Ann Lab Med.
2020 Jan;40(1):84-87. 10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.84.
Five Korean Cases of Respiratory Tract Infection by Filamentous Basidiomycetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yjpk@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, International St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Institute for Healthcare and Life Sciences, International St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University, Gangneung, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2457500
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.84
Abstract
- No abstract available.
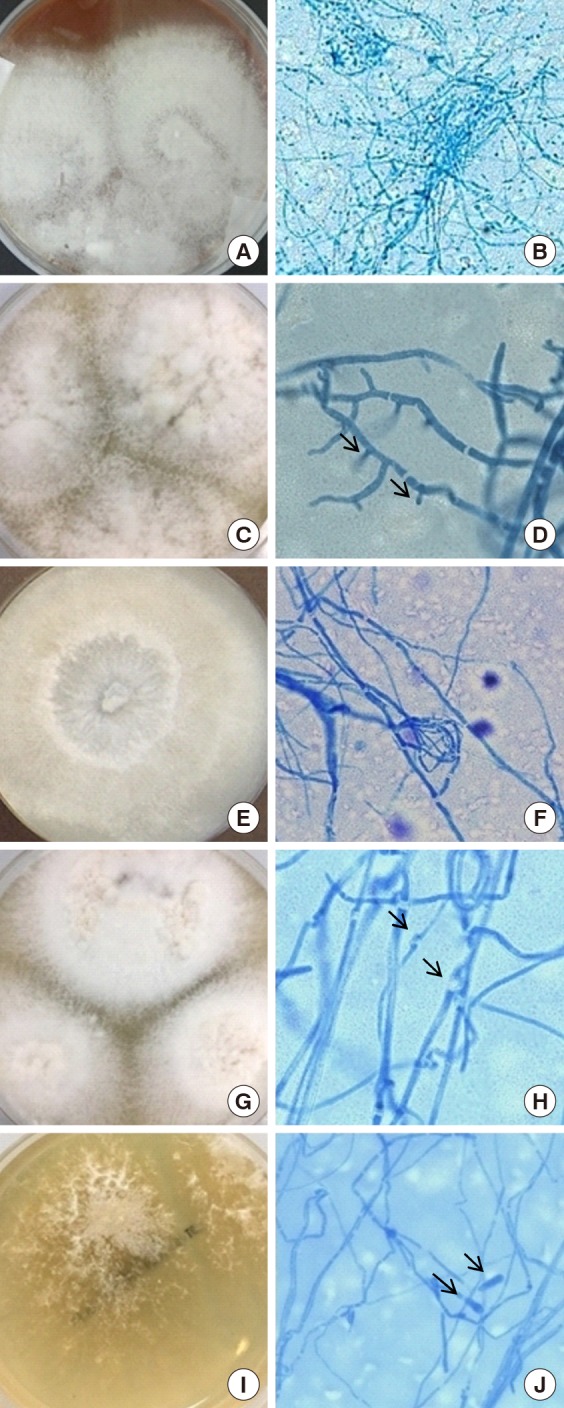
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Invasive
Hormographiella aspergillata Infection Identified Using DNA Sequencing
Eunbin Chong, Hui-Jin Yu, Tae Yeul Kim, Keon Hee Yoo, Yae-Jean Kim, Hee Jae Huh, Nam Yong Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(3):370-372. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.3.370.
Reference
-
1. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:1813–1821. PMID: 18462102.2. Chowdhary A, Kathuria S, Agarwal K, Meis JF. Recognizing filamentous basidiomycetes as agents of human disease: a review. Med Mycol. 2014; 52:782–797. PMID: 25202126.3. Singh PK, Kathuria S, Agarwal K, Gaur SN, Meis JF, Chowdhary A. Clinical significance and molecular characterization of nonsporulating molds isolated from the respiratory tracts of bronchopulmonary mycosis patients with special reference to basidiomycetes. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:3331–3337. PMID: 23903552.4. CLSI. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing. CLSI MM18-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2007.5. CLSI. Reference method for broth dilution antimicrobial susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi. Approved standard 3rd ed. CLSI M38. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2017.6. Abuali MM, Posada R, Del Toro G, Roman E, Ramani R, Chaturvedi S, et al. Rhizomucor variabilis var. regularior and Hormographiella aspergillata infections in a leukemic bone marrow transplant recipient with refractory neutropenia. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:4176–4179. PMID: 19846651.7. Chowdhary A, Agarwal K, Kathuria S, Singh PK, Roy P, Gaur SN, et al. Clinical significance of filamentous basidiomycetes illustrated by isolates of the novel opportunist Ceriporia lacerata from the human respiratory tract. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:585–590. PMID: 23241374.8. Brandt ME. Filamentous basidiomycetes in the clinical laboratory. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2013; 7:219–223. PMID: 26512308.9. Buzina W, Lass-Flörl C, Kropshofer G, Freund MC, Marth E. The polypore mushroom Irpex lacteus, a new causative agent of fungal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:2009–2011. PMID: 15815046.10. Sa HS, Ko KS, Woo KI, Peck KR, Kim YD. A case of sino-orbital infection caused by the Schizophyllum commune. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 73:376–377. PMID: 22673964.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute upper respiratory tract infection
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- Knowledge and Compliance with Prevention of Respiratory Tract Infection Among Workers in Geriatric Facilities
- Erratum: A Retrospective Analysis of Use in Hospitalized Children with Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
- Fatal and Near-fatal Cases of Lower Respiratory Tract Infection with Human Rhinovirus Group A