J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Jul;32(7):1062-1071. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.7.1062.
Self-Expandable Metallic Stent Placement for the Palliation of Esophageal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hysong@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Biomedical Engineering Center, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2379598
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.7.1062
Abstract
- Esophageal stents have been used to palliate patients with dysphagia caused by esophageal cancer. Early rigid plastic prostheses have been associated with a high risk of complications. However, with the development of self-expanding stents, it has developed into a widely accepted method for treating malignant esophageal strictures and esophagorespiratory fistulas (ERFs). The present review covers various aspects of self-expanding metallic stent placement for palliating esophageal cancer, including its types, placement procedures, indications, contraindications, complications, and some of innovations that will become available in the future.
MeSH Terms
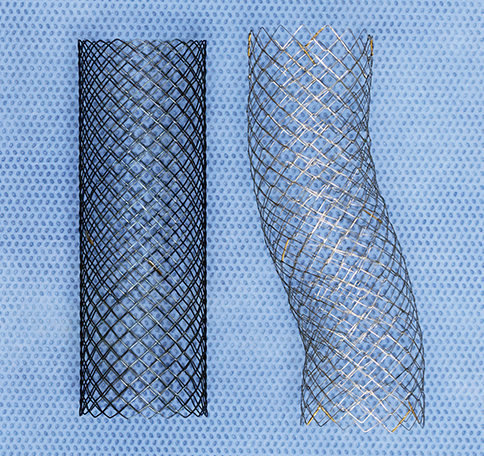
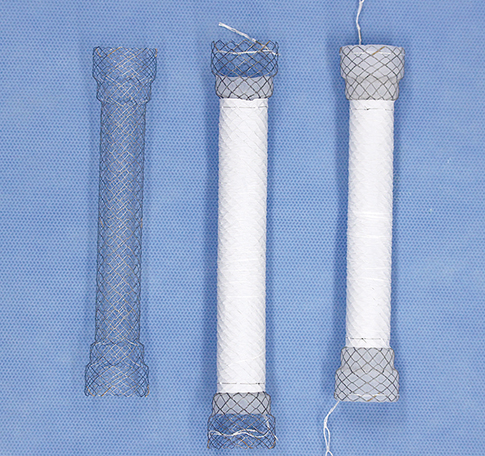
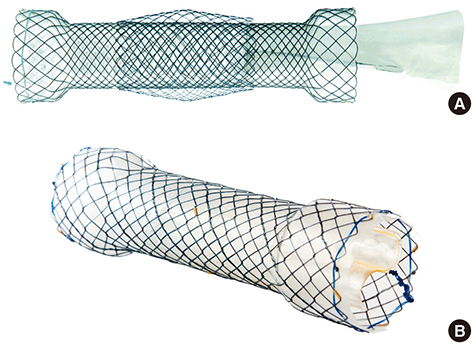
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Covered Self-expandable Metallic Stent Insertion as a Rescue Procedure for Postoperative Leakage after Primary Repair of Perforated Duodenal Ulcer
Young Jin Yoo, Yong Kang Lee, Joong Ho Lee, Hyung Soon Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;72(5):262-266. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.5.262.Self-expandable metallic stent-induced esophagorespiratory fistulas in patients with advanced esophageal cancer
Iatagan R. Josino, Bruno C. Martins, Andressa A. Machado, Gustavo R. de A. Lima, Martin A. C. Cordero, Amanda A. M. Pombo, Rubens A. A. Sallum, Ulysses Ribeiro Jr, Todd H. Baron, Fauze Maluf-Filho
Clin Endosc. 2023;56(6):761-768. doi: 10.5946/ce.2022.297.
