Korean J Radiol.
2018 Feb;19(1):47-53. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.47.
Impact of Pedal Arch Patency on Tissue Loss and Time to Healing in Diabetic Patients with Foot Wounds Undergoing Infrainguinal Endovascular Revascularization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence 50143, Italy. troisimd@gmail.com
- 2Diabetic Foot Center, Local Health Unit of Florence, Florence 50143, Italy.
- KMID: 2425108
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.47
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To retrospectively evaluate the impact of pedal arch quality on tissue loss and time to healing in diabetic patients with foot wounds undergoing infrainguinal endovascular revascularization.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2014 and June 2015, 137 consecutive diabetic patients with foot wounds underwent infrainguinal endovascular revascularization (femoro-popliteal or below-the-knee, arteries). Postprocedural angiography of the foot was used to divide the patients into the following three groups according to the pedal arch status: complete pedal arch (CPA), incomplete pedal arch (IPA), and absent pedal arch (APA). Time to healing and estimated 1-year outcomes in terms of freedom from minor amputation, limb salvage, and survival were evaluated and compared among the three groups.
RESULTS
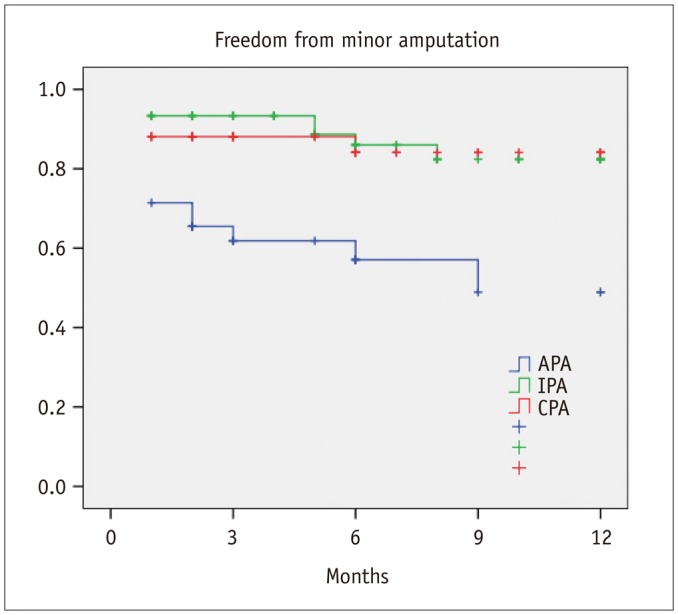
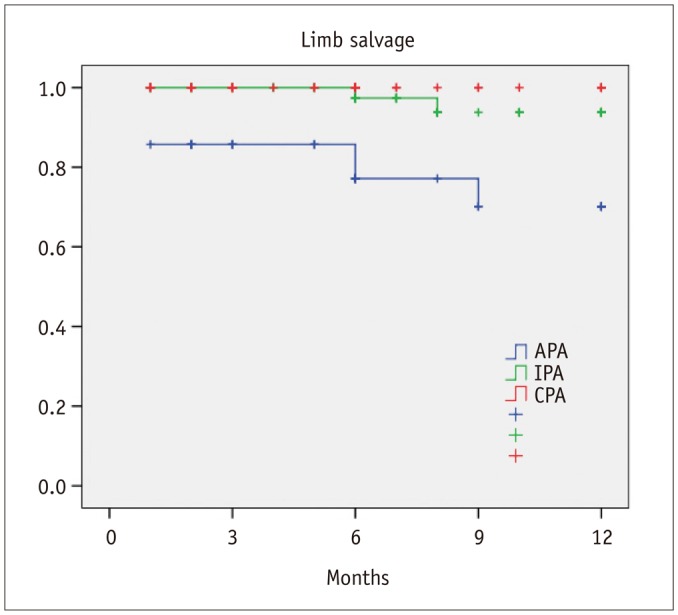
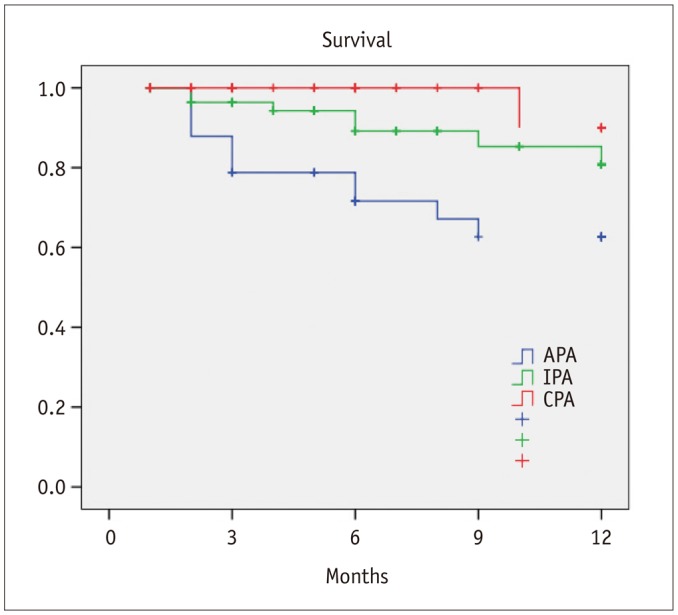
Postprocedural angiography showed the presence of a CPA in 42 patients (30.7%), IPA in 60 patients (43.8%), and APA in 35 patients (25.5%). Healing within 3 months from the procedure was achieved in 21 patients with CPA (50%), 17 patients with IPA (28.3%), and in 7 patients with APA (20%) (p = 0.01). There was a significant difference in terms of 1-year freedom from minor amputation among the three groups (CPA 84.1% vs. IPA 82.4% vs. APA 48.9%, p = 0.001). Estimated 1-year limb salvage was significantly better in patients with CPA (CPA 100% vs. IPA 93.8% vs. APA 70.1%, p < 0.001). Estimated 1-year survival was significantly better in patients with CPA (CPA 90% vs. IPA 80.8% vs. APA 62.7%, p = 0.004).
