Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2018 Nov;6(6):315-321. 10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.315.
Clinical characteristics of adverse reaction to radiocontrast media in children - A single center experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dongins0@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Drug Safety Monitoring Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2427491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.315
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Radiocontrast media are widely used in medical imaging to improve diagnostic accuracy. However, studies on the adverse reactions of radiocontrast media in children are limited. We aimed to describe the characteristics of adverse reactions to radiocontrast media among children who had a computed tomography scan or magnetic resonance imaging in a tertiary university hospital.
METHODS
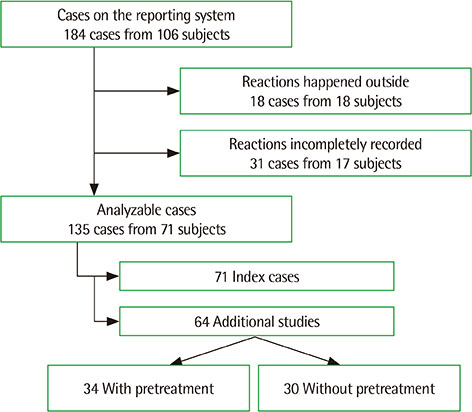
We retrospectively collected data on adverse reactions to radiocontrast media by the reporting system of a tertiary university hospital. We selected data from children under the age of 19 from July 2011 to December 2017 and analyzed their characteristics. We focused mainly on the characteristics of the index case which is defined by the first adverse event of each subject.
RESULTS
During the period, a total of 88,050 radiocontrast media-enhanced imaging studies were performed and 184 cases of adverse reactions were reported. A total of 71 were identified as index cases. Forty-nine (69.0%) were male and the mean age was 12.7±3.2 years. The incidence of radiocontrast media-related adverse reactions was 0.09% and severe reactions were 0.002%. The most common clinical feature was skin manifestations (54.9%), followed by gastrointestinal symptoms (40.8%) and neuropsychiatric symptoms (7.4%).
CONCLUSION
Adverse reactions to radiocontrast media rarely occur in children and the incidence of severe reactions is low. Most reactions are mild and are related to the skin and gastrointestinal system. This report would provide good evidence for establishing a management strategy in children scheduled for imaging studies using radiocontrast media.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Christiansen C. X-ray contrast media-an overview. Toxicology. 2005; 209:185–187.
Article2. Dillman JR, Strouse PJ, Ellis JH, Cohan RH, Jan SC. Incidence and severity of acute allergic-like reactions to i.v. nonionic iodinated contrast material in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:1643–1647.
Article3. Lee SY, Lim KW, Chang YS. Radiocontrast media hypersensitivity in the Asia Pacific region. Asia Pac Allergy. 2014; 4:119–125.
Article4. Beckett KR, Moriarity AK, Langer JM. Safe use of contrast media: what the radiologist needs to know. Radiographics. 2015; 35:1738–1750.
Article5. Bae K, Lee SM, Ha JY, Jeon KN, Moon JI, Choi BH, et al. Adverse drug reactions to CT contrast media in South Korea: incidence and risk factors. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2016; 75:41–48.
Article6. Kyung EJ, Ryu JH, Kim EY. Evaluation of adverse reactions to contrast media in the hospital. Br J Radiol. 2013; 86:20130418.
Article7. Napoleone E. Children and ADRs (Adverse Drug Reactions). Ital J Pediatr. 2010; 36:4.
Article8. Brockow K. Immediate and delayed cutaneous reactions to radiocontrast media. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2012; 97:180–190.
Article9. Brockow K. Immediate and delayed reactions to radiocontrast media: is there an allergic mechanism? Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009; 29:453–468.
Article10. American College of Radiology. ACR manual on contrast media. Version 10.3 [Internet]. Reston (VA): ACR;2017. cited 2018 Aug 9. Available from: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Clinical-Resources/Contrast_Media.pdf.11. Callahan MJ, Poznauskis L, Zurakowski D, Taylor GA. Nonionic iodinated intravenous contrast material-related reactions: incidence in large urban children's hospital-retrospective analysis of data in 12,494 patients. Radiology. 2009; 250:674–681.