Reference
-
1. Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49:1374–1403.2. Sihvo EI, Luostarinen ME, Salo JA. Fate of patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and the esophagogastric junction: a population-based analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:419–424.3. Spaander MC, Baron TH, Siersema PD, Fuccio L, Schumacher B, Escorsell À, Garcia-Pagán JC, Dumonceau JM, Conio M, de Ceglie A, et al. Esophageal stenting for benign and malignant disease: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:939–948.4. Hill JL, Norberg HP, Smith MD, Young JA, Reyes HM. Clinical technique and success of the esophageal stent to prevent corrosive strictures. J Pediatr Surg. 1976; 11:443–450.5. Varadarajulu S, Banerjee S, Barth B, Desilets D, Kaul V, Kethu S, Pedrosa M, Pfau P, Tokar J, Wang A, et al. Enteral stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:455–464.6. Domschke W, Foerster EC, Matek W, Rödl W. Self-expanding mesh stent for esophageal cancer stenosis. Endoscopy. 1990; 22:134–136.7. Seven G, Irani S, Ross AS, Gan SI, Gluck M, Low D, Kozarek RA. Partially versus fully covered self-expanding metal stents for benign and malignant esophageal conditions: a single center experience. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:2185–2192.8. Uitdehaag MJ, Siersema PD, Spaander MC, Vleggaar FP, Verschuur EM, Steyerberg EW, Kuipers EJ. A new fully covered stent with antimigration properties for the palliation of malignant dysphagia: a prospective cohort study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:600–605.9. Uitdehaag MJ, van Hooft JE, Verschuur EM, Repici A, Steyerberg EW, Fockens P, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD. A fully-covered stent (Alimaxx-E) for the palliation of malignant dysphagia: a prospective follow-up study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:1082–1089.10. Verschuur EM, Steyerberg EW, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD. Effect of stent size on complications and recurrent dysphagia in patients with esophageal or gastric cardia cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:592–601.11. Kozarek RA, Raltz S, Brugge WR, Schapiro RH, Waxman I, Boyce HW, Baillie J, Branch MS, Stevens PD, Lightdale CJ, et al. Prospective multicenter trial of esophageal Z-stent placement for malignant dysphagia and tracheoesophageal fistula. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:562–567.12. Verschuur EM, Repici A, Kuipers EJ, Steyerberg EW, Siersema PD. New design esophageal stents for the palliation of dysphagia from esophageal or gastric cardia cancer: a randomized trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:304–312.13. Verschuur EM, Homs MY, Steyerberg EW, Haringsma J, Wahab PJ, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD. A new esophageal stent design (Niti-S stent) for the prevention of migration: a prospective study in 42 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:134–140.14. Walter D, van den Berg MW, van Hooft JE, Boot H, Scheffer RC, Vleggaar FP, Siersema PD. A new fully covered metal stent with anti-migration features for the treatment of malignant dysphagia. Endoscopy. 2014; 46:1101–1105.15. Dua KS, Kozarek R, Kim J, Evans J, Medda BK, Lang I, Hogan WJ, Shaker R. Self-expanding metal esophageal stent with anti-reflux mechanism. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:603–613.16. Shim CS, Jung IS, Cheon YK, Ryu CB, Hong SJ, Kim JO, Cho JY, Lee JS, Lee MS, Kim BS. Management of malignant stricture of the esophagogastric junction with a newly designed self-expanding metal stent with an antireflux mechanism. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:335–339.17. Laasch HU, Marriott A, Wilbraham L, Tunnah S, England RE, Martin DF. Effectiveness of open versus antireflux stents for palliation of distal esophageal carcinoma and prevention of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux. Radiology. 2002; 225:359–365.18. Blomberg J, Wenger U, Lagergren J, Arnelo U, Agustsson T, Johnsson E, Toth E, Lagergren P. Antireflux stent versus conventional stent in the palliation of distal esophageal cancer. A randomized, multicenter clinical trial. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010; 45:208–216.19. Sabharwal T, Gulati MS, Fotiadis N, Dourado R, Botha A, Mason R, Adam A. Randomised comparison of the FerX Ella antireflux stent and the ultraflex stent: proton pump inhibitor combination for prevention of post-stent reflux in patients with esophageal carcinoma involving the esophago-gastric junction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:723–728.20. Coron E, David G, Lecleire S, Jacques J, Le Sidaner A, Barrioz T, Coumaros D, Volteau C, Vedrenne B, Bichard P, et al. Antireflux versus conventional self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) for distal esophageal cancer: results of a multicenter randomized trial. Endosc Int Open. 2016; 4:E730–6.21. Adam A, Ellul J, Watkinson AF, Tan BS, Morgan RA, Saunders MP, Mason RC. Palliation of inoperable esophageal carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial of laser therapy and stent placement. Radiology. 