Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
2017 Jul;6(2):160-163. 10.7774/cevr.2017.6.2.160.
Application of aptamers for assessment of vaccine efficacy
- Affiliations
-
- 1INTERPARK Bio-Convergence Center, Seoul, Korea. sanghwan.seo@imarketkorea.com
- KMID: 2391577
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2017.6.2.160
Abstract
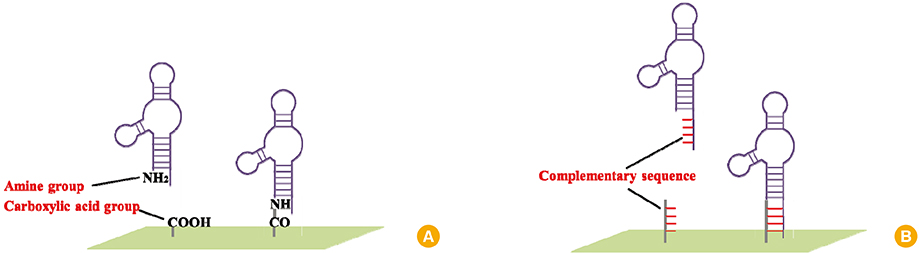
- Assessing antigen concentration of vaccine is essential step in determining the quality of the vaccine prior to vaccination. After vaccination, vaccine-induced antibody titer should also be measured to verify the vaccine efficacy. Since conventional assay used for vaccine concentrations and induced Ab-titers is antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, the assay inevitably brings drawbacks of antibody such as high cost for production, limited stability, and inconsistent quality between lot-to-lots. Aptamer is single-stranded nucleic acid having three-dimensional structure and has features overcoming limitations of antibody. This review will briefly introduce the features of aptamer and potential of aptamer-based system for evaluation of vaccine efficacy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization (WHO). Understanding vaccines [Internet]. PublichHealth;2017. cite 2017 Jun 1. Available from: http://www.publichealth.org/public-awareness/understanding-vaccines/goes-vaccine/.2. Liu JK. The history of monoclonal antibody development: progress, remaining challenges and future innovations. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2014; 3:113–116.
Article3. Stoltenburg R, Reinemann C, Strehlitz B. SELEX: a (r)evolutionary method to generate high-affinity nucleic acid ligands. Biomol Eng. 2007; 24:381–403.
Article4. Tsae PK, DeRosa MC. Outlook for aptamers after twenty five years. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015; 15:1153–1159.
Article5. Toh SY, Citartan M, Gopinath SC, Tang TH. Aptamers as a replacement for antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015; 64:392–403.
Article6. Song S, Wang L, Li J, Zhao J, Fan C. Aptamer-based biosensors. Trends Anal Chem. 2008; 27:108–117.
Article7. Chen L, Rashid F, Shah A, et al. The isolation of an RNA aptamer targeting to p53 protein with single amino acid mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112:10002–10007.
Article8. Bruno JG. Application of DNA aptamers and quantum dots to lateral flow test strips for detection of foodborne pathogens with improved sensitivity versus colloidal gold. Pathogens. 2014; 3:341–355.
Article9. Balamurugan S, Obubuafo A, Soper SA, Spivak DA. Surface immobilization methods for aptamer diagnostic applications. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008; 390:1009–1021.
Article10. Wan Y, Kim YT, Li N, et al. Surface-immobilized aptamers for cancer cell isolation and microscopic cytology. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:9371–9380.
Article11. Higuchi A, Siao YD, Yang ST, et al. Preparation of a DNA aptamer-Pt complex and its use in the colorimetric sensing of thrombin and anti-thrombin antibodies. Anal Chem. 2008; 80:6580–6586.
Article12. Lee KA, Ahn JY, Lee SH, et al. Aptamer-based sandwich assay and its clinical outlooks for detecting lipocalin-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Sci Rep. 2015; 5:10897.
Article13. Trausch JJ, Shank-Retzlaff M, Verch T. Replacing antibodies with modified DNA aptamers in vaccine potency assays. Vaccine. 2017; 04. 19. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.04.003.
Article14. Seo HB, Gu MB. Aptamer-based sandwich-type biosensors. J Biol Eng. 2017; 11:11.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Massive Identification of Cancer-Specific Nucleic Acid Ligands
- Cotinine-conjugated aptamer/anti-cotinine antibody complexes as a novel affinity unit for use in biological assays
- Nucleic Acid Aptamers: New Methods for Selection, Stabilization, and Application in Biomedical Science
- Rotavirus Vaccine
- Recent update in HIV vaccine development