Article12. Park BB, Park CH, Nho IY, Kim HS, Kang NK, Chang SI, et al. Prevalence and clinical features of hypersensitivity reaction to contrast media after prescreening skin test. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016; 4:442–448.
Article13. Kim SS, Park CH, Park MJ, Choi SH, Kim YS, Park HW, et al. Adverse reactions to radio-contrast media in computed tomography (CT) in general population: incidence and clinical features. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 27:157–161.14. Bae YJ, Hwang YW, Yoon SY, Kim S, Lee T, Lee YS, et al. The effectiveness of automatic recommending system for premedication in reducing recurrent radiocontrast media hypersensitivity reactions. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e66014.
Article15. Katayama H, Yamaguchi K, Kozuka T, Takashima T, Seez P, Matsuura K. Adverse reactions to ionic and nonionic contrast media. A report from the Japanese Committee on the Safety of Contrast Media. Radiology. 1990; 175:621–628.
Article16. Ho J, Kingston RJ, Young N, Katelaris CH, Sindhusake D. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions to IV non-ionic iodinated contrast in computed tomography. Asia Pac Allergy. 2012; 2:242–247.
Article17. Wang CL, Cohan RH, Ellis JH, Caoili EM, Wang G, Francis IR. Frequency, outcome, and appropriateness of treatment of nonionic iodinated contrast media reactions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 191:409–415.
Article18. Hunt CH, Hartman RP, Hesley GK. Frequency and severity of adverse effects of iodinated and gadolinium contrast materials: retrospective review of 456,930 doses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:1124–1127.
Article19. Mortelé KJ, Oliva MR, Ondategui S, Ros PR, Silverman SG. Universal use of nonionic iodinated contrast medium for CT: evaluation of safety in a large urban teaching hospital. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:31–34.
Article20. Brockow K, Christiansen C, Kanny G, Clément O, Barbaud A, Bircher A, et al. Management of hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media. Allergy. 2005; 60:150–158.
Article21. Ha SO, Kim DY, Sohn YD. Clinical characteristics of adverse reactions to nonionic low osmolality contrast media in patients transferred from the CT room to the emergency room. Springerplus. 2016; 5:929.
Article22. Goksel O, Aydın O, Atasoy C, Akyar S, Demirel YS, Misirligil Z, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to contrast media: prevalence, risk factors and the role of skin tests in diagnosis-a cross-sectional survey. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 155:297–305.
Article23. Idée JM, Pinès E, Prigent P, Corot C. Allergy-like reactions to iodinated contrast agents. A critical analysis. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005; 19:263–281.
Article24. McCormack PL. Iobitridol: a review of its use as a contrast medium in diagnostic imaging. Clin Drug Investig. 2013; 33:155–166.25. Gomi T, Nagamoto M, Hasegawa M, Katoh A, Sugiyama M, Murata N, et al. Are there any differences in acute adverse reactions among five low-osmolar non-ionic iodinated contrast media? Eur Radiol. 2010; 20:1631–1635.
Article26. Petersein J, Peters CR, Wolf M, Hamm B. Results of the safety and efficacy of iobitridol in more than 61,000 patients. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:2006–2011.
Article27. Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan RH, Strouse PJ, Jan SC. Frequency and severity of acute allergic-like reactions to gadolinium-containing i.v. contrast media in children and adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:1533–1538.
Article28. Li A, Wong CS, Wong MK, Lee CM, Au Yeung MC. Acute adverse reactions to magnetic resonance contrast media-gadolinium chelates. Br J Radiol. 2006; 79:368–371.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The efficacy of single premedication with antihistamines for radiocontrast media hypersensitivity
- Clinical Features of Adverse Drug Reactions in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Korea
- A case of anaphylactoid reaction to nonionic radiocontrast media iopromide (Ultravist)
- Management of adverse reaction to iodinated radiocontrast media
- A Delayed, Unusual Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema after Intravascular Administration of Non-Ionic, Low Osmolar Radiocontrast Media for Coronary Angiography