J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs.
2017 Mar;26(1):101-110. 10.12934/jkpmhn.2017.26.1.101.
Effects of Team-Based Learning on Communication Competence for Undergraduate Nursing Students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Gwangju Women's University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2School of Nursing, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. yrk@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2397828
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2017.26.1.101
Abstract
- PURPOSE
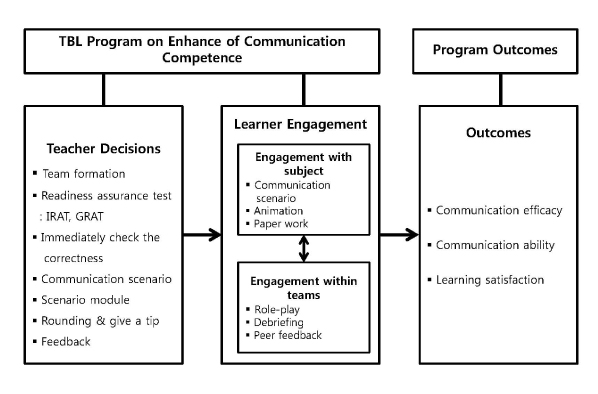
In this study an examination was done of the effects of a team-based learning program on enhancement of communication competence for undergraduate nursing students in South Korea.
METHODS
quasi-experimental method with a non-equivalent control group pre- and post-test design was used. Participants were 68 undergraduate nursing students recruited from two universities. The experimental group (n=35) received a 5-week team-based learning program on enhancement of communication competence, while the control group (n=33) received traditional lectures. Data were collected using self-report structured questionnaires before and after the intervention, and were analyzed using χ² tests, Fisher's exact tests, and t-tests.
RESULTS
Compared to the control group, the experimental group reported significant positive changes in communication efficacy (t=2.58, p=.012), communication ability (t=12.01, p<.001), and learning satisfaction (t=2.11, p=.039).
CONCLUSION
The findings indicate that this program is an effective intervention strategy to enhance communication competence for nursing students.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Accreditation Board of Nursing Education. Accreditation assessment standard for education of Korea. [Internet]. 2012. cited 2014 Feb 23. Available from: http://kabon.or.kr/kabon02/120120319133351.pdf.2. Kim HK. Influence of interpersonal relations, communication skills, creative behaviors and nursing service on self-leadership among nurses in hospital. Clin Nurs Res. 2007; 13(1):25–36.3. Idczak SE. I am a nurse: Nursing students learn the art and science of nursing. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2007; 28(2):66–71. DOI: 10.1043/1536-5026(2007)028[0066:IAANNS]2.0.CO;2.4. Son HM, Kim HS, Ko MH, Yu SJ. Analysis of the communication education in the undergraduate nursing curriculum of Korea. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2011; 17(3):426–434. DOI: 10.5977/JKASNE.2011.17.3.424.
Article5. Yoo MS, Chae SM. Effects of peer review on communication skills and learning motivation among nursing students. J Nurs Educ. 2011; 50(4):230–233. DOI: 10.3928/01484834-20110131-03.
Article6. Lubeck P, Tschetter L, Mennenga H. Team-based learning: An innovative approach to teaching maternal-newborn nursing care. J Nurs Educ. 2013; 52(2):112–115. DOI: 10.3928/01484834-20130121-02.
Article7. Michaelsen LK, Parmelee DX, McMahon KK, Levine RE, editors. Team-based learning for health professions education: A guide to using small groups for improving learning. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing;2008.8. Haidet P, Levin RE, Parmelee DX, Crow S, Kennedy F, Kelly PA, et al. Perspective: Guidelines for reporting team-based learning activities in the medical and health sciences education literature. Acad Med. 2012; 87(3):292–299. DOI: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318244759e.9. Roh YS, Ryoo EN, Choi DW, Baek SS, Kim SS. A survey of student perceptions, academic achievement, and satisfaction of team-based learning in a nursing course. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012; 18(2):239–247. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2012.18.2.239.
Article10. Cho AR, Han SI, Yoon SH, Park JH, Yoo NJ, Kim S. Methods of effective Team-based learning administration and expected effects on medical education. Korean J Med Educ. 2010; 22(1):47–55. DOI: 10.3946/kjme.2010.22.1.47.
Article11. Thomas PA, Bowen CW. A controlled trial of team-based learning in an ambulatory medicine clerkship for medical students. Teach Learn Medicat. 2011; 23(1):31–36. DOI: 10.1080/10401334.2011.536888.
Article12. Thompson BM, Schneider VF, Haidet P, Levine RE, McMahon KK, Perkowski LC, et al. Team-based learning at ten medical schools: Two years later. Med Educ. 2007; 41(3):250–257. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02684.x.
