J Rheum Dis.
2017 Apr;24(2):99-107. 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.2.99.
Meta-analysis of Circulating Adiponectin, Visfatin, and Ghrelin Levels in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Medical Center, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lyhcgh@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2378088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.2.99
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the association between circulating adiponectin, visfatin, and ghrelin levels and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
METHODS
We conducted a meta-analysis to compare serum/plasma adiponectin, visfatin, and ghrelin levels in patients with SLE to those of healthy controls.
RESULTS
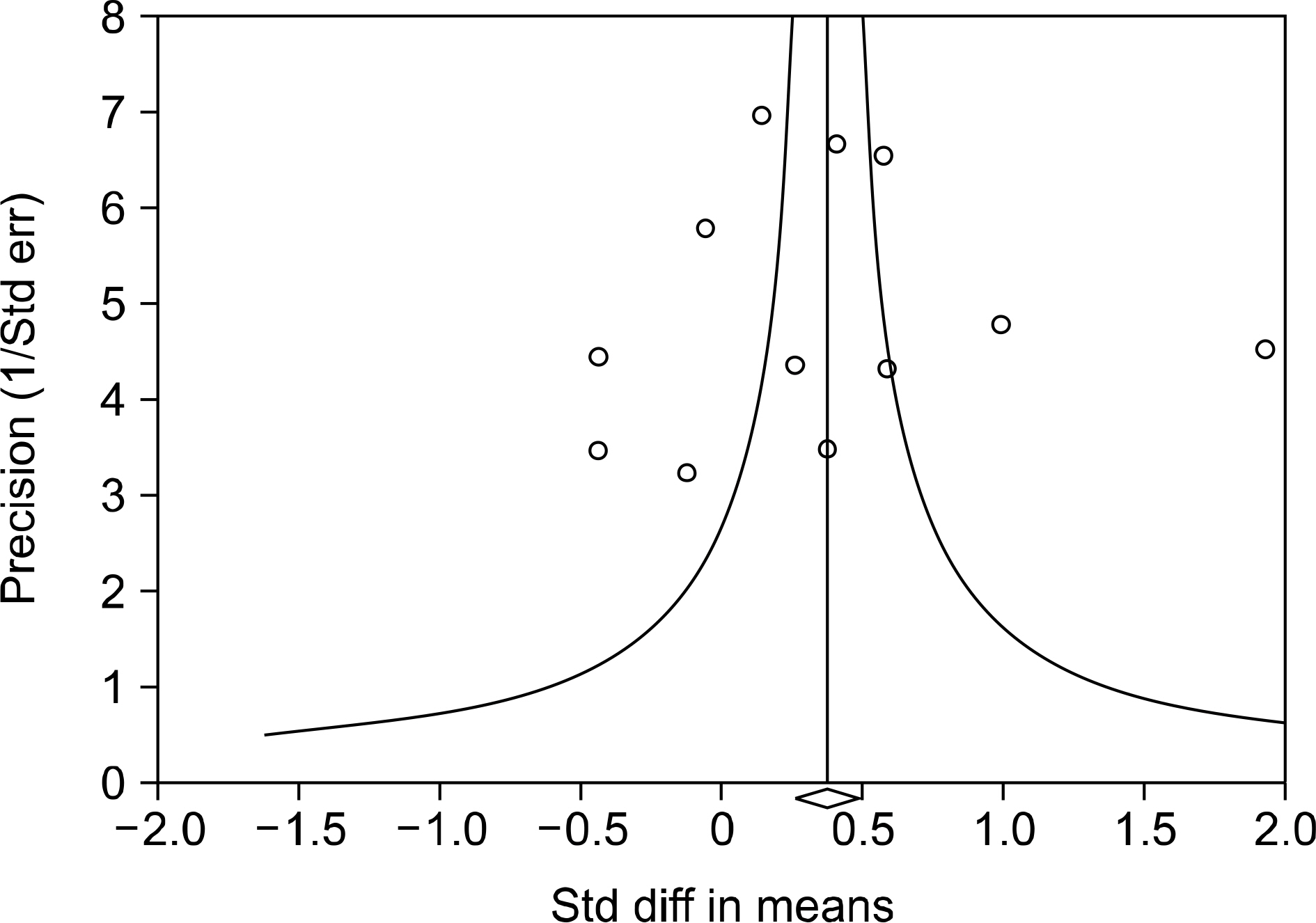
Eleven articles (822 patients with SLE and 676 controls) were included in the meta-analysis. The meta-analysis showed that the adiponectin level was significantly higher in the SLE group than in the control group (standardized mean difference [SMD]=0.360, 95% confidence interval [CI]=0.025∼0.695, p=0.035). Stratification according to region showed that high adiponectin levels were associated with SLE in the Western population (SMD=0.225, 95% CI=0.024∼0.426, p=0.028), but not in the South American population. A subgroup analysis that adiponectin level is significantly higher in the SLE group than in the control after adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, large sample size (n>100); and mean age>40 years (SMD=0.492, 95% CI=0.065∼0.920, p=0.024; SMD=0.492, 95% CI=0.065∼0.920, p=0.024; SMD=0.429, 95% CI=0.124∼0.733, p=0.006, respectively). Stratification by region showed significantly increased visfatin and ghrelin levels in the SLE group in Western and South American populations.
CONCLUSION
Our meta-analysis demonstrated that circulating adiponectin, visfatin, and ghrelin levels are significantly higher in SLE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Castellino G, Hughes GR. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2001; 357:1027–32.
Article2. Shao WH, Cohen PL. Disturbances of apoptotic cell clearance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13:202.
