Ann Lab Med.
2019 Jan;39(1):86-90. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.86.
Performance Evaluation of the Beckman Coulter DxN VERIS Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Assay in Comparison With the Abbott RealTime HBV Assay
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ejoh@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Catholic Laboratory Development and Evaluation Center, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Samkwang Medical Laboratories, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2420276
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.86
Abstract
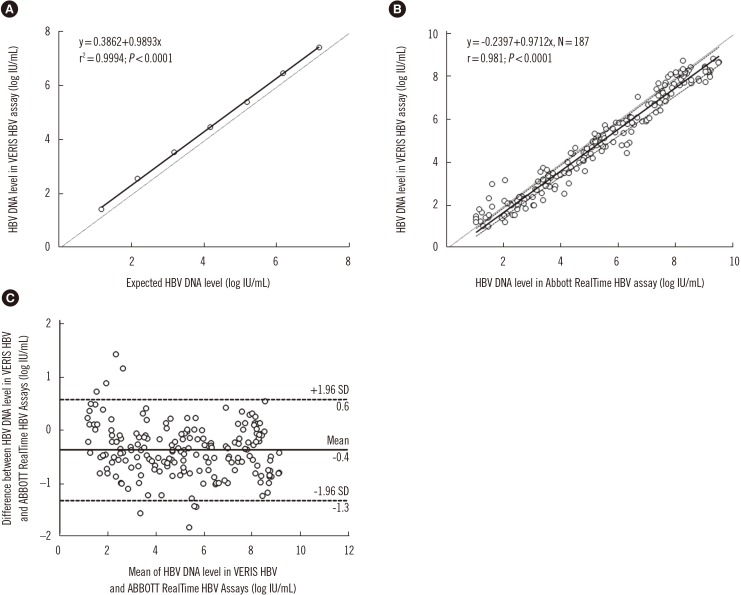
- The detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA plays an important role in diagnosing and monitoring HBV infection as well as in assessing the therapeutic response. We compared the analytical performance of a random access, fully automated HBV assay"”DxN VERIS Molecular Diagnostics System (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA)"”with that of Abbott RealTime HBV assay (Abbott Laboratories, Des Plaines, IL, USA). The between-day precision of the VERIS assay ranged from 0.92% (mean 4.68 log IU/mL) to 4.15% (mean 2.09 log IU/mL) for pooled sera from HBV patients. HBV DNA levels measured by the VERIS HBV assay correlated with the calculated HBV DNA levels (r²=0.9994; P < 0.0001). The lower limit of quantification was estimated as 8.76 IU/mL (Probit analysis, 95% confidence interval: 7.32-12.00 IU/mL). Passing-Bablok regression analysis showed good concordance between the VERIS and RealTime assays for 187 chronic HBV samples (y=−0.2397+0.9712x; r=0.981), as well as for 20 drug-resistant HBV genotype C positive samples (y=−0.5415+0.9954x; r=0.961). The VERIS assay demonstrated performance similar to the RealTime assay and is suitable for high-throughput HBV DNA monitoring in large hospital laboratories.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schweitzer A, Horn J, Mikolajczyk RT, Krause G, Ott JJ. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet. 2015; 386:1546–1555. PMID: 26231459.2. Zhang Q, Liao Y, Cai B, Li Y, Li L, Zhang J, et al. Incidence of natural resistance mutations in naïve chronic hepatitis B patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 30:252–261. PMID: 25318660.3. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017; 67:370–398. PMID: 28427875.4. Han MS, Park Y, Nah H, Kim HS. Comparison of the QIAGEN artus HBV QS-RGQ assay with the Roche COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HBV assay for quantifying viral DNA in sera of chronic Hepatitis B patients. Ann Lab Med. 2017; 37:248–253. PMID: 28224771.5. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH, et al. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016; 63:261–283. PMID: 26566064.6. Pawlotsky JM, Dusheiko G, Hatzakis A, Lau D, Lau G, Liang TJ, et al. Virologic monitoring of hepatitis B virus therapy in clinical trials and practice: recommendations for a standardized approach. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:405–415. PMID: 18242209.7. Chevaliez S, Bouvier-Alias M, Laperche S, Hézode C, Pawlotsky JM. Performance of version 2.0 of the Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan Real-time PCR assay for hepatitis B virus DNA quantification. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:3641–3647. PMID: 20720031.8. Chevaliez S, Rodriguez C, Pawlotsky JM. New virologic tools for management of chronic hepatitis B and C. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:1303–1313.e1. PMID: 22537437.9. Yeh ML, Huang CF, Hsieh MY, Huang JF, Dai CY, Yu ML, et al. Comparison of the Abbott RealTime HBV assay with the Roche Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan HBV assay for HBV DNA detection and quantification. J Clin Virol. 2014; 60:206–214. PMID: 24809730.10. Fourati S, Challine D, Poveda JD, Laperche S, Rallier S, Pawlotsky JM, et al. Evaluation of a new random-access HBV DNA molecular assay: The VERIS HBV assay. J Clin Virol. 2017; 92:69–74. PMID: 28549336.11. Braun P, Delgado R, Drago M, Fanti D, Fleury H, Izopet J, et al. A European multicentre study on the comparison of HBV viral loads between VERIS HBV assay and Roche COBAS® TAQMAN® HBV test, Abbott RealTime HBV assay, Siemens VERSANT HBV assay, and Qiagen artus HBV RG kit. J Clin Virol. 2017; 95:76–83. PMID: 28892764.12. The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016; 22:18–75. PMID: 27044762.13. Huh HJ, Park JE, Kim JY, Yun SA, Lee MK, Lee NY, et al. Performance of the Real-Q EBV quantification kit for Epstein-Barr virus DNA quantification in whole blood. Ann Lab Med. 2017; 37:147–150. PMID: 28029001.14. Kim H, Hur M, Kim JY, Moon HW, Yun YM, Cho HC. Automated nucleic acid extraction systems for detecting cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus using real-time PCR: a comparison study between the QIAsymphony RGQ and QIAcube systems. Ann Lab Med. 2017; 37:129–136. PMID: 28028999.15. Park JE, Kim JY, Yun SA, Lee MK, Huh HJ, Kim JW, et al. Performance evaluation of the Real-Q cytomegalovirus (CMV) quantification kit using two real-time PCR systems for quantifying CMV DNA in whole blood. Ann Lab Med. 2016; 36:603–606. PMID: 27578516.16. Cho JH, Yoon KH, Lee KE, Park DS, Lee YJ, Moon HB, et al. Distribution of hepatitis B virus genotypes in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2009; 15:140–147. PMID: 19581766.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance Evaluation of Hologic Panther Aptima System to Detect HBV, HCV, and HIV-1 Infections: A Comparison with Abbott Alinity m System
- Performance Evaluations of the Abbott Alinity m Assay in Comparison with the Abbott m2000 Assay for Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Viruses
- Performance Evaluation of Abbott RealTime HBV Quantification Kit for HBV Viral Load by Real-Time PCR
- Comparison of Hybrid Capture System, Hybrid Capture II and Quantiplex HBV DNA Assay for Quantitation of Hepatitis B Virus DNA
- Comparison of Hepatitis B Virus Detection by Direct Hybridization Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction