Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Apr;38(2):167-173.
The Comparison of Effects of Suprascapular Nerve Block, Intra-articular Steroid Injection, and a Combination Therapy on Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dong-Eui Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. oggum@naver.com
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the relative effectiveness of three injections methods suprascapular nerve block (SSNB) alone, intra-articular steroid injection (IAI) alone, or both-on relief of hemiplegic shoulder pain.
METHODS
We recruited 30 patients with hemiplegic shoulder pain after stroke. SSNB was performed in 10 patients, IAI in 10 patients, and a combination of two injections in 10 patients. All were ultrasonography guided. Each patient's maximum passive range of motion (ROM) in the shoulder was measured, and the pain intensity level was assessed with a visual analogue scale (VAS). Repeated measures were performed on pre-injection, and after injection at 1 hour, 1 week, and 1 month. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis and Friedman tests.
RESULTS
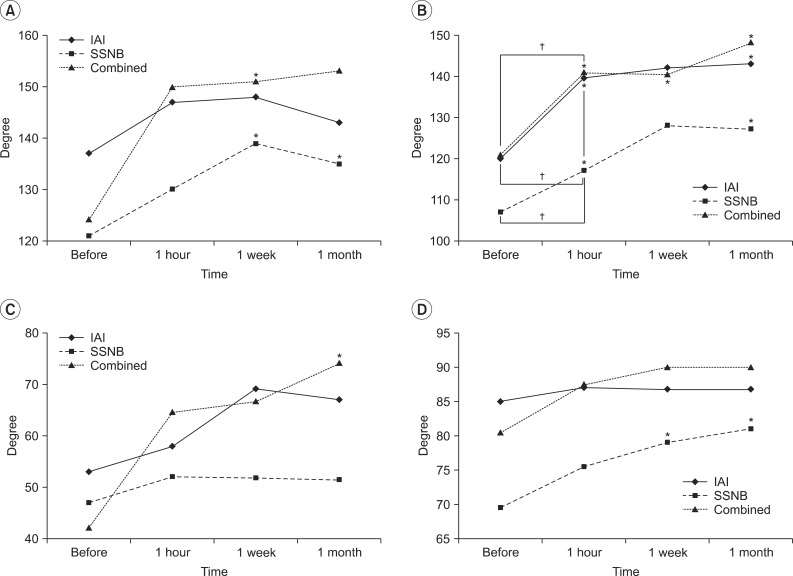
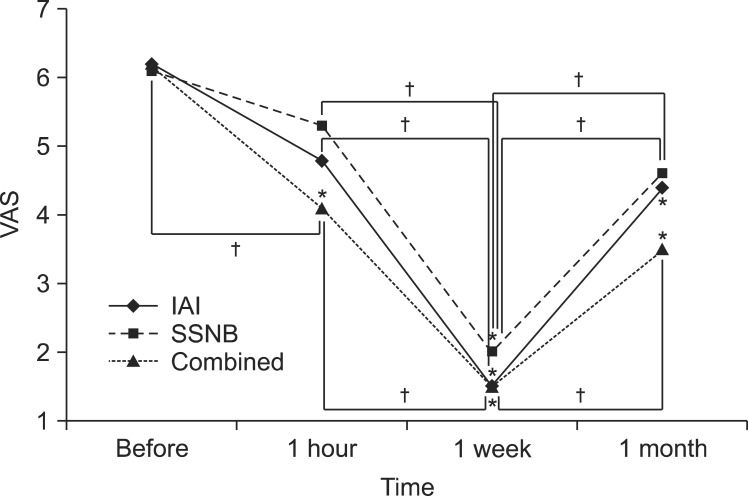
All variables that were repeatedly measured showed significant differences in shoulder ROM with time (p<0.05), but there was no difference according injection method. In addition, VAS was statistically significantly different with time, but there was no difference by injection method. Pain significantly decreased until a week after injection, but pain after a month was relatively increased. However, pain was decreased compared to pre-injection.
CONCLUSION
The three injection methods significantly improved shoulder ROM and pain with time, but no statistically significant difference was found between them.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Broeks JG, Lankhorst GJ, Rumping K, Prevo AJ. The long-term outcome of arm function after stroke: results of a follow-up study. Disabil Rehabil. 1999; 21:357–364. PMID: 10503976.2. Chantraine A, Baribeault A, Uebelhart D, Gremion G. Shoulder pain and dysfunction in hemiplegia: effects of functional electrical stimulation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999; 80:328–331. PMID: 10084443.
Article3. Jespersen HF, Jorgensen HS, Nakayama H, Olsen TS. Shoulder pain after a stroke. Int J Rehabil Res. 1995; 18:273–276. PMID: 7499042.
Article4. Najenson T, Yacubovich E, Pikielni SS. Rotator cuff injury in shoulder joints of hemiplegic patients. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1971; 3:131–137. PMID: 5156175.5. Krotenberg R. Shoulder pain in hemiplegia. Adv Clin Rehabil. 1990; 3:189–196. PMID: 2257044.6. Wanklyn P, Forster A, Young J. Hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP): natural history and investigation of associated features. Disabil Rehabil. 1996; 18:497–501. PMID: 8902421.