Article3. Coelho M, Oliveira T, Fernandes R. Biochemistry of adipose tissue: an endocrine organ. Arch Med Sci. 2013; 9:191–200.4. Shehzad A, Iqbal W, Shehzad O, Lee YS. Adiponectin: regulation of its production and its role in human diseases. Hormones (Athens). 2012; 11:8–20.
Article5. Cheng X, Folco EJ, Shimizu K, Libby P. Adiponectin induces proinflammatory programs in human macrophages and CD4+ T cells. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:36896–904.
Article6. Lee YA, Ji HI, Lee SH, Hong SJ, Yang HI, Chul Yoo M, et al. The role of adiponectin in the production of IL-6, IL-8, VEGF and MMPs in human endothelial cells and osteoblasts: implications for arthritic joints. Exp Mol Med. 2014; 46:e72.
Article7. Tang CH, Chiu YC, Tan TW, Yang RS, Fu WM. Adiponectin enhances IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblast via an AdipoR1 receptor, AMPK, p38, and NF-kappa B pathway. J Immunol. 2007; 179:5483–92.8. Luk T, Malam Z, Marshall JC. Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF)/visfatin: a novel mediator of innate immunity. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 83:804–16.
Article9. Brentano F, Schorr O, Ospelt C, Stanczyk J, Gay RE, Gay S, et al. Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor/visfatin, a new marker of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis with proinflammatory and matrix-degrading activities. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:2829–39.
Article10. Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Sawaguchi A, Mondal MS, Suganuma T, et al. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology. 2000; 141:4255–61.11. Karmiris K, Koutroubakis IE, Kouroumalis EA. Leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and ghrelin–implications for inflammatory bowel disease. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008; 52:855–66.12. Barbosa Vde S, Francescantônio PL, Silva NA. Leptin and adiponectin in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical and laboratory correlations. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2015; 55:140–5.13. McMahon M, Skaggs BJ, Grossman JM, Sahakian L, Fitzgerald J, Wong WK, et al. A panel of biomarkers is associated with increased risk of the presence and progression of atherosclerosis in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014; 66:130–9.
