J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2007 Nov;32(6):483-490.
The palato-gingival groove - anatomical anomaly occurred in maxillary lateral incisors: case reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Korea. mksdd@wonkwang.ac.kr
Abstract
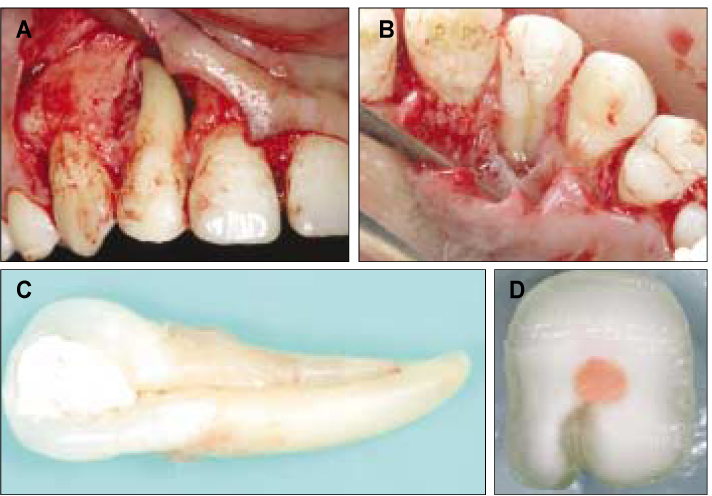
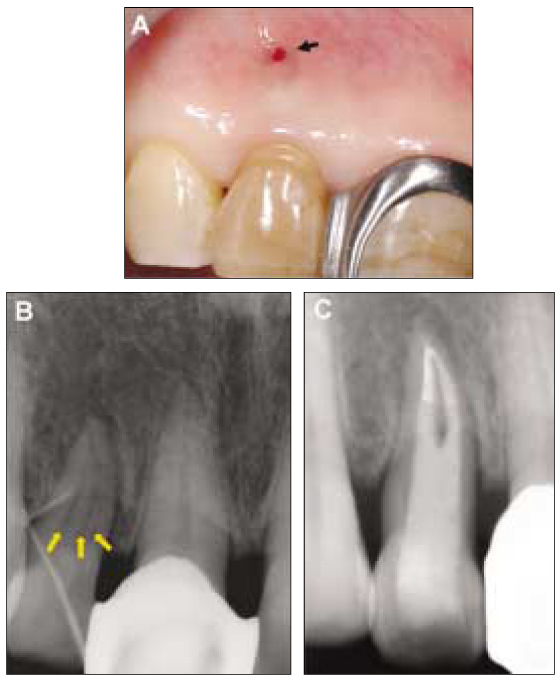
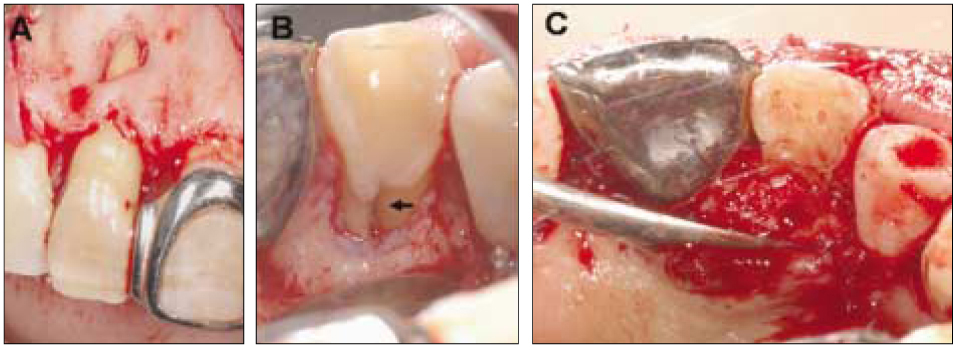
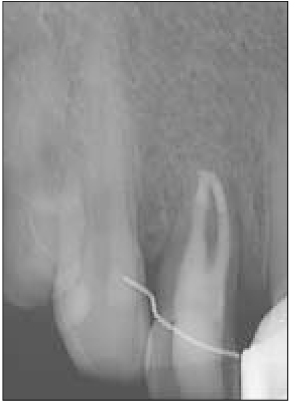
- This report describes clinical cases of a palato-gingival groove on a maxillary lateral incisor with associated localized periodontal disease and pulp necrosis. The tooth of the first case was extracted because of severe bone destruction. The palato-gingival groove of the second case was eliminated using a round bur, and the resulting defect was filled with synthetic graft and covered by an absorbable membrane. Both diagnosis and treatment of palato-gingival groove were very difficult and usually extraction of the involved tooth is the treatment of choice, but combined endodontic-periodontic treatment allowed the tooth to be saved.
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Association of Endodontists. Glossary of endodontic terms. 2003. 7th ed. Chicago, IL:2. Lee KW, Lee EC, Poon RY. Palato-gingival grooves in maxillary incisors. A possible predisposing factor to localized periodontal disease. Br Dent J. 1968. 124:14–18.3. Simon JH, Glick DH, frank AL. Predictable endodontic and periodontic failure as a result of radicular anomalies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1971. 31:823–826.
Article4. Ennes JP, Lara VS. Comparative morphological analysis of the root developmental groove with the palate-gingivalgroove. Oral Dis. 2004. 10:378–382.
Article5. Everett FG, Kramer GM. The disto-lingual groove in the maxillary lateral incisor; a periodontal hazard. J Periodontol. 1972. 43:352–361.
Article6. August DS. The radicular lingual groove: an overlooked differential diagnosis. J Am Dent Assoc. 1978. 96:1037–1039.
Article7. Kogon SL. The prevalence, location and conformation of palato-radicular grooves in maxillary incisors. J Periodontol. 1986. 57:231–234.
Article8. Pecora JD, Sousa Neto MD, Santos TC, Saquy PC. In vitro study of the incidence of radicular grooves in maxillary incisors. Braz Dent J. 1991. 2:69–73.9. Assaf ME, Roller N. The cingulo-radicular groove: its significance and management - two case report. Compendium. 1992. 13:94. 96. 98 passim.10. Schwartz SA, Koch MA, Deas DE, Powell CA. Combined endodontic-periodontic treatment of a palatal groove: a case report. J Endod. 2006. 32:573–578.
Article11. Withers JA, Brunsvold MA, Killoy WJ, Rahe AJ. The relationship of palato-gingival grooves to localized periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1981. 52:41–44.
Article12. Rosling B, Nyman S, Lindhe J. The effect of systematic plaque control on bone regeneration in infrabony pocket. J Clin Periodontol. 1976. 3:38–53.
Article13. Fabra Campos H, Millet Part J. Developmental radicular groove as a cause of endodontic failure. Rev Esp Endodoncia. 1989. 7:118–123.14. Pack AR, Chandler NP. A combined endodontic-periodontal lesion of development origin: a case report. N Z Dent J. 1996. 92:46–48.15. Peikoff MD, Trott JR. An endodontic failure caused by an unusual anatomical anomaly. J Endod. 1977. 3:356–359.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical management with intentional replantation on a tooth with palato-radicular groove
- Study of Normative Gingival Proportion in Anterior Maxilla
- Correlation between degree of gingival curvature and gingival recession in orthognathic surgery patients
- Color Distribution of Maxillary Permanent Incisors in Korean Pediatric Patients Using a Spectrophotometer
- Color Comparison of Maxillary Primary Anterior Teeth and Various Composite Resins using a Spectrophotometer