J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Jun;59(6):505-510. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.6.505.
Effect of the Corneal Incision Direction Using an Image-guided System on Residual Astigmatism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. sara514@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2413812
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.6.505
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated the effect of corneal incision direction using an image-guided system on cataract surgery.
METHODS
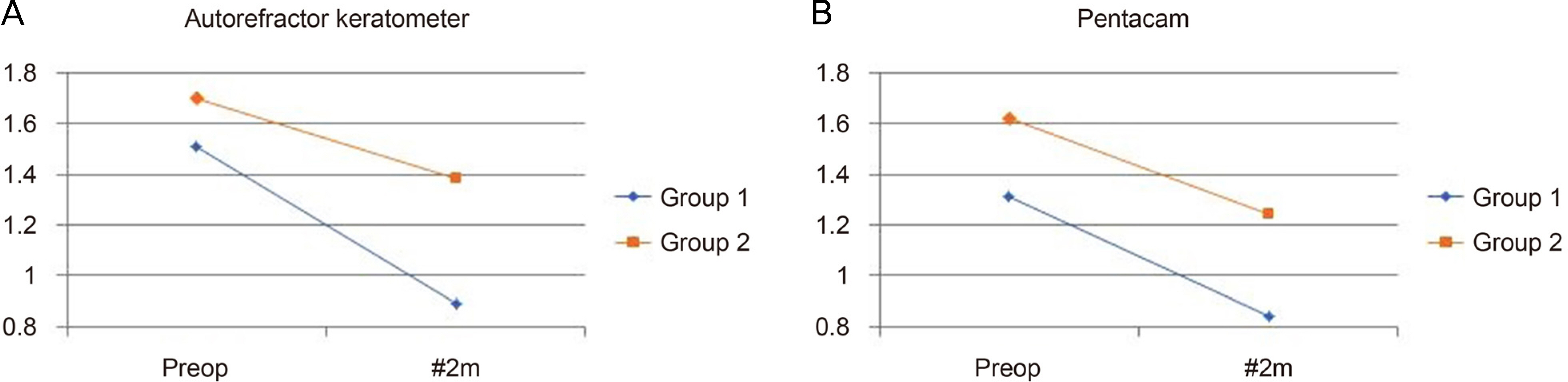
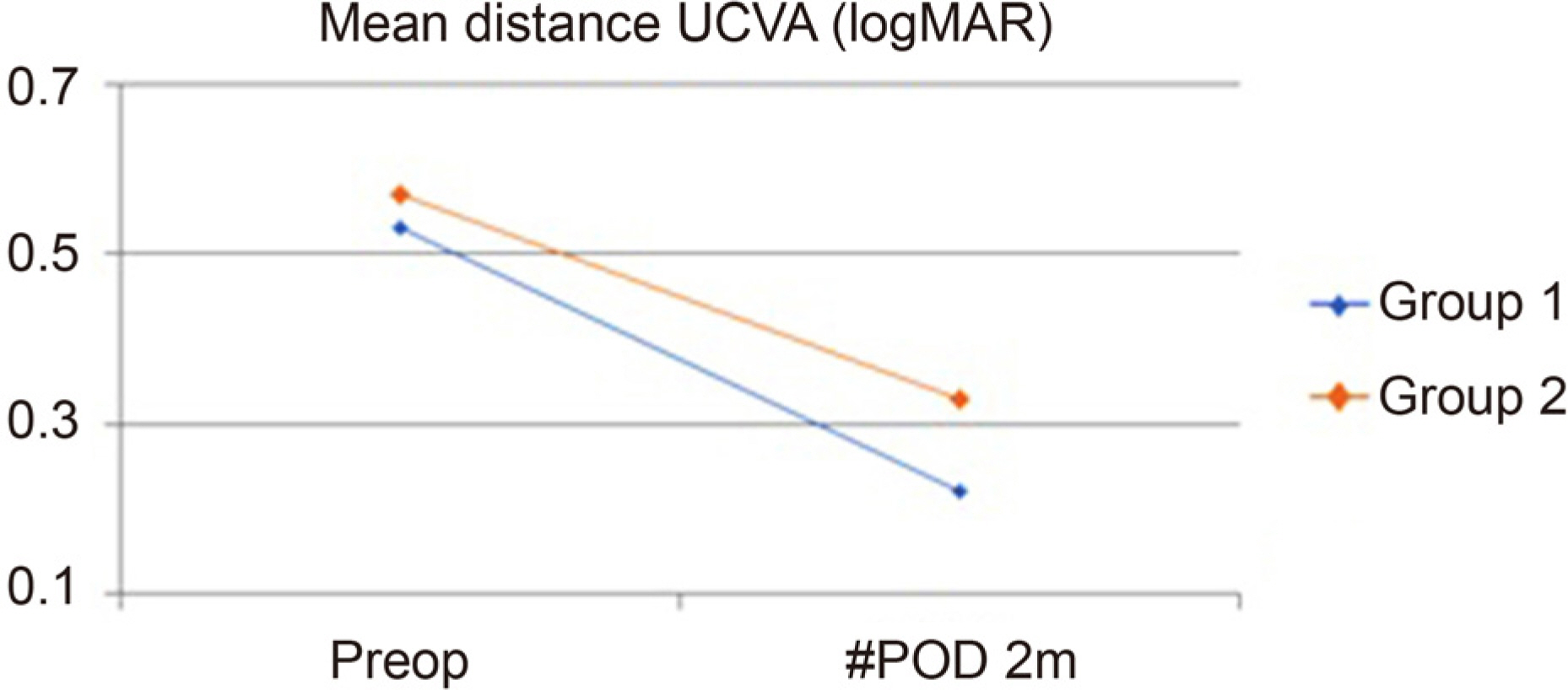
We retrospectively reviewed patients who underwent cataract surgery at The Catholic University of Korea Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital. The patients were divided into two groups. In group 1 (20 eyes), the corneal incision was made along the steepest axis using the VERION image-guided system (Alcon, Fort Worth, TX, USA). In the control group, group 2 (20 eyes), the incision was made at the vertical or horizontal axis closest to the patient's steepest axis. We compared residual astigmatism and the mean difference in astigmatism before and after cataract surgery between the two groups using an autorefractor keratometer (RK-F1®; Canon, Tokyo, Japan) and a Pentacam system (Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany).
