Healthc Inform Res.
2018 Oct;24(4):371-375. 10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.371.
Laboratory Environment Monitoring: Implementation Experience and Field Study in a Tertiary General Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Healthcare ICT Research Centre, Office of eHealth Research and Businesses, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. yoosoo0@snubh.org
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Office of eHealth Research and Businesses, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2434552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.371
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To successfully introduce an Internet of Things (IoT) system in the hospital environment, this study aimed to identify issues that should be considered while implementing an IoT based on a user demand survey and practical experiences in implementing IoT environment monitoring systems.
METHODS
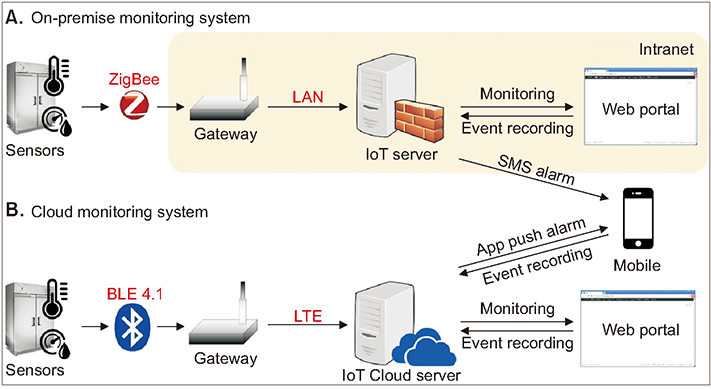
In a field test, two types of IoT monitoring systems (on-premises and cloud) were used in Department of Laboratory Medicine and tested for approximately 10 months from June 16, 2016 to April 30, 2017. Information was collected regarding the issues that arose during the implementation process.
RESULTS
A total of five issues were identified: sensing and measuring, transmission method, power supply, sensor module shape, and accessibility.
CONCLUSIONS
It is expected that, with sufficient consideration of the various issues derived from this study, IoT monitoring systems can be applied to other areas, such as device interconnection, remote patient monitoring, and equipment/environmental monitoring.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Da Xu L, He W, Li S. Internet of things in industries: a survey. IEEE Trans Industr Inform. 2014; 10(4):2233–2243.
Article2. Zhang Y, Zhang G, Wang J, Sun S, Si S, Yang T. Real-time information capturing and integration framework of the internet of manufacturing things. Int J Comput Integr Manuf. 2015; 28(8):811–822.
Article3. Hossain MS, Muhammad G. Cloud-assisted industrial internet of things (IIOT): enabled framework for health monitoring. Comput Netw. 2016; 101:192–202.
Article4. Zanella A, Bui N, Castellani A, Vangelista L, Zorzi M. Internet of things for smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014; 1(1):22–32.
Article5. Ferrandez-Pastor FJ, Garcia-Chamizo JM, Nieto-Hidalgo M, Mora-Pascual J, Mora-Martinez J. Developing ubiquitous sensor network platform using Internet of Things: application in precision agriculture. Sensors (Basel). 2016; 16(7):E1141.6. Tarouco LM, Bertholdo LM, Granville LZ, Arbiza LM, Carbone F, Marotta M, et al. Internet of Things in healthcare: interoperatibility and security issues. In : Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC); 2012 Jun 10–15; Ottawa, Canada. p. 6121–6125.7. Islam SR, Kwak D, Kabir MH, Hossain M, Kwak KS. The Internet of Things for health care: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Access. 2015; 3:678–708.
Article8. Ahmed MU, Bjorkman M, Causevic A, Fotouhi H, Linden M. An overview on the Internet of Things for health monitoring systems. In : Mandler B, editor. Internet of Things: IoT infrastructures. Cham, Swizerland: Springer;2016.9. Rohokale VM, Prasad NR, Prasad R. A cooperative Internet of Things (IoT) for rural healthcare monitoring and control. In : Proceedings of 2011 2nd International Conference on Wireless Communication, Vehicular Technology, Information Theory and Aerospace & Electronic Systems Technology (Wireless VITAE); 2011 Feb 28–Mar 3; Chennai, India. p. 1–6.10. Balaguera HU, Wise D, Ng CY, Tso HW, Chiang WL, Hutchinson AM, et al. Using a medical Intranet of Things system to prevent bed falls in an acute care hospital: a pilot study. J Med Internet Res. 2017; 19(5):e150.
Article11. Alyami A, Campion R, Atkins A. Performance improvement in hospital management using RFID and Zigbee technologies for tracking and monitoring patients and assets in Saudi Arabia. In : Proceedings of the IIER 64th International Conference on Science, Innovation and Management (ICSIM); 2015 Jun 5; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.12. Cannistraro G, Cannistraro M. Hypothermia risk, monitoring and environment control in operating rooms. Intl J Heat Technol. 2016; 34(2):165–171.
Article13. Ezzelle J, Rodriguez-Chavez IR, Darden JM, Stirewalt M, Kunwar N, Hitchcock R, et al. Guidelines on good clinical laboratory practice: bridging operations between research and clinical research laboratories. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008; 46(1):18–29.
Article14. Chojnacky M, Miller W, Ripple D, Strouse G. Thermal analysis of refrigeration systems used for vaccine storage. Gaithersburg (MD): National Institute of Standards and Technology;2009.15. World Health Organization. WHO Expert Committee on specifications for pharmaceutical preparations: thirty-ninth report. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2005.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of tertiary hospital nurses' ageism and nursing practice environment on geriatric nursing performance
- The influence of Critical Reflection Competency, Nursing Work Environment and Job Crafting on Person-Centered Care in Tertiary Hospital Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
- An Analysis of Effects of Differential Coinsurance Policy and Utilization of Outpatients Care by Types of Medical Institutions
- A Study On The Factors Influencing Degree Of Job Satisfaction After Implementation Of Hospital Information System
- Impacts of Implementation of Patient Referral System in terms of Medical Expenditures and Medical Utilization