1997; 202:344–348.22. Alderson D, Wright PD. Laser recanalization versus endoscopic intubation in the palliation of malignant dysphagia. Br J Surg. 1990; 77:1151–1153.23. Aoki T, Osaka Y, Takagi Y, Okada R, Shinohara M, Tsuchida A, Sato S, Koyanagi Y. Comparative study of self-expandable metallic stent and bypass surgery for inoperable esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2001; 14:208–211.24. Carter R, Smith JS, Anderson JR. Laser recanalization versus endoscopic intubation in the palliation of malignant dysphagia: a randomized prospective study. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:1167–1170.25. Dallal HJ, Smith GD, Grieve DC, Ghosh S, Penman ID, Palmer KR. A randomized trial of thermal ablative therapy versus expandable metal stents in the palliative treatment of patients with esophageal carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:549–557.26. Fuchs KH, Freys SM, Schaube H, Eckstein AK, Selch A, Hamelmann H. Randomized comparison of endoscopic palliation of malignant esophageal stenoses. Surg Endosc. 1991; 5:63–67.27. Sharma P, Kozarek R; Practice Parameters Committee of American College of Gastroenterology. Role of esophageal stents in benign and malignant diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:258–273.28. Hindy P, Hong J, Lam-Tsai Y, Gress F. A comprehensive review of esophageal stents. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2012; 8:526–534.29. Nagaraja V, Cox MR, Eslick GD. Safety and efficacy of esophageal stents preceding or during neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014; 5:119–126.30. Hussain Z, Diamantopoulos A, Krokidis M, Katsanos K. Double-layered covered stent for the treatment of malignant oesophageal obstructions: systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:7841–7850.31. Conio M, Repici A, Battaglia G, De Pretis G, Ghezzo L, Bittinger M, Messmann H, Demarquay JF, Blanchi S, Togni M, et al. A randomized prospective comparison of self-expandable plastic stents and partially covered self-expandable metal stents in the palliation of malignant esophageal dysphagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:2667–2677.32. Bergquist H, Wenger U, Johnsson E, Nyman J, Ejnell H, Hammerlid E, Lundell L, Ruth M. Stent insertion or endoluminal brachytherapy as palliation of patients with advanced cancer of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Dis Esophagus. 2005; 18:131–139.33. Homs MY, Steyerberg EW, Eijkenboom WM, Tilanus HW, Stalpers LJ, Bartelsman JF, van Lanschot JJ, Wijrdeman HK, Mulder CJ, Reinders JG, et al. Single-dose brachytherapy versus metal stent placement for the palliation of dysphagia from oesophageal cancer: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2004; 364:1497–1504.34. Welsch J, Kup PG, Nieder C, Khosrawipour V, Bühler H, Adamietz IA, Fakhrian K. Survival and symptom relief after palliative radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. J Cancer. 2016; 7:125–130.35. Shin JH, Song HY, Kim JH, Kim SB, Lee GH, Park SI, Han YM, Kang W. Comparison of temporary and permanent stent placement with concurrent radiation therapy in patients with esophageal carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:67–74.36. Park JH, Song HY, Park JY, Kim JH, Kim YH, Kim JH, Kim SB. Temporary stent placement with concurrent chemoradiation therapy in patients with unresectable oesophageal carcinoma: is there an optimal time for stent removal? Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:1940–1945.37. Javed A, Pal S, Dash NR, Ahuja V, Mohanti BK, Vishnubhatla S, Sahni P, Chattopadhyay TK. Palliative stenting with or without radiotherapy for inoperable esophageal carcinoma: a randomized trial. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2012; 43:63–69.38. Langer FB, Schoppmann SF, Prager G, Tomaselli F, Pluschnig U, Hejna M, Schmid R, Zacherl J. Temporary placement of self-expanding oesophageal stents as bridging for neo-adjuvant therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:470–475.39. Nishimura Y, Nagata K, Katano S, Hirota S, Nakamura K, Higuchi F, Soejima T, Sai H; Japanese Society for Esophageal Diseases. Severe complications in advanced esophageal cancer treated with radiotherapy after intubation of esophageal stents: a questionnaire survey of the Japanese Society for Esophageal Diseases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 56:1327–1332.40. Zhong J, Wu Y, Xu Z, Liu X, Xu B, Zhai Z. Treatment of medium and late stage esophageal carcinoma with combined endoscopic metal stenting and radiotherapy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003; 116:24–28.41. Walsh TN. Oesophageal cancer: who needs neoadjuvant therapy? Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:615–616.42. Vleggaar FP. Stent placement in esophageal cancer as a bridge to surgery. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:620–622.43. Mariette C, Gronnier C, Duhamel A, Mabrut JY, Bail JP, Carrere N, Lefevre JH, Meunier B, Collet D, Piessen G, et al. Self-expanding covered metallic stent as a bridge to surgery in esophageal cancer: impact on oncologic outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2015; 220:287–296.44. Kjaer DW, Nassar M, Jensen LS, Svendsen LB, Mortensen FV. A bridging stent to surgery in patients with esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer has a dramatic negative impact on patient survival: a retrospective cohort study through data acquired from a prospectively maintained national database. Dis Esophagus. 2017; 30:1–7.45. Hirdes MM, Vleggaar FP, de Beule M, Siersema PD. In vitro evaluation of the radial and axial force of self-expanding esophageal stents. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:997–1005.46. Maruthachalam K, Lash GE, Shenton BK, Horgan AF. Tumour cell dissemination following endoscopic stent insertion. Br J Surg. 2007; 94:1151–1154.47. Lecleire S, Di Fiore F, Ben-Soussan E, Antonietti M, Hellot MF, Paillot B, Lerebours E, Ducrotté P, Michel P. Prior chemoradiotherapy is associated with a higher life-threatening complication rate after palliative insertion of metal stents in patients with oesophageal cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23:1693–1702.48. Löser C, Aschl G, Hébuterne X, Mathus-Vliegen EM, Muscaritoli M, Niv Y, Rollins H, Singer P, Skelly RH. ESPEN guidelines on artificial enteral nutrition--percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG). Clin Nutr. 2005; 24:848–861.49. Toussaint E, Van Gossum A, Ballarin A, Arvanitakis M. Enteral access in adults. Clin Nutr. 2015; 34:350–358.50. Park JH, Song HY, Shin JH, Kim JH, Kim YH, Kim SB, Kim JH. Preliminary results of temporary placement of retrievable expandable metallic stents during preoperative neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with resectable esophageal cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015; 26:883–888.51. Shin JH, Song HY, Ko GY, Lim JO, Yoon HK, Sung KB. Esophagorespiratory fistula: long-term results of palliative treatment with covered expandable metallic stents in 61 patients. Radiology. 2004; 232:252–259.52. Balazs A, Kupcsulik PK, Galambos Z. Esophagorespiratory fistulas of tumorous origin. Non-operative management of 264 cases in a 20-year period. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008; 34:1103–1107.53. Na HK, Song HY, Kim JH, Park JH, Kang MK, Lee J, Oh SJ. How to design the optimal self-expandable oesophageal metallic stents: 22 years of experience in 645 patients with malignant strictures. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:786–796.54. Saxon RR, Barton RE, Katon RM, Lakin PC, Timmermans HA, Uchida BT, Keller FS, Rösch J. Treatment of malignant esophagorespiratory fistulas with silicone-covered metallic Z stents. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1995; 6:237–242.55. Morgan RA, Ellul JP, Denton ER, Glynos M, Mason RC, Adam A. Malignant esophageal fistulas and perforations: management with plastic-covered metallic endoprostheses. Radiology. 1997; 204:527–532.56. Low DE, Kozarek RA. Comparison of conventional and wire mesh expandable prostheses and surgical bypass in patients with malignant esophagorespiratory fistulas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998; 65:919–923.57. May A, Ell C. Palliative treatment of malignant esophagorespiratory fistulas with Gianturco-Z stents. A prospective clinical trial and review of the literature on covered metal stents. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998; 93:532–535.58. Siersema PD, Schrauwen SL, van Blankenstein M, Steyerberg EW, van der Gaast A, Tilanus HW, Dees J; Rotterdam Esophageal Tumor Study Group. Self-expanding metal stents for complicated and recurrent esophagogastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:579–586.59. Wang MQ, Sze DY, Wang ZP, Wang ZQ, Gao YA, Dake MD. Delayed complications after esophageal stent placement for treatment of malignant esophageal obstructions and esophagorespiratory fistulas. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001; 12:465–474.60. Sarper A, Oz N, Cihangir C, Demircan A, Isin E. The efficacy of self-expanding metal stents for palliation of malignant esophageal strictures and fistulas. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003; 23:794–798.61. Murthy S, Gonzalez-Stawinski GV, Rozas MS, Gildea TR, Dumot JA. Palliation of malignant aerodigestive fistulae with self-expanding metallic stents. Dis Esophagus. 