Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Sep;20(3):147-152. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.147.
Important Role of Medical Training Curriculum to Promote the Rate of Human Milk Feeding
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyjoo@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2390545
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.147
Abstract
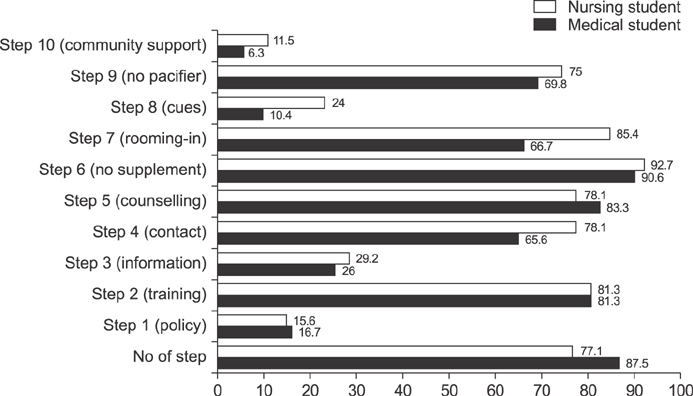
- The rate of human milk feeding has been decreasing despite the diverse efforts of many physicians and nurses, as well as numerous professional organizations and various international health institutions. The number of physicians and nurses who can provide proper guidance for human milk feeding and offer appropriate knowledge and techniques to allow the most beneficial and convenient manner of breastfeeding is quite deficient. It is suggested that physicians and nurses be trained to teach and educate about the medical importance of human milk feeding to lactating mothers. This can be accomplished through systemic changes in medical education and clinical practice. However, the curricula of medical schools in Korea do not provide enough education and training to effect an increase in human milk feeding. The author strongly recommends that the educational objectives for medical schools and resident training offer more education and training concerning so that they are well aware of breastfeeding basics and techniques, and have ability to solve lactation-associated clinical problems.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Positive Effect of Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiatives on Improving Mothers' Intention for Successful Breastfeeding in Korea
Hyun Woo Park, Keun Ho Ryu, Yongjun Piao, Peipei Li, Jae Shik Hong, Hee Bum Kim, Hwanwook Chung, Jeong-Kyu Hoh, Yong Joo Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(43):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e272.Macronutrient Analysis of Human Milk according to Storage and Processing in Korean Mother
Min Hyung Kim, Kyu Seok Shim, Dae Yong Yi, In Seok Lim, Soo Ahn Chae, Sin Weon Yun, Na Mi Lee, Su Yeong Kim, Seung Kim
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(3):262-269. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.3.262.
Reference
-
1. Anderson JW, Johnstone BM, Remley DT. Breast-feeding and cognitive development: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999; 70:525–535.
Article2. World Health Organization and UNICEF. Baby friendly hospital initiative: revised, updated and expanded for integrated care. Section 1: background and implementation [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2009. cited 2017 Jul 2. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/nutrition/files/BFHI_2009_s1.pdf.3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vital signs: hospital practices to support breastfeeding--United States, 2007 and 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011; 60:1020–1025.4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Breastfeeding-related maternity practices at hospitals and birth centers--United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008; 57:621–625.5. O'Connor NR, Tanabe KO, Siadaty MS, Hauck FR. Pacifiers and breastfeeding: a systematic review. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2009; 163:378–382.6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Breastfeeding report cards: progressing toward national breastfeeding goals United States, 2016 [Internet]. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2016. cited 2017 Jul 3. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/pdf/2016breastfeedingreportcard.pdf.7. Lee SS. The 2015 National Survey on Fertility and Family Health and Welfare. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2015. 12. Report No.:2015-31.8. Kim DJ, Kim MH, Chae SM, Kim SE, Kim JH, Cha MR. Health Plan 2020. Sejong: Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea Health Promotion Foundation;2015.9. Choi EJ, Park EJ, Kim HR, Oh MA, Lee NH, Choi JH. Report on the status of BF in Korea by Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2016. p. 10.10. Lu MC, Lange L, Slusser W, Hamilton J, Halfon N. Provider encouragement of breast-feeding: evidence from a national survey. Obstet Gynecol. 2001; 97:290–295.
Article11. Ryan AS, Wenjun Z, Acosta A. Breastfeeding continues to increase into the new millennium. Pediatrics. 2002; 110:1103–1109.
Article12. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Breast-feeding practices: results from the national immunization survey [Internet]. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2013. cited 2017 Jun 25. Available from: https://eclkc.ohs.acf.hhs.gov/nutrition/article/breastfeeding-practices-results-national-immunization-survey.13. Feldman-Winter LB, Schanler RJ, O'Connor KG, Lawrence RA. Pediatricians and the promotion and support of breastfeeding. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008; 162:1142–1149.
Article14. American Academy of Pediatrics. Breastfeeding: welcome to the breastfeeding residency curriculum [Internet]. American Academy of Pediatrics;cited 2017 Jul 27. Available from: https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Breastfeeding/Pages/Residency-Curriculum.aspx.15. American Academy of Pediatrics. Breastfeeding: implementation strategies [Internet]. American Academy of Pediatrics;cited 2017 Jul 27. Available from: https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-healthinitiatives/Breastfeeding/Pages/Implementation-Strategies.aspx.16. Kakrani VA, Rathod Waghela HK, Mammulwar MS, Bhawalkar JS. Awareness about “Ten Steps for Successful Breastfeeding” among medical and nursing students. Int J Prev Med. 2015; 6:40.
Article17. Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine. Educational objectives and skills for the physician with respect to breastfeeding. Breastfeed Med. 2011; 6:99–105.18. Taylor J, Macnamara M, Groskin A, Petras L. Medical student-mothers. R I Med J (2013). 2013; 96:42–45.19. Naylor A, Cataldo J, Creer E. Lactation management curriculum: a faculty guide for schools of medicine, nursing, and nutrition. 4th ed. San Diego: Wellstart International;1999.20. Ogburn T, Espey E, Leeman L, Alvarez K. A breastfeeding curriculum for residents and medical students: a multidisciplinary approach. J Hum Lact. 2005; 21:458–464.
Article21. Lewin LO, O'Connor ME. “BreastfeedingBasics”: webbased education that meets current knowledge competencies. J Hum Lact. 2012; 28:407–413.22. Haughwout JC, Eglash AR, Plane MB, Mundt MP, Fleming MF. Improving residents' breastfeeding assessment skills: a problem-based workshop. Fam Pract. 2000; 17:541–546.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Knowledges and Attitudes about Breast Milk Feeding and Needs for Breast Milk Feeding Education among High School Students
- Breastfeeding in Korea : Problems and Solutions
- Comparison of Maternal Attachment and Maternal Role Confidence between Breast Milk in Sanitary Pack Feeding Infant's Mothers and Bottle Feeding Infant's Mothers of Low Birth Weight Infants in NICU
- A Survey of Breast-Feeding
- A Study on the Incidence of Breast-Feeding by Married Nurses