Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2017 Nov;60(6):616-620. 10.5468/ogs.2017.60.6.616.
Persistent low-level elevation of serum human chorionic gonadotropin after termination of pregnancy: a rare case of peritoneal trophoblastic implant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Paul's Hospital, College of medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jiyoungk@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2418367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.6.616
Abstract
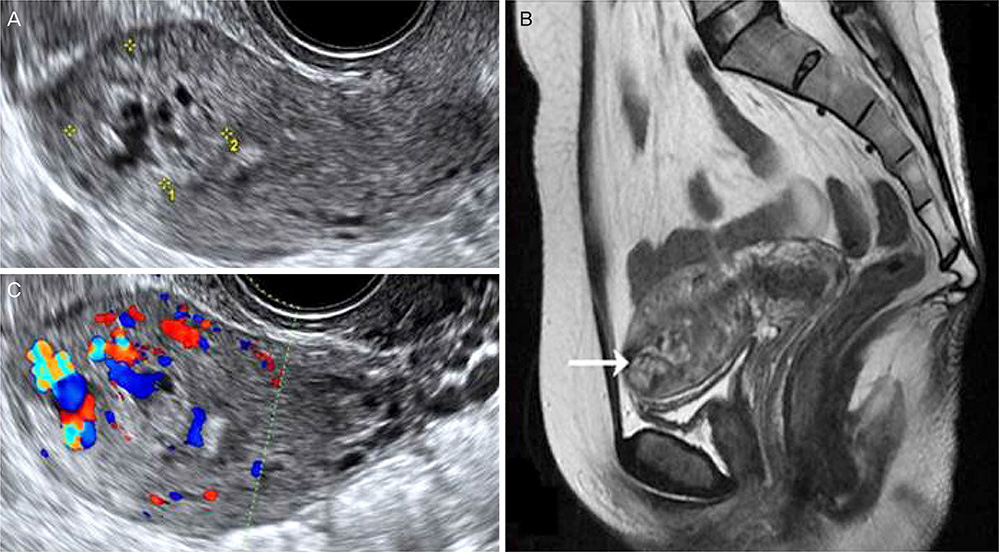
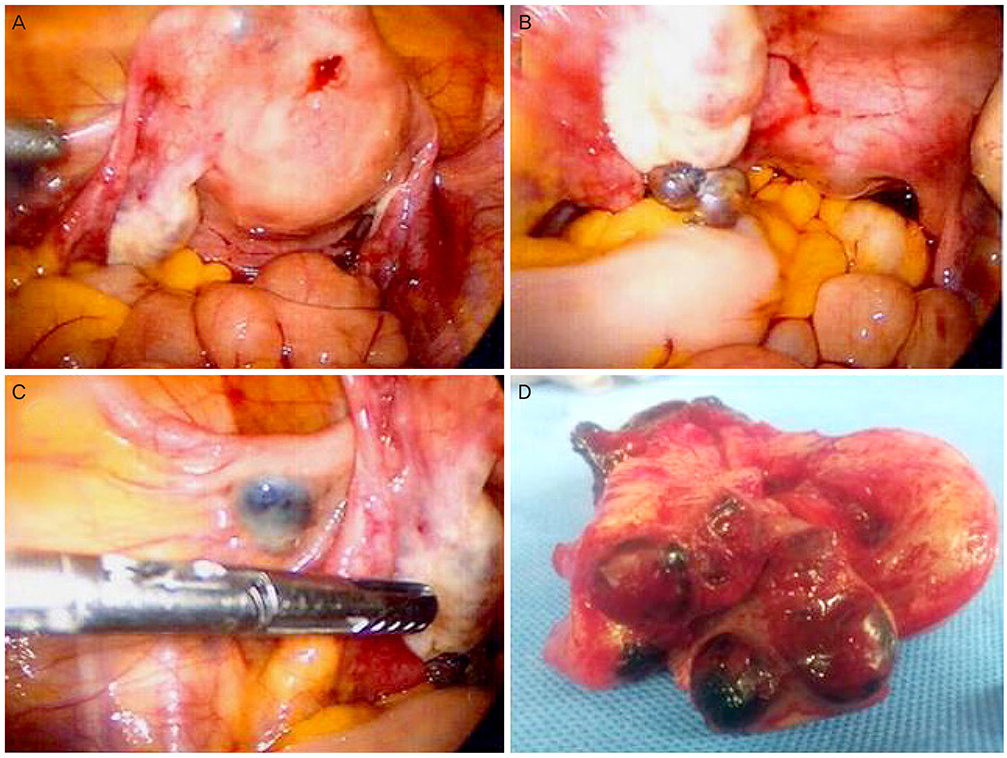
- Peritoneal trophoblastic implant can occur after treatment of ectopic pregnancy. Similarly, after termination of intrauterine pregnancy, trophoblastic implants are rare but can be a complication of perforation during dilatation and curettage. We report an extremely rare case of trophoblastic implant on the myometrium, ovarian surface, and peritoneal wall 4 months after uncomplicated dilatation and curettage. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of peritoneal trophoblastic implant following dilatation and curettage without uterine perforation. Knowledge of this case is useful for the management of patients with persistent low-level elevation of serum human chorionic gonadotropin after termination of pregnancy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kohorn EI. Persistent low-level “real” human chorionic gonadotropin: a clinical challenge and a therapeutic dilemma. Gynecol Oncol. 2002; 85:315–320.2. Cole LA, Khanlian SA, Giddings A, Butler SA, Muller CY, Hammond C, et al. Gestational trophoblastic diseases: 4. Presentation with persistent low positive human chorionic gonadotropin test results. Gynecol Oncol. 2006; 102:165–172.3. Qian XQ, Chen LL, Li BH, Cheng XD, Wan XY. Long-term outcome of patients with persistent low-level elevation of human chorionic gonadotrophin. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016; 42:694–700.4. Muller CY, Cole LA. The quagmire of hCG and hCG testing in gynecologic oncology. Gynecol Oncol. 