2007; 20:386–389.62. Ross WA, Alkassab F, Lynch PM, Ayers GD, Ajani J, Lee JH, Bismar M. Evolving role of self-expanding metal stents in the treatment of malignant dysphagia and fistulas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:70–76.63. Hu Y, Zhao YF, Chen LQ, Zhu ZJ, Liu LX, Wang Y, Kou YL. Comparative study of different treatments for malignant tracheoesophageal/bronchoesophageal fistulae. Dis Esophagus. 2009; 22:526–531.64. Herth FJ, Peter S, Baty F, Eberhardt R, Leuppi JD, Chhajed PN. Combined airway and oesophageal stenting in malignant airway-oesophageal fistulas: a prospective study. Eur Respir J. 2010; 36:1370–1374.65. Van Heel NC, Haringsma J, Spaander MC, Didden P, Bruno MJ, Kuipers EJ. Esophageal stents for the palliation of malignant dysphagia and fistula recurrence after esophagectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:249–254.66. Chen YH, Li SH, Chiu YC, Lu HI, Huang CH, Rau KM, Liu CT. Comparative study of esophageal stent and feeding gastrostomy/jejunostomy for tracheoesophageal fistula caused by esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e42766.67. Zori AG, Jantz MA, Forsmark CE, Wagh MS. Simultaneous dual scope endotherapy of esophago-airway fistulas and obstructions. Dis Esophagus. 2014; 27:428–434.68. Shin JH, Kim JH, Song HY. Interventional management of esophagorespiratory fistula. Korean J Radiol. 2010; 11:133–140.69. Verschuur EM, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD. Esophageal stents for malignant strictures close to the upper esophageal sphincter. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:1082–1090.70. Katsanos K, Sabharwal T, Adam A. Stenting of the upper gastrointestinal tract: current status. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33:690–705.71. Conigliaro R, Battaglia G, Repici A, De Pretis G, Ghezzo L, Bittinger M, Messmann H, Demarquay JF, Togni M, Blanchi S, et al. Polyflex stents for malignant oesophageal and oesophagogastric stricture: a prospective, multicentric study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 19:195–203.72. Yakami M, Mitsumori M, Sai H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Nishimura Y. Development of severe complications caused by stent placement followed by definitive radiation therapy for T4 esophageal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2003; 8:395–398.73. Schowengerdt CG. Tracheoesophageal fistula caused by a self-expanding esophageal stent. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999; 67:830–831.74. Nagahama T, Maruyama M, Kato K, Shinoura H, Hasegawa K, Takashima I, Ebuchi M. Complication after self expandable metallic stent for esophageal cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2003; 30:1750–1753.75. Saito Y, Tanaka T, Andoh A, Minematsu H, Hata K, Tsujikawa T, Nitta N, Murata K, Fujiyama Y. Novel biodegradable stents for benign esophageal strictures following endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Dis Sci. 2008; 53:330–333.76. Jung GE, Sauer P, Schaible A. Tracheoesophageal fistula following implantation of a biodegradable stent for a refractory benign esophageal stricture. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:Suppl 2. E338–9.77. Guo JH, Teng GJ, Zhu GY, He SC, Deng G, He J. Self-expandable stent loaded with 125I seeds: feasibility and safety in a rabbit model. Eur J Radiol. 2007; 61:356–361.78. Guo JH, Teng GJ, Zhu GY, He SC, Fang W, Deng G, Li GZ. Self-expandable esophageal stent loaded with 125I seeds: initial experience in patients with advanced esophageal cancer. Radiology. 2008; 247:574–581.79. Zhu HD, Guo JH, Mao AW, Lv WF, Ji JS, Wang WH, Lv B, Yang RM, Wu W, Ni CF, et al. Conventional stents versus stents loaded with (125)iodine seeds for the treatment of unresectable oesophageal cancer: a multicentre, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:612–619.80. Moon S, Yang SG, Na K. An acetylated polysaccharide-PTFE membrane-covered stent for the delivery of gemcitabine for treatment of gastrointestinal cancer and related stenosis. Biomaterials. 2011; 32:3603–3610.81. Kim SY, Kim M, Kim MK, Lee H, Lee DK, Lee DH, Yang SG. Paclitaxel-eluting nanofiber-covered self-expanding nonvascular stent for palliative chemotherapy of gastrointestinal cancer and its related stenosis. Biomed Microdevices. 2014; 16:897–904.82. Lei L, Liu X, Guo S, Tang M, Cheng L, Tian L. 5-Fluorouracil-loaded multilayered films for drug controlled releasing stent application: Drug release, microstructure, and ex vivo permeation behaviors. J Control Release. 2010; 146:45–53.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pyloric Obstruction Caused by Self-expandable Metallic Stent for Palliation of Malignant Dysphagia
- Expandable Metallic Stent Placement for Nutcracker Syndrome
- Self-expandable metallic stent-induced esophagorespiratory fistulas in patients with advanced esophageal cancer
- Self-expandable Metallic Stents for Palliative Treatment of Malignant Esophagogastric Strictures: Experiences in 103 Patients
- Percutaneous retrograde approach and perioral placement of a covered esophageal stent in a patient with a complex esophageal cancer