Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Oct;32(5):391-399. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0102.
Effects of Early Postoperative Intraocular Pressure after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation on Long-term Surgical Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckpark@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2422069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0102
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the long-term effects of early postoperative intraocular pressure (IOP) after Ahmed glaucoma valve (AGV) implantation on long-term surgical outcomes.
METHODS
This retrospective, non-randomized study included 100 eyes of 100 patients who underwent AGV surgery. We divided the enrolled patients into four groups according to the presence of transient hypotony within the first postoperative week or the presence of a hypertensive phase during the first three postoperative months. Postoperative IOP, the number of glaucoma medications, and cumulative success rate were compared among the groups.
RESULTS
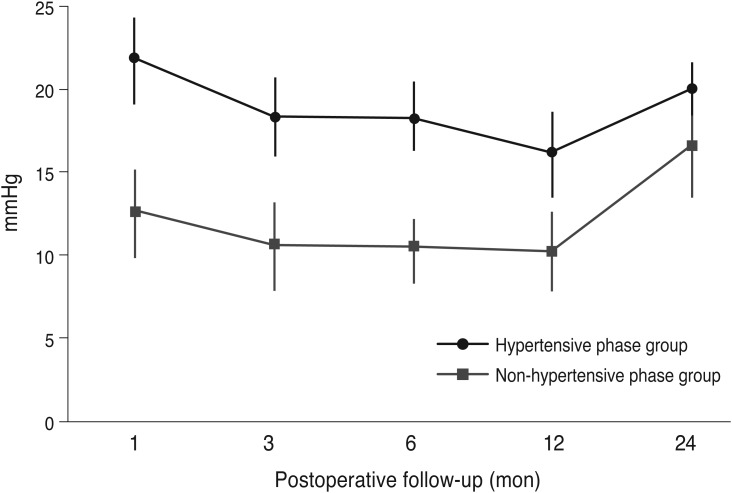
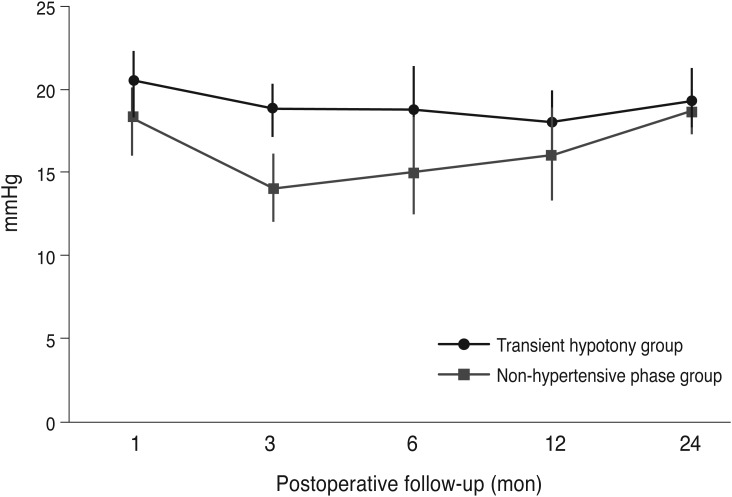
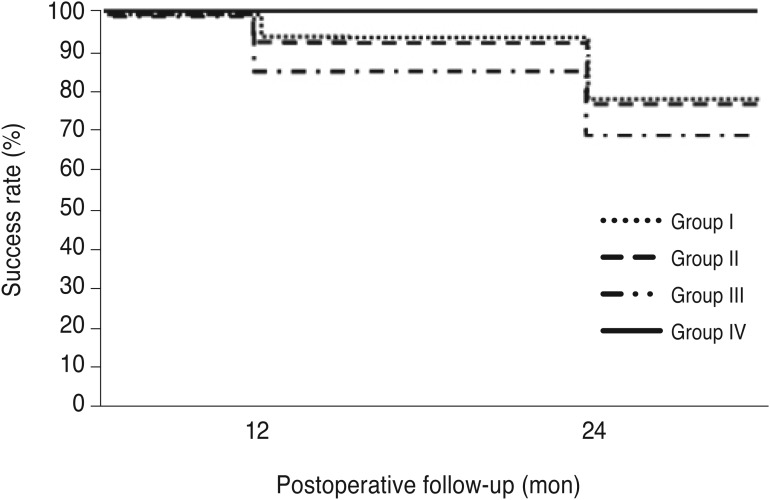
There was significantly better IOP control and a better success rate in the non-hypertensive phase group 2 years postoperatively. However, no significant difference was found in the IOP or success rate at 2 years postoperatively between the transient hypotony and non-hypotony groups. Further subgroup analysis showed that the non-hypotony, non-hypertensive phase group had a significantly higher success rate (100%) at 2 years postoperatively.
CONCLUSIONS
We can predict the long-term prognosis after AGV implantation by considering the early postoperative IOP state and the presence of a hypertensive phase.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rosenberg LF, Krupin T. Implants in glaucoma surgery. In : Ritch R, Shields MB, Krupin T, editors. The glaucomas. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;1996. p. 1783–1807.2. Schwartz K, Budenz D. Current management of glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:119–126. PMID: 15021223.