Article14. Vadacca M, Zardi EM, Margiotta D, Rigon A, Cacciapaglia F, Arcarese L, et al. Leptin, adiponectin and vascular stiffness parameters in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Intern Emerg Med. 2013; 8:705–12.
Article15. Reynolds HR, Buyon J, Kim M, Rivera TL, Izmirly P, Tunick P, et al. Association of plasma soluble E-selectin and adiponectin with carotid plaque in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 210:569–74.
Article16. De Sanctis JB, Zabaleta M, Bianco NE, Garmendia JV, Rivas L. Serum adipokine levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 2009; 42:272–4.
Article17. Chung CP, Long AG, Solus JF, Rho YH, Oeser A, Raggi P, et al. Adipocytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship to inflammation, insulin resistance and coronary atherosclerosis. Lupus. 2009; 18:799–806.
Article18. Al M, Ng L, Tyrrell P, Bargman J, Bradley T, Silverman E. Adipokines as novel biomarkers in paediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:497–501.
Article19. Sada KE, Yamasaki Y, Maruyama M, Sugiyama H, Yamamura M, Maeshima Y, et al. Altered levels of adipocytokines in association with insulin resistance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2006; 33:1545–52.20. Rovin BH, Song H, Hebert LA, Nadasdy T, Nadasdy G, Birmingham DJ, et al. Plasma, urine, and renal expression of adiponectin in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Kidney Int. 2005; 68:1825–33.
Article21. Ozgen M, Koca SS, Aksoy K, Dagli N, Ustundag B, Isik A. Visfatin levels and intima-media thicknesses in rheumatic diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 2011; 30:757–63.
Article22. Kim HA, Choi GS, Jeon JY, Yoon JM, Sung JM, Suh CH. Leptin and ghrelin in Korean systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2010; 19:170–4.
Article23. Lee YH, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. Associations between osteoprotegerin polymorphisms and bone mineral density: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2010; 37:227–34.
Article24. Lee YH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. PADI4 polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2007; 27:827–33.
Article25. Lee YH, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. Induction and maintenance therapy for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lupus. 2010; 19:703–10.
Article26. Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40:1725.
Article27. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article28. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005; 5:13.
Article29. Ridout KK, Ridout SJ, Price LH, Sen S, Tyrka AR. Depression and telomere length: A meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016; 191:237–47.
Article30. Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Ottawa Hospital Research Institute;2000. [cited 2016]. Available from:. http://www.ohri.-ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.31. McGough JJ, Faraone SV. Estimating the size of treatment effects: moving beyond p values. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2009; 6:21–9.32. Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN. Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ. 1997; 315:1533–7.
Article33. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–88.
Article34. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1539–58.
Article35. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–34.
Article36. Li HM, Zhang TP, Leng RX, Li XP, Li XM, Pan HF. Plasma/serum leptin levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Arch Med Res. 2015; 46:551–6.
Article37. Sun Z, Lei H, Zhang Z. Pre-B cell colony enhancing factor (PBEF), a cytokine with multiple physiological functions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013; 24:433–42.
Article38. Moschen AR, Kaser A, Enrich B, Mosheimer B, Theurl M, Niederegger H, et al. Visfatin, an adipocytokine with proinflammatory and immunomodulating properties. J Immunol. 2007; 178:1748–58.
Article39. Dixit VD, Schaffer EM, Pyle RS, Collins GD, Sakthivel SK, Palaniappan R, et al. Ghrelin inhibits leptin- and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:57–66.
Article40. Korbonits M, Goldstone AP, Gueorguiev M, Grossman AB. Ghrelin–a hormone with multiple functions. Front Neu-roendocrinol. 2004; 25:27–68.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Circulating Interleukin-18 Level in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Associations Between Circulating Interleukin-17 Levels and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Between Interleukin-17 Gene Polymorphisms and Disease Susceptibility: A Meta-analysis
- Circulating Interleukin-37 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Their Correlations With Disease Activity: A Meta-analysis
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case Of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated With Hyperthyroidism And Severe Retinopathy