Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2016 Sep;4(5):382-385. 10.4168/aard.2016.4.5.382.
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with intestinal obstruction after ingesting raw yellow tail fish and oyster
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. sangminlee77@naver.com
- KMID: 2391930
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2016.4.5.382
Abstract
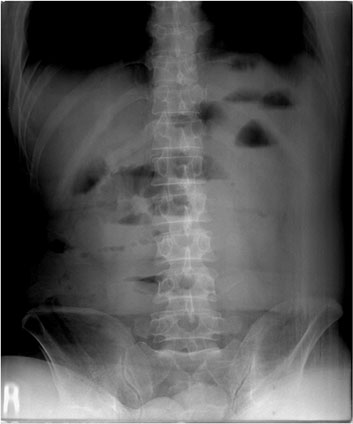
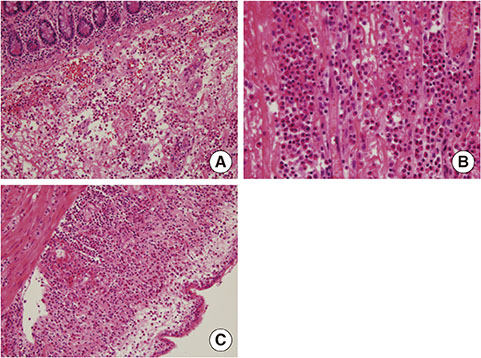
- Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare disease in which the symptoms are associated with eosinophilic infiltration in various layers of the gastrointestinal tract. A 56-year-old man complained of severe abdominal pain after eating yellow tail fish and oyster. There was no peripheral blood eosinophilia in the initial laboratory test. Abdominal computed tomography demonstrated circumferential wall thickening and dilatation of small intestine with ascites. An emergency laparotomy accompanied by segmental resection of the ileum and end-to-end anastomosis was performed. Histologically, there was a dense infiltration of eosinophils throughout the entire layers of ileal wall, through which this case could be diagnosed as eosinophilic enteritis. We did not prescribe systemic glucocorticosteroid, but asked him to avoid fish and oyster. He did not complain of recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms anymore after discharge. This is the case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis with intestinal obstruction requiring emergency surgery, which was developed or aggravated after ingestion of yellow tail fish and oyster that were suspected to be culprit foods. In patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis, foods which are related to this abnormal condition should be identified and avoided to control this disease and prevent from aggravation or flare-up.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Talley NJ, Shorter RG, Phillips SF, Zinsmeister AR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a clinicopathological study of patients with disease of the mucosa, muscle layer, and subserosal tissues. Gut. 1990; 31:54–58.
Article2. Biswas S, Hoo W, Katsoulas N, Munro J, Oke O. Eosinophilic enteritis: a rare cause of abdominal pain. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007; 22:87–88.
Article3. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. In : Adkinson NF, Bochner BS, Burks AW, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF, editors. Middleton's allergy: principles and practice. 8th ed. London: Elsevier Health Saunders;2013. p. 1095–1106.4. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:11–28.
Article5. Lucendo AJ, Arias A. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: an update. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 6:591–601.
Article6. Spergel JM, Book WM, Mays E, Song L, Shah SS, Talley NJ, et al. Variation in prevalence, diagnostic criteria, and initial management options for eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the United States. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 52:300–306.
Article7. Frigas E, Gleich GJ. The eosinophil and the pathophysiology of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986; 77:527–537.
Article8. Yun MY, Cho YU, Park IS, Choi SK, Kim SJ, Shin SH, et al. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis presenting as small bowel obstruction: a case report and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:1758–1760.
Article9. Aguilar-Jiménez J, Jiménez-Ballester MÁ, Valero-Navarro G, Navarro-Martínez MN, Plasencia-Martínez JM, Aguayo-Albasini JL. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis and bowel obstruction. Can surgery be avoided. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2015; 107:185–187.10. Lwin T, Melton SD, Genta RM. Eosinophilic gastritis: histopathological characterization and quantification of the normal gastric eosinophil content. Mod Pathol. 2011; 24:556–563.
Article11. Chen MJ, Chu CH, Lin SC, Shih SC, Wang TE. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: clinical experience with 15 patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2003; 9:2813–2816.
Article12. Liacouras CA, Markowitz JE. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a subset of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 1999; 1:253–258.
Article13. Alexander P, Jacob S, Paul V. Laparoscopy in eosinophilic jejunitis presenting as subacute bowel obstruction: a case report. Trop Gastroenterol. 2003; 24:97–98.14. Antonini F, Saltarelli P, Frieri G, Latella G. Education and Imaging: gastrointestinal: eosinophilic ascites. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:1759.15. Bouhmidi A, Lorente Poyatos R, Romero Cara P, Ibáñez Martín JJ, Casado Caballero F, Quintero Fuientes D, et al. Eosinophilic enteritis as a rare cause of ascites. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 26:480–481.16. Pineton de Chambrun G, Desreumaux P, Cortot A. Eosinophilic enteritis. Dig Dis. 2015; 33:183–189.
Article17. Yan BM, Shaffer EA. Primary eosinophilic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 2009; 58:721–732.
Article18. Khan S. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 19:177–198.
Article19. Lim KC, Tan HK, Rajnakova A, Venkatesh SK. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis presenting with duodenal obstruction and ascites. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2011; 40:379–381.20. Khan S, Orenstein SR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008; 37:333–348.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiographic and pathologic observations of eosinophilic gastroenteritis
- Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Causing Gastro- intestinal Obstruction
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis with Intestinal Obstruction
- Diffuse Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis with Tumor-like Antral Obstruction
- Intestinal Obstruction Caused by Anisakiasis