2009; 112:663–672.5. Ben-Arie A, Goldchmit R, Dgani R, Hazan Y, Ben-Hur H, Open M, et al. Trophoblastic peritoneal implants after laparoscopic treatment of ectopic pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2001; 96:113–115.6. Levin I, Grisaru D, Pauzner D, Almog B. Trophoblastic tissue spread to the sigmoid colon after uterine perforation. Obstet Gynecol. 2004; 104:1172–1174.7. Pascual MA, Tresserra F, Dexeus D, Grases PJ, Dexeus S. Myometrial trophoblastic implant as a complication of surgically induced first-trimester termination of pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 22:194–195.8. Lam PM, Yim SF, Leung TN. Entrapment of viable trophoblastic tissue in a uterine hematoma after surgical evacuation. A case report. J Reprod Med. 2002; 47:170–172.9. Bucella D, Buxant F, Anaf V, Simon P, Fayt I, Noël JC. Omental trophoblastic implants after surgical management of ectopic pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2009; 280:115–117.10. Cole LA, Butler SA, Khanlian SA, Giddings A, Muller CY, Seckl MJ, et al. Gestational trophoblastic diseases: 2. Hyperglycosylated hCG as a reliable marker of active neoplasia. Gynecol Oncol. 2006; 102:151–159.11. Seckl MJ, Sebire NJ, Berkowitz RS. Gestational trophoblastic disease. Lancet. 2010; 376:717–729.12. Kim JH, Lee SK, Hwang SH, Kim JS, Yoon G, Lee YY, et al. Extrauterine epithelioid trophoblastic tumor in hysterectomized woman. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2017; 60:124–128.13. Lima LL, Parente RC, Maestá I, Amim J Junior, de Rezende Filho JF, Montenegro CA, et al. Clinical and radiological correlations in patients with gestational trophoblastic disease. Radiol Bras. 2016; 49:241–250.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Persistent Gestational Trophoblastic Disease after Complete Hydatidiform Mole
- A case of treatment of peritoneal trophoblastic tissue implants after laparoscopic salpingectomy
- Patterns of the decline in serum beta-human chorionic gonadotropin level in patients with tubal pregnancy following surgery by pelviscopy and by laparotomy
- The value of elevated second trimester human chorionic gonadotropin levels in predicting development of pregnancy - induced hypertension
- A Case of Choriocarcinoma following Term Pregnancy