RESULTS
Group 1's residual astigmatism was significantly lower than that of group 2 ([VERION group 1; before, 0.89 ± 0.58 D; after, 0.84 ± 0.51 D; p = 0.049] and [control group 2; before, 1.38 ± 0.62 D; after, 1.24 ± 0.62 D; p = 0.043]). The mean difference in astigmatism before and after cataract surgery for group 1 was also larger than group 2 ([VERION group 1; before, 0.71 ± 0.81 D; after, 0.61 ± 0.69 D; p = 0.034] and [control group 2; before, 0.61 ± 0.69 D; after, 0.43 ± 0.61 D; p = 0.048]).
CONCLUSIONS
Using an image-guided system, postoperative residual astigmatism from cataract surgery can be minimized using an incision direction that is aligned with the corneal astigmatic axis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ferrer-Blasco T, Montés-Micó R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:70–5.
Article2. Li Z, Han Y, Hu B, et al. Effect of Limbal relaxing incisions during implantable collamer lens surgery. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017; 17:63.
Article3. Qin B, Li M, Chen X, et al. Early visual outcomes and optical abdominal after femtosecond laser small-incision lenticule extraction for myopia and myopic astigmatism correction of over-10 dioptres. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018; 96:e341–6.4. Blehm C, Potvin R. Pseudophakic astigmatism reduction with abdominal laser-assisted corneal arcuate incisions: a pilot study. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017; 11:201–7.5. Borasio E, Mehta JS, Maurino V. Surgically induced astigmatism after phacoemulsification in eyes with mild to moderate corneal abdominal: temporal versus on-axis clear corneal incisions. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:565–72.6. Shentu X, Zhang X, Tang X, Yu X. Coaxial microincision cataract surgery versus standard coaxial small-incision cataract surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0146676.
Article7. Zhao F, Li L, Zhou W, et al. Correlative factors' analysis of postur-al-related ocular cyclotorsion with image-guided system. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2018; 62:237–42.
Article8. Ahmed II, Rocha G, Slomovic AR, et al. Visual function and abdominal experience after bilateral implantation of toric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:609–16.9. Bauer NJ, de Vries NE, Webers CA, et al. Astigmatism abdominal in cataract surgery with the AcrySof toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1483–8.10. Entabi M, Harman F, Lee N, Bloom PA. Injectable 1-piece abdominal acrylic toric intraocular lens for cataract surgery: efficacy and stability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:235–40.11. Mendicute J, Irigoyen C, Aramberri J, et al. Foldable toric abdominal lens for astigmatism correction in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:601–7.12. Poll JT, Wang L, Koch DD, Weikert MP. Correction of astigmatism during cataract surgery: toric intraocular lens compared to abdominal corneal relaxing incisions. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:165–71.13. Carvalho MJ, Suzuki SH, Freitas LL, et al. Limbal relaxing abdominals to correct corneal astigmatism during phacoemulsification. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:499–504.14. Velasco-Barona C, Cervantes-Coste G, Mendoza-Schuster E, et al. Comparison of biometric measurements obtained by the Verion Image-Guided System versus the auto-refracto-keratometer. Int Ophthalmol 2017 Apr 25. doi:. DOI: 10.1007/s10792-017-0541-3. [Epub ahead of print].
Article15. Asena L, Güngör SG, Akman A. Comparison of keratometric measurements obtained by the Verion Image Guided System with optical biometry and auto-keratorefractometer. Int Ophthalmol. 2017; 37:391–9.
Article16. Ruiz-Belda C, Rodrigo F, Piñero DP. Validation of keratometric measurements obtained with an intraoperative image-guided abdominal: abdominal repeatability and interchangeability with an abdominalal biometer. Clin Exp Optom. 2018; 101:200–5.17. Nemeth G, Szalai E, Hassan Z, et al. Repeatability data and abdominal of keratometry with the VERION system compared to the IOLMaster. J Refract Surg. 2015; 31:333–7.18. Lin HY, Chen HY, Fam HB, et al. Comparison of corneal power abdominal from VERION image-guided surgery system and four other devices. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017; 11:1291–9.19. Webers VS, Bauer NJ, Visser N, et al. Image-guided system versus manual marking for toric intraocular lens alignment in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017; 43:781–8.
Article20. Artal P, Guirao A, Berrio E, Williams DR. Compensation of corneal aberrations by the internal optics in the human eye. J Vis. 2001; 1:1–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Change of Corneal Astigmatism Following Varying Incision Locations and Methods for Cataract Surgery in Case of Against-the-Rule Astigmatism
- Comparison of Refractive Power and Astigmatism between Digital Keratometer and Autorefractor
- Corneal Astigmatism after Cataract Surgery: The Effect of Electrocautery
- Corneal Astigmatic Change after 3.2mm Temporal Clear Corneal Incision in Cataract Surgery: Comparative Study with 3.2mm Superior Scleral Incision
- Pseudophakic Residual Astigmatism