CONCLUSION
Pedal arch status has a positive impact on time to healing, limb salvage, and survival in diabetic patients with foot wounds undergoing infrainguinal endovascular revascularization.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ramsey SD, Newton K, Blough D, McCulloch DK, Sandhu N, Reiber GE, et al. Incidence, outcomes, and cost of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:382–387. PMID: 10097914.
Article2. Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005; 293:217–228. PMID: 15644549.
Article3. Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, Apelqvist J. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet. 2005; 366:1719–1724. PMID: 16291066.
Article4. Graziani L, Silvestro A, Bertone V, Manara E, Andreini R, Sigala A, et al. Vascular involvement in diabetic subjects with ischemic foot ulcer: a new morphologic categorization of disease severity. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007; 33:453–460. PMID: 17196848.
Article5. Manzi M, Cester G, Palena LM, Alek J, Candeo A, Ferraresi R. Vascular imaging of the foot: the first step toward endovascular recanalization. Radiographics. 2011; 31:1623–1636. PMID: 21997985.
Article6. Karacagil S, Almgren B, Bowald S, Eriksson I. Arterial lesions of the foot vessels in diabetic and non-diabetic patients undergoing lower limb revascularisation. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1989; 3:239–244. PMID: 2744155.
Article7. Ciavarella A, Silletti A, Mustacchio A, Gargiulo M, Galaverni MC, Stella A, et al. Angiographic evaluation of the anatomic pattern of arterial obstructions in diabetic patients with critical limb ischaemia. Diabete Metab. 1993; 19:586–589. PMID: 8026611.8. Karacagil S, Almgren B, Lörelius LE, Bowald S, Eriksson I. Angiographic runoff patterns in patients undergoing lower limb revascularization. Acta Chir Scand. 1989; 155:19–24. PMID: 2929199.9. Rashid H, Slim H, Zayed H, Huang DY, Wilkins CJ, Evans DR, et al. The impact of arterial pedal arch quality and angiosome revascularization on foot tissue loss healing and infrapopliteal bypass outcome. J Vasc Surg. 2013; 57:1219–1226. PMID: 23523278.
Article10. Manzi M, Fusaro M, Ceccacci T, Erente G, Dalla Paola L, Brocco E. Clinical results of below-the knee intervention using pedalplantar loop technique for the revascularization of foot arteries. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2009; 50:331–337.11. Gandini R, Del Giudice C, Simonetti G. Pedal and plantar loop angioplasty: technique and results. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2014; 55:665–670.12. Palena LM, Manzi M. Antegrade pedal approach for recanalizing occlusions in the opposing circulatory pathway of the foot when a retrograde puncture is not possible. J Endovasc Ther. 2014; 21:775–778. PMID: 25453877.
Article13. Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, Harkless LB. Validation of a diabetic wound classification system. The contribution of depth, infection, and ischemia to risk of amputation. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:855–859. PMID: 9589255.
Article14. Lea Thomas M, Tanqueray AB, Burnand KG. Visualization of the plantar arch by aortography: technique and value. Br J Radiol. 1988; 61:469–472. PMID: 3370428.15. O'Mara CS, Flinn WR, Neiman HL, Bergan JJ, Yao JS. Correlation of foot arterial anatomy with early tibial bypass patency. Surgery. 1981; 89:743–752. PMID: 7245037.16. Gloviczki P, Bower TC, Toomey BJ, Mendonca C, Naessens JM, Schabauer AM, et al. Microscope-aided pedal bypass is an effective and low-risk operation to salvage the ischemic foot. Am J Surg. 1994; 168:76–84. PMID: 8053532.
Article17. Davidson JT 3rd, Callis JT. Arterial reconstruction of vessels in the foot and ankle. Ann Surg. 1993; 217:699–708. discussion 708-710. PMID: 8507116.
Article18. Nakama T, Watanabe N, Kimura T, Ogata K, Nishino S, Furugen M, et al. Clinical implications of additional pedal artery angioplasty in critical limb ischemia patients with infrapopliteal and pedal artery disease. J Endovasc Ther. 2016; 23:83–91. PMID: 26442951.
Article19. Nakama T, Watanabe N, Haraguchi T, Sakamoto H, Kamoi D, Tsubakimoto Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of pedal artery angioplasty for patients with ischemic wounds: results from the multicenter RENDEZVOUS registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017; 10:79–90. PMID: 28057289.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Algorithm for the Revascularization of Infrainguinal Arterial Disease
- Clinical analysis of the communicating artery between the dorsal and plantar aspects of the foot
- Transcutaneous Oxygen Pressure to Predict Wound Healing in Mild Diabetic Feet
- Advancements in Endovascular Therapy for Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: A Focus on Below-the-Ankle Interventions and Wound Healing Strategies
- Serum Collagen Level as a Predictor of Healing Wounds in Diabetic Foot Patients