Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2019 Nov;23(4):359-364. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.359.
Acute respiratory distress-syndrome in the general complications of severe acute pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Intensive Care Unit, Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Surgery Named after Academician V.Vakhidov, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. dr.sardor.ibragimov@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan.
- KMID: 2464325
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.359
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Improvement of efficiency of treatment of patients with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP), complicated by acute respiratory distress-syndrome (ARDS).
METHODS
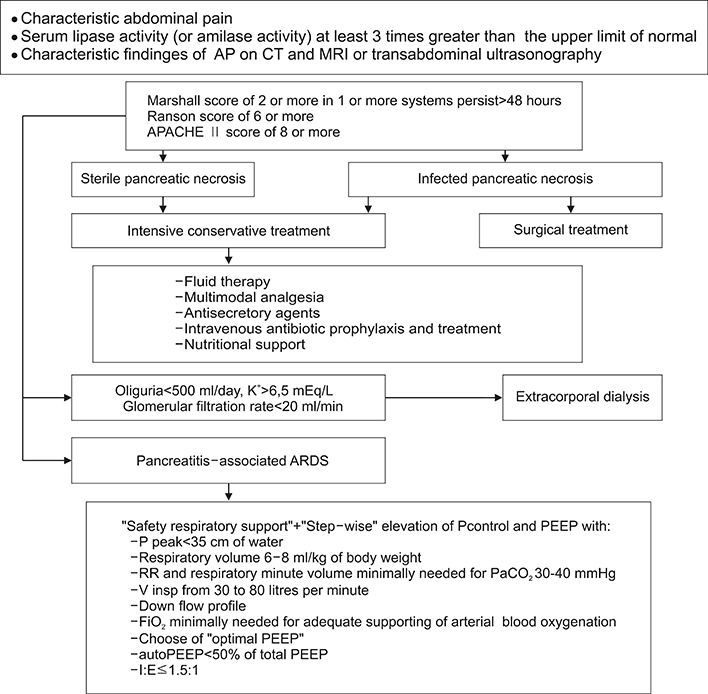
The retrospective research of 67 SAP patients treated at the ICU of the NSSPCS has been conducted from 2008 to 2017. The basic criterion of patient inclusion was stable respiration impairment leading to hypoxia with PaOâ‚‚/FiOâ‚‚<300 mmHg that required mechanical ventilatory support.
RESULTS
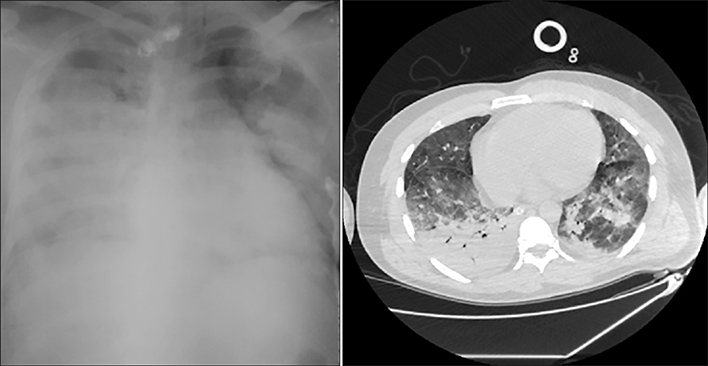
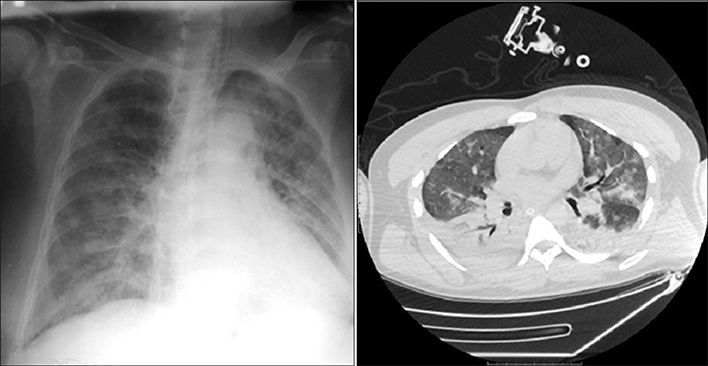
Pancreatitis-associated ARDS was diagnosed in 36 cases (53.7%). The most frequent clinical form (15 cases) was ARDS of moderate severity (41.5%). The total mortality due to pancreatitis-associated ARDS made 44.5%. Close relationship between ARDS severity and mortality was evident. All lethal outcomes occurred due to progressing multiple organ dysfunction. No deaths were caused by uncontrollable hypoxemia.
CONCLUSIONS
The research has confirmed the leading role of pancreatitis-associated ARDS in development and high mortality rate of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in SAP. Early recognition of the complication and application of ventilatory support techniques resulted in fast restoration of oxygenation and improvement of treatment efficiency.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tonsi AF, Bacchion M, Crippa S, Malleo G, Bassi C. Acute pancreatitis at the beginning of the 21st century: the state of the art. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:2945–2959.2. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. ; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013; 62:102–111.3. Büchler MW, Gloor B, Müller CA, Friess H, Seiler CA, Uhl W. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis: treatment strategy according to the status of infection. Ann Surg. 2000; 232:619–626.4. Wada K, Takada T, Hirata K, Mayumi T, Yoshida M, Yokoe M, et al. Treatment strategy for acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010; 17:79–86.5. Buter A, Imrie CW, Carter CR, Evans S, McKay CJ. Dynamic nature of early organ dysfunction determines outcome in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2002; 89:298–302.6. Pastor CM, Matthay MA, Frossard JL. Pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury: new insights. Chest. 2003; 124:2341–2351.7. Zhou MT, Chen CS, Chen BC, Zhang QY, Andersson R. Acute lung injury and ARDS in acute pancreatitis: mechanisms and potential intervention. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2094–2099.8. Zhao X, Andersson R, Wang X, Dib M, Wang X. Acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury: pathophysiological mechanisms and potential future therapies. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37:1351–1358.9. ARDS Definition Task Force. Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA. 2012; 307:2526–2533.10. Cruz-Santamaría DM, Taxonera C, Giner M. Update on pathogenesis and clinical management of acute pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2012; 3:60–70.11. Hirota M, Takada T, Kitamura N, Ito T, Hirata K, Yoshida M, et al. Fundamental and intensive care of acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010; 17:45–52.12. Rittayamai N, Brochard L. Recent advances in mechanical ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur Respir Rev. 2015; 24:132–140.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Complications
- Treatment of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome after Viscum album Pleurodesis for Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax
- Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a Young Adult without Hypertriglyceridemia: A Case Report
- Case of Late-onset Acute Lung Injury Developed as a Complication of Organophosphate Intoxication-induced Acute Pancreatitis