966; 132:537–550.7. Shakked RJ, Karnovsky S, Drakos MC. Operative treatment of lateral ligament instability. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017; 10:113–121.
Article8. Ferran NA, Maffulli N. Epidemiology of sprains of the lateral ankle ligament complex. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006; 11:659–662.
Article9. Taser F, Shafiq Q, Ebraheim NA. Anatomy of lateral ankle ligaments and their relationship to bony landmarks. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006; 28:391–397.
Article10. Ventura A, Terzaghi C, Legnani C, Borgo E. Arthroscopic four-step treatment for chronic ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2012; 33:29–36.
Article11. Matsui K, Takao M, Tochigi Y, Ozeki S, Glazebrook M. Anatomy of anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligament for minimally invasive surgery: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017; 25:1892–1902.
Article12. Kakegawa A, Mori Y, Tsuchiya A, Sumitomo N, Fukushima N, Moriizumi T. Independent Attachment of Lateral Ankle Ligaments: Anterior Talofibular and Calcaneofibular Ligaments - A Cadaveric Study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019; 58:717–722.
Article13. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174.
Article14. Yildiz S, Yalcin B. The anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments: an anatomic study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2013; 35:511–516.
Article15. Edama M, Kageyama I, Kikumoto T, Nakamura M, Ito W, Nakamura E, et al. Morphological features of the anterior talofibular ligament by the number of fiber bundles. Ann Anat. 2018; 216:69–74.
Article16. Wenny R, Duscher D, Meytap E, Weninger P, Hirtler L. Dimensions and attachments of the ankle ligaments: evaluation for ligament reconstruction. Anat Sci Int. 2015; 90:161–171.
Article17. Clanton TO, Campbell KJ, Wilson KJ, Michalski MP, Goldsmith MT, Wijdicks CA, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Anatomic Investigation of the Lateral Ankle Ligaments for Surgical Reconstruction Procedures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96:e98.
Article18. McDermott JE, Scranton PE Jr, Rogers JV. Variations in fibular position, talar length, and anterior talofibular ligament length. Foot Ankle Int. 2004; 25:625–629.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ankle Sprains: Epidemiology, Anatomy and Injury Mechanism
- Arthrography of the ankle sprains
- Irreducible Anterior Subluxation of the Ankle Joint Caused by Os Trigonum and Transverse Ligament: A Case Report
- Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis of the Ankle and Subtalar Joint Treated by Surgical Excision and Ligament Reconstructions: A Case Report
- Anatomical Characteristics of the Calcaneofibular Ligament of Ankle Joint in Korean Population