Article13. Clark MC, Nguyen HT, Bray C, Levine RE. Team-based learning in an undergraduate nursing course. J Nurs Educ. 2008; 47(3):111–117.
Article14. Kang HY, Choi EY, Kim HR. Nursing student's experiences in team based simulation learning. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2013; 19(1):5–15. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2013.19.1.5.
Article15. Kim SO, Kim SM. Effects of team-based learning applying for nursing students on critical thinking ability, problem solving ability and communication ability. J Korean Data Anal Soc. 2016; 18(2B):1151–1161.16. Sisk RJ. Team-based learning: Systematic research review. J Nurs Educ. 2011; 50(12):665–669. DOI: 10.3928/01484834-20111017-01.
Article17. Ayres HW. Factors related to motivation to learn and motivation to transfer learning in a nursing population [dissertation]. Los Angeles: North Carolina State University;2005. 325. https://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.16/3773.18. Park SY, Kweon YR. The effect of using standardized patients in psychiatric nursing practice training for nursing college students. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2012; 21(1):79–88. DOI: 10.12934/jkpmhn.2012.21.1.79.
Article19. Rubin RB, Martin MM, Bruning SS, Power DE. Interpersonal communication competence: Scale development and test of a self-efficacy model. Paper presented at: The meeting of the communication association. 1991; Atlanta.20. Hur GH. Construction and validation of a global interpersonal communication competence scale. Korean J Journal Commun Stud. 2003; 47(6):380–408.21. Kang EJ, Cheon SM. The effect of a group cinematherapy program on the emotional regulation ability and problem behaviors of the youth at-risk. Korean J Youth Couns. 2011; 19(2):23–46.
Article22. Midgley C, Kaplan A, Middleton M. Performance approach goals: Good for what, for whom, under that circumstances, and at what cost. J Educ Psychol. 2001; 93(1):77–86. DOI: 10.1037/0022-0663.93.1.77.
Article23. Mennenga HA, Smyer T. A model for easily incorporating team-based learning into nursing education. Int J Nurs Educ Scholarsh. 2010; 7:Article4. DOI: 10.2202/1548-923X.1924.
Article24. Yedidia MJ, Gillespie CC, Kachur E, Ockene J, Chepaitis AE, Snyder CW, et al. Effect of communications training on medical student performance. JAMA. 2003; 290(9):1157–1165. DOI: 10.1001/jama.290.9.1157.
Article25. Kesten KS. Role-play using SBAR technique to improve observed communication skills in senior nursing students. J Nurs Educ. 2011; 50(2):79–87. DOI: 10.3928/01484834-20101230-02.
Article26. Baghcheghi N, Koohestani HR, Rezaei K. A comparison of the cooperative learning and traditional learning methods in theory classes on nursing students' communication skill with patients at clinical settings. Nurse Educ Today. 2011; 31(8):877–882. DOI: 10.1016/j.nedt.2011.01.006.
Article27. Andersen EA, Strumpel C, Fensom I, Andrews W. Implementing team based learning in large classes: Nurse educators' experiences. Int J Nurs Educ Scholarsh. 2011; 8:pii: /j/ijnes.2011.8.issue-1/1548-923X.2197/1548-923X.2197.xml. DOI: 10.2202/1548-923X.2197.
Article28. Arthur C, Kable A, Levett-Jones T. Human patient simulation manikins and information communication technology use in Australian schools of nursing: A cross-sectional survey. Clin Simul Nurs. 2011; 7(6):219–227. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2010.03.002.
Article29. Rosenbaum ME, Ferguson KJ. Using patient-generated cases to teach students skills in responding to patients' emotions. Med Teach. 2006; 28(2):180–182. DOI: 10.1080/01421590500314165.
Article30. Vasan NS, DeFouw DO, Holland BK. Modified use of team based learning for effective delivery of medical gross anatomy and embryology. Anat Sci Educ. 2008; 1(1):3–9. DOI: 10.1002/ase.5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Action-Learning based Simulation Practice Program on Interpersonal Communication Competence and Problem Solving Ability of the Nursing Students
- Effect of Practical Delivery-nursing Simulation Education on Team-based Learning on the Nursing Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Clinical Competence of Nursing Students
- The Effect of the Flipped Learning on Self-efficacy, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Communication Competence of Nursing Students
- The Relationship among Clinical Competence on Diabetic Diet Education Using Standardized Patients, Self-efficacy, Communication, Learning Satisfaction, and Professional Values of Nursing Students
- Effects of Simulation-based Education Combined Team-based Learning on Self-directed Learning, Communication Skills, Nursing Performance Confidence and Team Efficacy in Nursing Students