Article7. Snels IA, Dekker JH, van der Lee JH, Lankhorst GJ, Beckerman H, Bouter LM. Treating patients with hemiplegic shoulder pain. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:150–160. PMID: 11807352.
Article8. Dekker JH, Wagenaar RC, Lankhorst GJ, de Jong BA. The painful hemiplegic shoulder: effects of intraarticular triamcinolone acetonide. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1997; 76:43–48. PMID: 9036910.10. Aras MD, Gokkaya NK, Comert D, Kaya A, Cakci A. Shoulder pain in hemiplegia: results from a national rehabilitation hospital in Turkey. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:713–719. PMID: 15314536.11. Jonsson AC, Lindgren I, Hallstrom B, Norrving B, Lindgren A. Prevalence and intensity of pain after stroke: a population based study focusing on patients' perspectives. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006; 77:590–595. PMID: 16354737.
Article12. Joynt RL. The source of shoulder pain in hemiplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992; 73:409–413. PMID: 1580765.13. Yoon TS, Kim DH, Park JW, Kwon BS, Ryu KH, Lee HJ, et al. Causes of the hemiplegic shoulder pain. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:158–162.14. Teasell R, Foley N, Bhogal SK, Salter K. Management of post stroke pain [Internet]. London, Canada: Evidence-Based Review of Stroke Rehabilitation;2012. cited 2014 Mar 1. Available from: http://www.ebrsr.com/~ebrsr/uploads/Appendix-Pain.pdf.15. Teasell RW, Foley NC, Bhogal SK, Speechley MR. An evidence-based review of stroke rehabilitation. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2003; 10:29–58. PMID: 12970830.
Article16. Niessen MH, Veeger DH, Meskers CG, Koppe PA, Konijnenbelt MH, Janssen TW. Relationship among shoulder proprioception, kinematics, and pain after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:1557–1564. PMID: 19735784.
Article17. Boyd EA, Torrance GM. Clinical measures of shoulder subluxation: their reliability. Can J Public Health. 1992; 83(Suppl 2):S24–S28. PMID: 1468045.18. Van Ouwenaller C, Laplace PM, Chantraine A. Painful shoulder in hemiplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1986; 67:23–26. PMID: 3942479.19. Davis SW, Petrillo CR, Eichberg RD, Chu DS. Shoulder-hand syndrome in a hemiplegic population: a 5-year retrospective study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1977; 58:353–356. PMID: 69426.20. Veldman PH, Reynen HM, Arntz IE, Goris RJ. Signs and symptoms of reflex sympathetic dystrophy: prospective study of 829 patients. Lancet. 1993; 342:1012–1016. PMID: 8105263.
Article21. Gokkaya NK, Aras M, Yesiltepe E, Koseoglu F. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy in hemiplegia. Int J Rehabil Res. 2006; 29:275–279. PMID: 17106342.22. Lo SF, Chen SY, Lin HC, Jim YF, Meng NH, Kao MJ. Arthrographic and clinical findings in patients with hemiplegic shoulder pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:1786–1791. PMID: 14669184.23. Kim MS, Moon ES. Treatment of shoulder pain using ultrasound-guided intervention. J Korean Orthop Ultrasound Soc. 2011; 4:50–58.24. Snels IA, Beckerman H, Twisk JW, Dekker JH, De Koning P, Koppe PA, et al. Effect of triamcinolone acetonide injections on hemiplegic shoulder pain: a randomized clinical trial. Stroke. 2000; 31:2396–2401. PMID: 11022070.25. Boonsong P, Jaroenarpornwatana A, Boonhong J. Preliminary study of suprascapular nerve block (SSNB) in hemiplegic shoulder pain. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009; 92:1669–1674. PMID: 20043571.26. Taskaynatan MA, Yilmaz B, Ozgul A, Yazicioglu K, Kalyon TA. Suprascapular nerve block versus steroid injection for non-specific shoulder pain. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2005; 205:19–25. PMID: 15635270.
Article27. Yasar E, Vural D, Safaz I, Balaban B, Yilmaz B, Goktepe AS, et al. Which treatment approach is better for hemiplegic shoulder pain in stroke patients: intra articular steroid or suprascapular nerve block? A randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2011; 25:60–68. PMID: 20943716.28. Yi TI, Kim ST, Kim DH, Kim JS, Park JS, Lee JH. Comparison of blind technique and ultrasonography guided technique of intraarticular injection of the shoulder. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2006; 30:45–50.29. Lee JH, Kim SB, Lee KW, Joe YL, Kim YD. Comparison of blind and ultasonography guided approach of suprascapular nerve block. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:219–224.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Suprascapular Nerve Block versus Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection in Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain
- Comparison of Suprascapular Nerve Block and Shoulder Joint Injection for Treatment of Frozen Shoulder
- Effects of Intra-Articular Injection and Subscapularis Motor Point Block on Painful Hemiplegic Shoulder
- Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block Following Suprascapular Nerve Block for Humeral Head Surgery in a Patient with Difficult Supine Position: A case report
- Comparison of Blind and Ultasonography Guided Approach of Suprascapular Nerve Block