Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Dec;40(6):1057-1063. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1057.
Diagnostic Cutoff Value for Ultrasonography of the Common Fibular Neuropathy at the Fibular Head
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. gstinfog@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2371338
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1057
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To establish the diagnostic cutoff value of ultrasonographic measurement for common fibular neuropathy (CFN) at the fibular head (FH).
METHODS
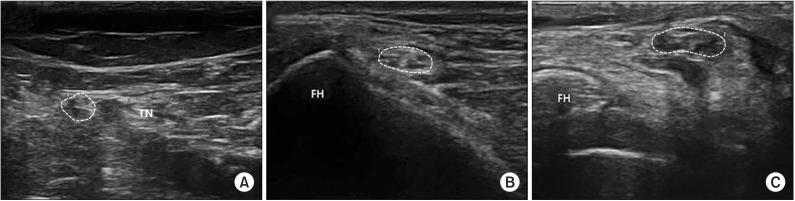
Twenty patients with electrodiagnostically diagnosed CFN at the FH and 30 healthy controls were included in the study. The cross-sectional area (CSA) of sciatic nerve at mid-thigh level, common fibular nerve at popliteal fossa (PF), and common fibular (CF) nerve at FH were measured. Additionally, the difference of CF nerve CSA at the FH between symptomatic side and asymptomatic side (ΔSx-Asx), the ratio of CF nerve CSA at FH to at PF (FH/PF), and the ratio of CF nerve CSA at the FH symptomatic side to asymptomatic side (Ratio Sx-Asx) were calculated.
RESULTS
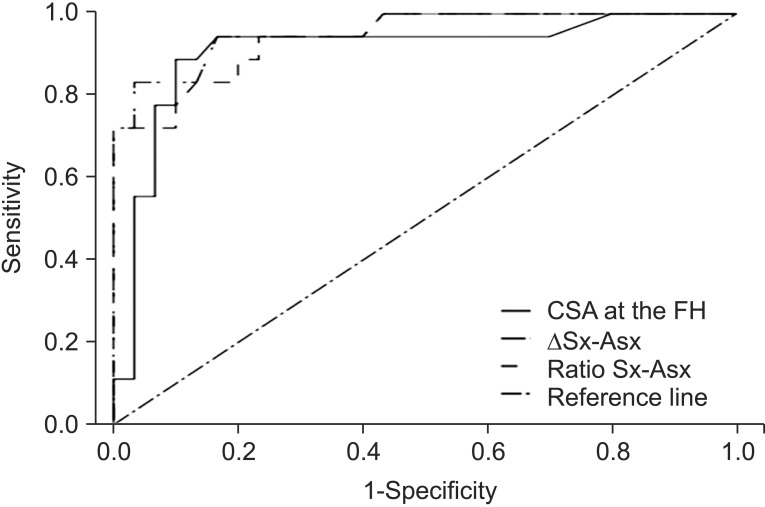
CSA at the FH, FH/PF, ΔSx-Asx, and Ratio Sx-Asx showed significant differences between the patient and control groups. The cutoff value for diagnosing CFN at the FH was 11.7 mm² for the CSA at the FH (sensitivity 85.0%, specificity 90.0%), 1.70 mm² for the ΔSx-Asx (sensitivity 83.3%, specificity 97.0%), 1.11 for the FH/PF (sensitivity 47.1%, specificity 93.3%), and 1.24 for the Ratio Sx-Asx (sensitivity 72.2%, specificity 96.7%).
CONCLUSION
The ultrasonographic measurement and cutoff value could be a valuable reference in diagnosing CFN at the FH and improving diagnostic reliability and efficacy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Grant TH, Omar IM, Dumanian GA, Pomeranz CB, Lewis VA. Sonographic evaluation of common peroneal neuropathy in patients with foot drop. J Ultrasound Med. 2015; 34:705–711. PMID: 25792587.
Article2. Kim DH, Kline DG. Management and results of peroneal nerve lesions. Neurosurgery. 1996; 39:312–319. PMID: 8832668.
Article3. Masakado Y, Kawakami M, Suzuki K, Abe L, Ota T, Kimura A. Clinical neurophysiology in the diagnosis of peroneal nerve palsy. Keio J Med. 2008; 57:84–89. PMID: 18677088.
Article4. Van Langenhove M, Pollefliet A, Vanderstraeten G. A retrospective electrodiagnostic evaluation of footdrop in 303 patients. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1989; 29:145–152. PMID: 2721427.5. Kang S, Kwon HK, Kim KH, Yun HS. Ultrasonography of median nerve and electrophysiologic severity in carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012; 36:72–79. PMID: 22506238.
Article6. Cartwright MS, Passmore LV, Yoon JS, Brown ME, Caress JB, Walker FO. Cross-sectional area reference values for nerve ultrasonography. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37:566–571. PMID: 18351581.
