J Gastric Cancer.
2013 Jun;13(2):117-120.
Adenocarcinoma Occurring in a Gastric Hyperplastic Polyp Treated with Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. mhs1357@cnuh.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
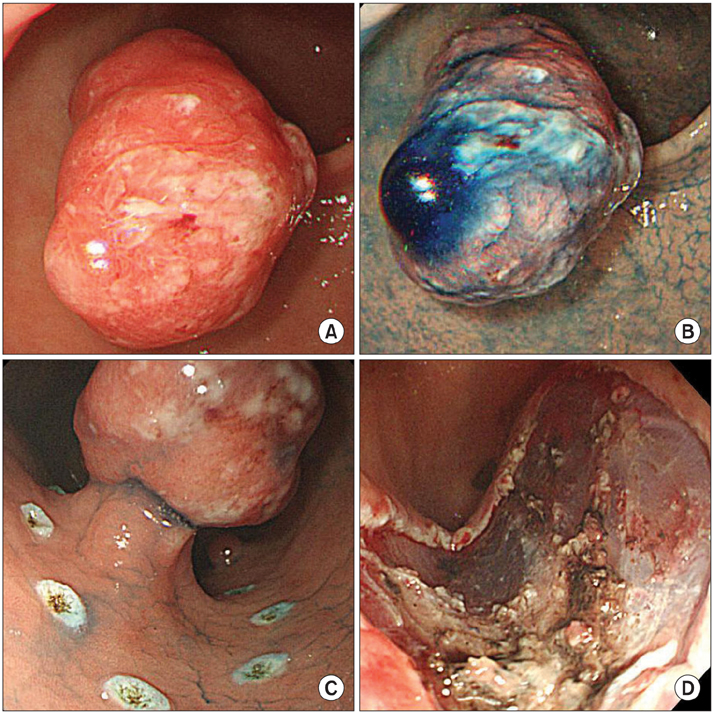
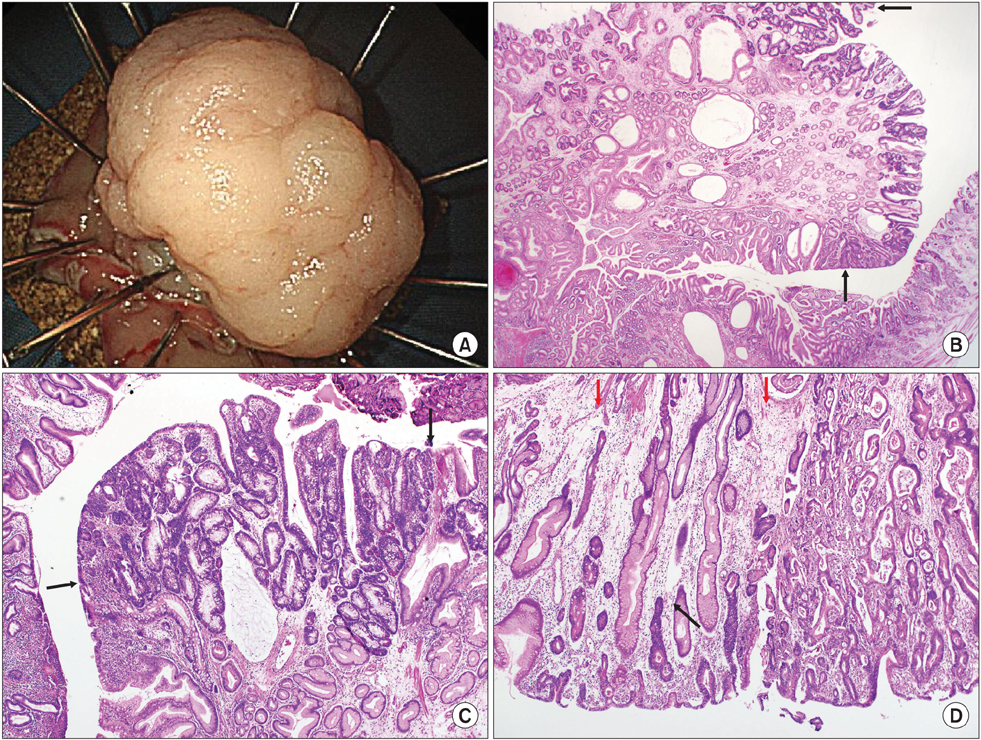
- Gastric hyperplastic polyps are generally considered benign lesions, although rare cases of adenocarcinoma have been reported. Although, the underlying mechanism of carcinogenesis in gastric hyperplastic polyps is still uncertain, most malignant polyps are seen to originate from dysplastic epithelium rather than from hyperplastic epithelium. Herein, we report the case of a woman diagnosed with adenocarcinoma that originated from a hyperplastic gastric polyp that was successfully removed by endoscopic submucosal dissection. In this case, we observed adenomatous changes around the cancerous component.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morais DJ, Yamanaka A, Zeitune JM, Andreollo NA. Gastric polyps: a retrospective analysis of 26,000 digestive endoscopies. Arq Gastroenterol. 2007. 44:14–17.
