J Korean Med Assoc.
2017 Aug;60(8):618-621. 10.5124/jkma.2017.60.8.618.
What is needed for the success of national responsibility for dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Repubic of Korea. dwlee@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2388113
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2017.60.8.618
Abstract
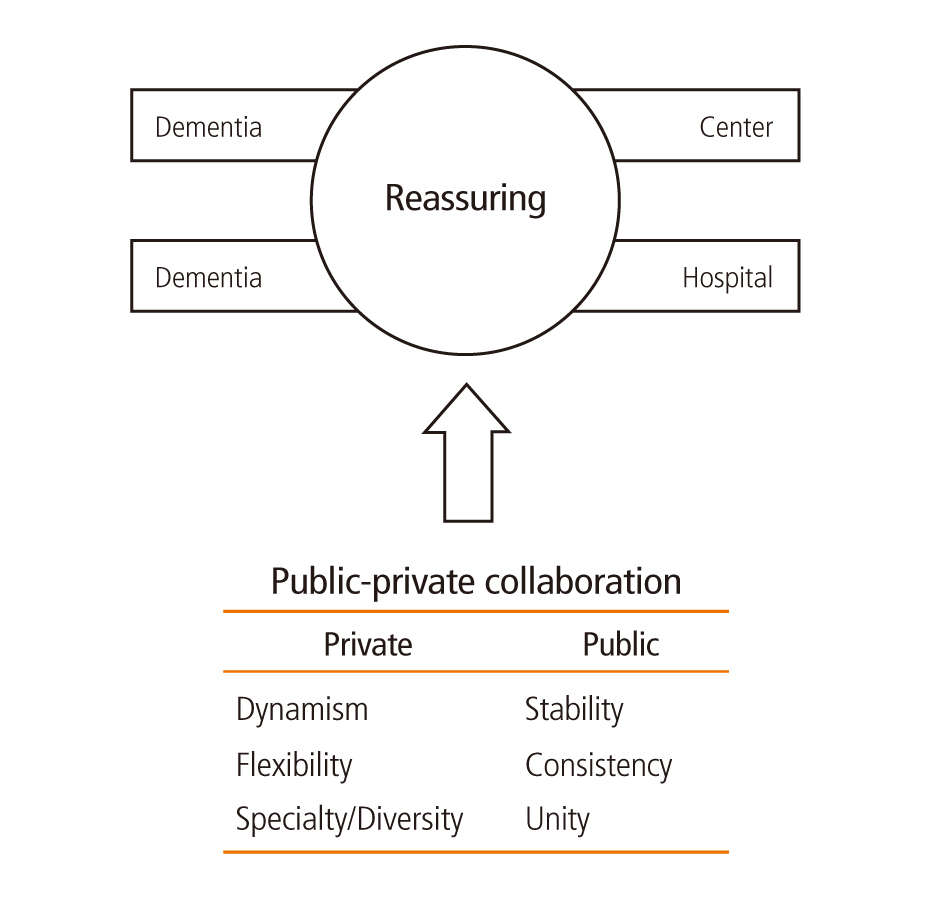
- Dementia is a chronic, disabling illness which is most feared by elderly people. Dementia causes heavy caregiver burden on the family. Dementia also imposes much burden on the society, making it one of the major public health problem in many countries. Actually, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development recommended to pose a priority to dementia management as a public health task. As the Korean population is rapidly aging, there is a rapid increase of people with dementia in Korea. In Korea, the people with dementia doubles every 15 years, and the economic burden of care for dementia doubles every 10 years. To cope with this rapidly increasing burden of dementia, Korean government has launched: plan for national responsibility for dementia. The plan is composed of distributing dementia reassuring center nationwide, setting up dementia reassuring hospital, and decreasing the burden of paid money for medical treatment and long-term care for dementia. The major hurdles in implementing the plan and the strategies to overcome such hurdles by public-private collaboration are suggested.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Clinical Significance of Cognitive Interventions for the Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Seung-Ho Ryu
J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2018;57(1):23-29. doi: 10.4306/jknpa.2018.57.1.23.A Study on Verification of Equivalence and Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacologic Dementia Prevention and Early Detection Contents : Non-Randomly Equivalent Design
Hyun-Seok Jeong, Oh-Lyong Kim, Bon-Hoon Koo, Ki-Hyun Kim, Gi-Hwan Kim, Dai-Seg Bai, Ji-Yean Kim, Mun-Seon Chang, Hye-Geum Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(2):315-324. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0153.
Reference
-
1. National Institute of Dementia. Current condition of demen-tia [Internet]. Seongnam: National Institute of Dementia;cited 2017 Aug 7. Available from: https://www.nid.or.kr/info/diction_list2.aspx?gubun=0201.2. National Institute of Dementia. Korean dementia observatory 2016. Seongnam: National Institute of Dementia;2017.3. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Nationwide survey on the dementia epidemiology of Korea 2012. Seongnam: Seoul National University Bundang Hospital;2012.4. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Survey on dementia elderly. Seongnam: Seoul National University Bundang Hospital;2011.5. World Health Organization. Alzheimer's Disease Interna-tional. Dementia: a public health priority. Geneva: World Health Organization;2012.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Awareness of Dementia National Responsibility of Elders: Oral Health Items
- Policy of national responsibility and dementia care
- National Responsibility Policy for Dementia Care: Current and Future
- Future policy directions for planning of national responsibility for dementia care
- Dementia Incidence Rate Before and After Implementing the National Responsibility Policy for Dementia Care in Patients With Vascular Risk Factors in Korea