Article3. Ceballos EM, Parrish RK 2nd, Schiffman JC. Outcome of Baerveldt glaucoma drainage implants for the treatment of uveitic glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:2256–2260. PMID: 12466167.
Article4. Wilson MR, Mendis U, Smith SD, Paliwal A. Ahmed glaucoma valve implant vs trabeculectomy in the surgical treatment of glaucoma: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:267–273. PMID: 11020403.
Article5. Siegner SW, Netland PA, Urban RC Jr, et al. Clinical experience with the Baerveldt glaucoma drainage implant. Ophthalmology. 1995; 102:1298–1307. PMID: 9097766.
Article6. Wilson RP, Cantor L, Katz LJ, et al. Aqueous shunts: Molteno versus Schocket. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:672–676. PMID: 1594210.7. Coleman AL, Smyth RJ, Wilson MR, Tam M. Initial clinical experience with the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant in pediatric patients. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997; 115:186–191. PMID: 9046253.
Article8. Coleman AL, Hill R, Wilson MR, et al. Initial clinical experience with the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 120:23–31. PMID: 7611326.
Article9. Huang MC, Netland PA, Coleman AL, et al. Intermediate-term clinical experience with the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve implant. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 127:27–33. PMID: 9932995.10. Park HY, Lee NY, Park CK. Risk factors of shallow anterior chamber other than hypotony after Ahmed glaucoma valve implant. J Glaucoma. 2009; 18:44–48. PMID: 19142134.
Article11. Ayyala RS, Zurakowski D, Smith JA, et al. A clinical study of the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant in advanced glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:1968–1976. PMID: 9787371.12. Nouri-Mahdavi K, Caprioli J. Evaluation of the hypertensive phase after insertion of the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:1001–1008. PMID: 14644209.
Article13. Fellenbaum PS, Almeida AR, Minckler DS, et al. Krupin disk implantation for complicated glaucomas. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1178–1182. PMID: 8035980.
Article14. Ayyala RS, Zurakowski D, Monshizadeh R, et al. Comparison of double-plate Molteno and Ahmed glaucoma valve in patients with advanced uncontrolled glaucoma. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2002; 33:94–101. PMID: 11942556.
Article15. Won HJ, Sung KR. Hypertensive phase following silicone plate Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation. J Glaucoma. 2016; 25:e313–e317. PMID: 25774945.
Article16. Yuen D, Buys Y, Jin YP, et al. Corticosteroids versus NSAIDs on intraocular pressure and the hypertensive phase after Ahmed glaucoma valve surgery. J Glaucoma. 2011; 20:439–444. PMID: 20852441.
Article17. Molteno TE, Dempster AG. Methods of controlling bleb fibrosis around drainage implants. In : Mills KB, editor. Fourth international symposium of the Northern Eye Institute. 1st ed. Manchester, UK: Pergamon Press;1988. p. 192–211.18. Lloyd MA, Sedlak T, Heuer DK, et al. Clinical experience with the single-plate Molteno implant in complicated glaucomas: update of a pilot study. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:679–687. PMID: 1594211.19. Heuer DK, Lloyd MA, Abrams DA, et al. Which is better? One or two? A randomized clinical trial of single-plate versus double-plate Molteno implantation for glaucomas in aphakia and pseudophakia. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:1512–1519. PMID: 1454316.20. Budenz DL, Barton K, Feuer WJ, et al. Treatment outcomes in the Ahmed Baerveldt Comparison Study after 1 year of follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:443–452. PMID: 20932583.
Article21. Law SK, Kornmann HL, Giaconi JA, et al. Early aqueous suppressant therapy on hypertensive phase following glaucoma drainage device procedure: a randomized prospective trial. J Glaucoma. 2016; 25:248–257. PMID: 25265004.22. Pakravan M, Rad SS, Yazdani S, et al. Effect of early treatment with aqueous suppressants on Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation outcomes. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:1693–1698. PMID: 24819857.
Article23. Rachmiel R, Trope GE, Buys YM, et al. Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation in uveitic glaucoma versus open-angle glaucoma patients. Can J Ophthalmol. 2008; 43:462–467. PMID: 18711462.
Article24. Da Mata AP, Foster CS. Ahmed valve and uveitic glaucoma. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1999; 39:155–167. PMID: 10083913.
Article25. Ozdal PC, Vianna RN, Deschenes J. Ahmed valve implantation in glaucoma secondary to chronic uveitis. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:178–183. PMID: 15761478.26. Gil-Carrasco F, Salinas-VanOrman E, Recillas-Gispert C, et al. Ahmed valve implant for uncontrolled uveitic glaucoma. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 1998; 6:27–37. PMID: 9798191.
Article27. Kotliar KE, Kozlova TV, Lanzl IM. Postoperative aqueous outflow in the human eye after glaucoma filtration surgery: biof luidmechanical considerations. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2009; 54:14–22. PMID: 19182869.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-Term Results of Ahmed Valve Implantation in Neovascular Glaucoma and the Effects of Intracameral Bevacizumab
- Ahmed Valve Implantation for Refractory Glaucoma following Pars Plana Vitrectomy
- Clinical Experience with the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implant in Refractory Glaucoma
- Two Cases of Malignant Glaucoma after Ahmed Valve Implantation
- Tissue Incarceration after Ahmed Valve Implantation