Article2. Jain R, Chetty R. Gastric hyperplastic polyps: a review. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. 54:1839–1846.
Article3. Kang HM, Oh TH, Seo JY, Joen TJ, Seo DD, Shin WC, et al. Clinical factors predicting for neoplastic transformation of gastric hyperplastic polyps. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011. 58:184–189.
Article4. Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard DM, Walker MM, Warren B. British Society of Gastroenterology. The management of gastric polyps. Gut. 2010. 59:1270–1276.
Article5. Snover DC. Benign epithelial polyps of the stomach. Pathol Annu. 1985. 20:303–329.6. Hirasaki S, Suzuki S, Kanzaki H, Fujita K, Matsumura S, Matsumoto E. Minute signet ring cell carcinoma occurring in gastric hyperplastic polyp. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. 13:5779–5780.
Article7. Varis O, Laxén F, Valle J. Helicobacter pylori infection and fasting serum gastrin levels in a series of endoscopically diagnosed gastric polyps. APMIS. 1994. 102:759–764.
Article8. Ljubicić N, Banić M, Kujundzić M, Antić Z, Vrkljan M, Kovacević I, et al. The effect of eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection on the course of adenomatous and hyperplastic gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999. 11:727–730.
Article9. Ohkusa T, Takashimizu I, Fujiki K, Suzuki S, Shimoi K, Horiuchi T, et al. Disappearance of hyperplastic polyps in the stomach after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. A randomized, clinical trial. Ann Intern Med. 1998. 129:712–715.
Article10. Veereman Wauters G, Ferrell L, Ostroff JW, Heyman MB. Hyperplastic gastric polyps associated with persistent Helicobacter pylori infection and active gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990. 85:1395–1397.11. Davaris P, Petraki K, Archimandritis A, Haritopoulos N, Papacharalampous N. Mucosal hyperplastic polyps of the stomach. Do they have any potential to malignancy? Pathol Res Pract. 1986. 181:385–389.12. Daibo M, Itabashi M, Hirota T. Malignant transformation of gastric hyperplastic polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987. 82:1016–1025.13. Nogueira AM, Carneiro F, Seruca R, Cirnes L, Veiga I, Machado JC, et al. Microsatellite instability in hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps of the stomach. Cancer. 1999. 86:1649–1656.
Article14. Han AR, Sung CO, Kim KM, Park CK, Min BH, Lee JH, et al. The clinicopathological features of gastric hyperplastic polyps with neoplastic transformations: a suggestion of indication for endoscopic polypectomy. Gut Liver. 2009. 3:271–275.
Article15. Orlowska J, Jarosz D, Pachlewski J, Butruk E. Malignant transformation of benign epithelial gastric polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995. 90:2152–2159.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastric Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp Removed Using Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- A Case of Gastric Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp Found with Gastritis Cystica Profunda and Early Gastric Cancer
- Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp in Stomach: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Multifocal Adenocarcinomas Arising within a Gastric Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp
- A Giant Hyperplastic Polyp of the Stomach Complicated by Intussusceptions and Intraepithelial Malignant Transformation