Article7. Zaidman CM, Seelig MJ, Baker JC, Mackinnon SE, Pestronk A. Detection of peripheral nerve pathology: comparison of ultrasound and MRI. Neurology. 2013; 80:1634–1640. PMID: 23553474.
Article8. Bargfrede M, Schwennicke A, Tumani H, Reimers CD. Quantitative ultrasonography in focal neuropathies as compared to clinical and EMG findings. Eur J Ultrasound. 1999; 10:21–29. PMID: 10502636.
Article9. Seok HY, Jang JH, Won SJ, Yoon JS, Park KS, Kim BJ. Cross-sectional area reference values of nerves in the lower extremities using ultrasonography. Muscle Nerve. 2014; 50:564–570. PMID: 24639103.
Article10. Visser LH, Hens V, Soethout M, De Deugd-Maria V, Pijnenburg J, Brekelmans GJ. Diagnostic value of high-resolution sonography in common fibular neuropathy at the fibular head. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 48:171–178. PMID: 23801382.
Article11. Lo YL, Fook-Chong S, Leoh TH, Dan YF, Tan YE, Lau WH, et al. High-resolution ultrasound as a diagnostic adjunct in common peroneal neuropathy. Arch Neurol. 2007; 64:1798–1800. PMID: 18071050.
Article12. Cruz-Martinez A, Arpa J, Palau F. Peroneal neuropathy after weight loss. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2000; 5:101–105. PMID: 10905469.
Article13. Preston DC, Shapiro BE. Electromyography and neuromuscular disorders: clinical-electrophysiological correlations. 3rd ed. New York: Elsevier;2013.14. Marciniak C, Armon C, Wilson J, Miller R. Practice parameter: utility of electrodiagnostic techniques in evaluating patients with suspected peroneal neuropathy: an evidence-based review. Muscle Nerve. 2005; 31:520–527. PMID: 15768387.
Article15. Visser LH. High-resolution sonography of the common peroneal nerve: detection of intraneural ganglia. Neurology. 2006; 67:1473–1475. PMID: 17060577.
Article16. Beekman R, Schoemaker MC, Van Der Plas JP, Van Den Berg LH, Franssen H, Wokke JH, et al. Diagnostic value of high-resolution sonography in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Neurology. 2004; 62:767–773. PMID: 15007128.
Article17. Tsukamoto H, Granata G, Coraci D, Paolasso I, Padua L. Ultrasound and neurophysiological correlation in common fibular nerve conduction block at fibular head. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014; 125:1491–1495. PMID: 24461795.
Article18. El Miedany YM, Aty SA, Ashour S. Ultrasonography versus nerve conduction study in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: substantive or complementary tests? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004; 43:887–895. PMID: 15100417.
Article19. Kerasnoudis A, Tsivgoulis G. Nerve ultrasound in peripheral neuropathies: a review. J Neuroimaging. 2015; 25:528–538. PMID: 25996962.
Article20. Gruber H, Peer S, Meirer R, Bodner G. Peroneal nerve palsy associated with knee luxation: evaluation by sonography--initial experiences. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 185:1119–1125. PMID: 16247119.
Article21. Peeters EY, Nieboer KH, Osteaux MM. Sonography of the normal ulnar nerve at Guyon’s canal and of the common peroneal nerve dorsal to the fibular head. J Clin Ultrasound. 2004; 32:375–380. PMID: 15372443.
Article22. Tagliafico A, Cadoni A, Fisci E, Bignotti B, Padua L, Martinoli C. Reliability of side-to-side ultrasound cross-sectional area measurements of lower extremity nerves in healthy subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 46:717–722. PMID: 23055313.
Article23. Hobson-Webb LD, Massey JM, Juel VC, Sanders DB. The ultrasonographic wrist-to-forearm median nerve area ratio in carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008; 119:1353–1357. PMID: 18387336.
Article24. Yalcin E, Unlu E, Akyuz M, Karaahmet OZ. Ultrasound diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy: comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic nerve thickness. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014; 39:167–171. PMID: 23592536.
Article25. Bayrak AO, Bayrak IK, Turker H, Elmali M, Nural MS. Ultrasonography in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: comparison of cross-sectional area and swelling ratio with electrophysiological severity. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41:661–666. PMID: 19941341.
Article26. Fu T, Cao M, Liu F, Zhu J, Ye D, Feng X, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome assessment with ultrasonography: value of inlet-to-outlet median nerve area ratio in patients versus healthy volunteers. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0116777. PMID: 25617835.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Peroneal Neuropathy after Tibio-Fibular Fracture
- Surgical Treatment of Avulsion Fracture of the Fibular Head Associated with Lateral Instability of the Knee
- Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve Action Potential in Common Peroneal Neuropathy
- Relationship of Tibial Nonunion with Fibular Nonunion in the Tibio-fibular Shaft Fracture
- A reproducible reference point for the common peroneal nerve during surgery at the posterolateral corner of the knee: a cadaveric study